bignumber.js
+ +A JavaScript library for arbitrary-precision arithmetic.
+ + +API
+ ++ See the README on GitHub for a + quick-start introduction. +
+
+ In all examples below, var and semicolons are not shown, and if a commented-out
+ value is in quotes it means toString has been called on the preceding expression.
+
CONSTRUCTOR
+ + +
+ BigNumberBigNumber(n [, base]) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number: integer, 2 to 36 inclusive. (See
+ ALPHABET to extend this range).
+
+ Returns a new instance of a BigNumber object with value n, where n
+ is a numeric value in the specified base, or base 10 if
+ base is omitted or is null or undefined.
+
+x = new BigNumber(123.4567) // '123.4567' +// 'new' is optional +y = BigNumber(x) // '123.4567'+
+ If n is a base 10 value it can be in normal (fixed-point) or
+ exponential notation. Values in other bases must be in normal notation. Values in any base can
+ have fraction digits, i.e. digits after the decimal point.
+
+new BigNumber(43210) // '43210'
+new BigNumber('4.321e+4') // '43210'
+new BigNumber('-735.0918e-430') // '-7.350918e-428'
+new BigNumber('123412421.234324', 5) // '607236.557696'
+
+ Signed 0, signed Infinity and NaN are supported.
+
+new BigNumber('-Infinity') // '-Infinity'
+new BigNumber(NaN) // 'NaN'
+new BigNumber(-0) // '0'
+new BigNumber('.5') // '0.5'
+new BigNumber('+2') // '2'
+
+ String values in hexadecimal literal form, e.g. '0xff', are valid, as are
+ string values with the octal and binary prefixs '0o' and '0b'.
+ String values in octal literal form without the prefix will be interpreted as
+ decimals, e.g. '011' is interpreted as 11, not 9.
+
+new BigNumber(-10110100.1, 2) // '-180.5'
+new BigNumber('-0b10110100.1') // '-180.5'
+new BigNumber('ff.8', 16) // '255.5'
+new BigNumber('0xff.8') // '255.5'
+
+ If a base is specified, n is rounded according to the current
+ DECIMAL_PLACES and
+ ROUNDING_MODE settings. This includes base
+ 10 so don't include a base parameter for decimal values unless
+ this behaviour is wanted.
+
BigNumber.config({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 5 })
+new BigNumber(1.23456789) // '1.23456789'
+new BigNumber(1.23456789, 10) // '1.23457'
+ An error is thrown if base is invalid. See Errors.
+ There is no limit to the number of digits of a value of type string (other than
+ that of JavaScript's maximum array size). See RANGE to set
+ the maximum and minimum possible exponent value of a BigNumber.
+
+new BigNumber('5032485723458348569331745.33434346346912144534543')
+new BigNumber('4.321e10000000')
+ BigNumber NaN is returned if n is invalid
+ (unless BigNumber.DEBUG is true, see below).
+new BigNumber('.1*') // 'NaN'
+new BigNumber('blurgh') // 'NaN'
+new BigNumber(9, 2) // 'NaN'
+
+ To aid in debugging, if BigNumber.DEBUG is true then an error will
+ be thrown on an invalid n. An error will also be thrown if n is of
+ type number with more than 15 significant digits, as calling
+ toString or valueOf on
+ these numbers may not result in the intended value.
+
+console.log(823456789123456.3) // 823456789123456.2 +new BigNumber(823456789123456.3) // '823456789123456.2' +BigNumber.DEBUG = true +// '[BigNumber Error] Number primitive has more than 15 significant digits' +new BigNumber(823456789123456.3) +// '[BigNumber Error] Not a base 2 number' +new BigNumber(9, 2)+
+ A BigNumber can also be created from an object literal.
+ Use isBigNumber to check that it is well-formed.
+
new BigNumber({ s: 1, e: 2, c: [ 777, 12300000000000 ], _isBigNumber: true }) // '777.123'
+
+
+
+
+ Methods
+The static methods of a BigNumber constructor.
+ + + + +clone
+ .clone([object]) ⇒ BigNumber constructor
+
+ object: object
+ Returns a new independent BigNumber constructor with configuration as described by
+ object (see config), or with the default
+ configuration if object is null or undefined.
+
+ Throws if object is not an object. See Errors.
+
BigNumber.config({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 5 })
+BN = BigNumber.clone({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 9 })
+
+x = new BigNumber(1)
+y = new BN(1)
+
+x.div(3) // 0.33333
+y.div(3) // 0.333333333
+
+// BN = BigNumber.clone({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 9 }) is equivalent to:
+BN = BigNumber.clone()
+BN.config({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 9 })
+
+
+
+ configset([object]) ⇒ object
+
+ object: object: an object that contains some or all of the following
+ properties.
+
Configures the settings for this particular BigNumber constructor.
+ +-
+
DECIMAL_PLACES
+ -
+ number: integer,
0to1e+9inclusive
+ Default value:20+
+ -
+ The maximum number of decimal places of the results of operations involving
+ division, i.e. division, square root and base conversion operations, and power
+ operations with negative exponents.
+
+ -
+
BigNumber.config({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 5 }) +BigNumber.set({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 5 }) // equivalent+
+
+
+
+ ROUNDING_MODE
+ -
+ number: integer,
0to8inclusive
+ Default value:4(ROUND_HALF_UP) +
+ -
+ The rounding mode used in the above operations and the default rounding mode of
+
decimalPlaces, +precision, +toExponential, +toFixed, +toFormatand +toPrecision. +
+ - The modes are available as enumerated properties of the BigNumber constructor. +
-
+
BigNumber.config({ ROUNDING_MODE: 0 }) +BigNumber.set({ ROUNDING_MODE: BigNumber.ROUND_UP }) // equivalent+
+
+
+
+ EXPONENTIAL_AT
+ -
+ number: integer, magnitude
0to1e+9inclusive, or +
+ number[]: [ integer-1e+9to0inclusive, integer +0to1e+9inclusive ]
+ Default value:[-7, 20]+
+ -
+ The exponent value(s) at which
toStringreturns exponential notation. +
+ -
+ If a single number is assigned, the value is the exponent magnitude.
+ If an array of two numbers is assigned then the first number is the negative exponent + value at and beneath which exponential notation is used, and the second number is the + positive exponent value at and above which the same. +
+ -
+ For example, to emulate JavaScript numbers in terms of the exponent values at which they
+ begin to use exponential notation, use
[-7, 20]. +
+ -
+
BigNumber.config({ EXPONENTIAL_AT: 2 }) +new BigNumber(12.3) // '12.3' e is only 1 +new BigNumber(123) // '1.23e+2' +new BigNumber(0.123) // '0.123' e is only -1 +new BigNumber(0.0123) // '1.23e-2' + +BigNumber.config({ EXPONENTIAL_AT: [-7, 20] }) +new BigNumber(123456789) // '123456789' e is only 8 +new BigNumber(0.000000123) // '1.23e-7' + +// Almost never return exponential notation: +BigNumber.config({ EXPONENTIAL_AT: 1e+9 }) + +// Always return exponential notation: +BigNumber.config({ EXPONENTIAL_AT: 0 })+
+ -
+ Regardless of the value of
EXPONENTIAL_AT, thetoFixedmethod + will always return a value in normal notation and thetoExponentialmethod + will always return a value in exponential form. +
+ -
+ Calling
toStringwith a base argument, e.g.toString(10), will + also always return normal notation. +
+
+
+
+ RANGE
+ -
+ number: integer, magnitude
1to1e+9inclusive, or +
+ number[]: [ integer-1e+9to-1inclusive, integer +1to1e+9inclusive ]
+ Default value:[-1e+9, 1e+9]+
+ -
+ The exponent value(s) beyond which overflow to
Infinityand underflow to + zero occurs. +
+ -
+ If a single number is assigned, it is the maximum exponent magnitude: values wth a
+ positive exponent of greater magnitude become
Infinityand those with a + negative exponent of greater magnitude become zero. +- + If an array of two numbers is assigned then the first number is the negative exponent + limit and the second number is the positive exponent limit. +
+- + For example, to emulate JavaScript numbers in terms of the exponent values at which they + become zero and
+Infinity, use[-324, 308]. +- +
+BigNumber.config({ RANGE: 500 }) +BigNumber.config().RANGE // [ -500, 500 ] +new BigNumber('9.999e499') // '9.999e+499' +new BigNumber('1e500') // 'Infinity' +new BigNumber('1e-499') // '1e-499' +new BigNumber('1e-500') // '0' + +BigNumber.config({ RANGE: [-3, 4] }) +new BigNumber(99999) // '99999' e is only 4 +new BigNumber(100000) // 'Infinity' e is 5 +new BigNumber(0.001) // '0.01' e is only -3 +new BigNumber(0.0001) // '0' e is -4+- + The largest possible magnitude of a finite BigNumber is +
+ + + +9.999...e+1000000000.
+ The smallest possible magnitude of a non-zero BigNumber is1e-1000000000. + CRYPTO
+ -
+ boolean:
trueorfalse.
+ Default value:false+
+ - + The value that determines whether cryptographically-secure pseudo-random number + generation is used. + +
-
+ If
CRYPTOis set totruethen the +randommethod will generate random digits using +crypto.getRandomValuesin browsers that support it, or +crypto.randomBytesif using Node.js. +
+ -
+ If neither function is supported by the host environment then attempting to set
+
CRYPTOtotruewill fail and an exception will be thrown. +
+ -
+ If
CRYPTOisfalsethen the source of randomness used will be +Math.random(which is assumed to generate at least30bits of + randomness). +
+ - See
random.
+ -
+
+// Node.js +global.crypto = require('crypto') + +BigNumber.config({ CRYPTO: true }) +BigNumber.config().CRYPTO // true +BigNumber.random() // 0.54340758610486147524+
+
+
+
+ MODULO_MODE
+ -
+ number: integer,
0to9inclusive
+ Default value:1(ROUND_DOWN) +
+ - The modulo mode used when calculating the modulus:
a mod n.
+ -
+ The quotient,
q = a / n, is calculated according to the +ROUNDING_MODEthat corresponds to the chosen +MODULO_MODE. +
+ - The remainder,
r, is calculated as:r = a - n * q.
+ - + The modes that are most commonly used for the modulus/remainder operation are shown in + the following table. Although the other rounding modes can be used, they may not give + useful results. + +
-
+
+
+Property Value Description + +ROUND_UP 0 ++ The remainder is positive if the dividend is negative, otherwise it is negative. + ++ +ROUND_DOWN 1 ++ The remainder has the same sign as the dividend. +
+ This uses 'truncating division' and matches the behaviour of JavaScript's + remainder operator%. ++ +ROUND_FLOOR 3 ++ The remainder has the same sign as the divisor. +
+ This matches Python's%operator. ++ +ROUND_HALF_EVEN 6 +The IEEE 754 remainder function. ++ +EUCLID 9 ++ The remainder is always positive. Euclidian division: +
+q = sign(n) * floor(a / abs(n))+
+ - + The rounding/modulo modes are available as enumerated properties of the BigNumber + constructor. + +
- See
modulo.
+ -
+
BigNumber.config({ MODULO_MODE: BigNumber.EUCLID }) +BigNumber.config({ MODULO_MODE: 9 }) // equivalent+
+
+
+
+ POW_PRECISION
+ -
+ number: integer,
0to1e+9inclusive.
+ Default value:0+
+ - + The maximum precision, i.e. number of significant digits, of the result of the power + operation (unless a modulus is specified). + +
- If set to
0, the number of significant digits will not be limited.
+ - See
exponentiatedBy.
+ BigNumber.config({ POW_PRECISION: 100 })
+
+
+
+ FORMAT
+ - object +
-
+ The
FORMATobject configures the format of the string returned by the +toFormatmethod. +
+ -
+ The example below shows the properties of the
FORMATobject that are + recognised, and their default values. +
+ -
+ Unlike the other configuration properties, the values of the properties of the
+
FORMATobject will not be checked for validity. The existing +FORMATobject will simply be replaced by the object that is passed in. + The object can include any number of the properties shown below. +
+ - See
toFormatfor examples of usage.
+ -
+
+BigNumber.config({ + FORMAT: { + // string to prepend + prefix: '', + // decimal separator + decimalSeparator: '.', + // grouping separator of the integer part + groupSeparator: ',', + // primary grouping size of the integer part + groupSize: 3, + // secondary grouping size of the integer part + secondaryGroupSize: 0, + // grouping separator of the fraction part + fractionGroupSeparator: ' ', + // grouping size of the fraction part + fractionGroupSize: 0, + // string to append + suffix: '' + } +});+
+
+
+
+ ALPHABET
+ -
+ string
+ Default value:'0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'+
+ -
+ The alphabet used for base conversion. The length of the alphabet corresponds to the
+ maximum value of the base argument that can be passed to the
+
BigNumberconstructor or +toString. +
+ -
+ There is no maximum length for the alphabet, but it must be at least 2 characters long, and
+ it must not contain whitespace or a repeated character, or the sign indicators
+
'+'and'-', or the decimal separator'.'. +
+ -
+
// duodecimal (base 12) +BigNumber.config({ ALPHABET: '0123456789TE' }) +x = new BigNumber('T', 12) +x.toString() // '10' +x.toString(12) // 'T'+
+
+
+
+
+
Returns an object with the above properties and their current values.
+
+ Throws if object is not an object, or if an invalid value is assigned to
+ one or more of the above properties. See Errors.
+
+BigNumber.config({
+ DECIMAL_PLACES: 40,
+ ROUNDING_MODE: BigNumber.ROUND_HALF_CEIL,
+ EXPONENTIAL_AT: [-10, 20],
+ RANGE: [-500, 500],
+ CRYPTO: true,
+ MODULO_MODE: BigNumber.ROUND_FLOOR,
+ POW_PRECISION: 80,
+ FORMAT: {
+ groupSize: 3,
+ groupSeparator: ' ',
+ decimalSeparator: ','
+ },
+ ALPHABET: '0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ$_'
+});
+
+obj = BigNumber.config();
+obj.DECIMAL_PLACES // 40
+obj.RANGE // [-500, 500]
+
+
+
+
+ isBigNumber.isBigNumber(value) ⇒ boolean
+
+ value: any
+ Returns true if value is a BigNumber instance, otherwise returns
+ false.
+
x = 42 +y = new BigNumber(x) + +BigNumber.isBigNumber(x) // false +y instanceof BigNumber // true +BigNumber.isBigNumber(y) // true + +BN = BigNumber.clone(); +z = new BN(x) +z instanceof BigNumber // false +BigNumber.isBigNumber(z) // true+
+ If value is a BigNumber instance and BigNumber.DEBUG is true,
+ then this method will also check if value is well-formed, and throw if it is not.
+ See Errors.
+
+ The check can be useful if creating a BigNumber from an object literal. + See BigNumber. +
++x = new BigNumber(10) + +// Change x.c to an illegitimate value. +x.c = NaN + +BigNumber.DEBUG = false + +// No error. +BigNumber.isBigNumber(x) // true + +BigNumber.DEBUG = true + +// Error. +BigNumber.isBigNumber(x) // '[BigNumber Error] Invalid BigNumber'+ + + +
maximum.max(n...) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the maximum of the arguments. +
+The return value is always exact and unrounded.
+x = new BigNumber('3257869345.0378653')
+BigNumber.maximum(4e9, x, '123456789.9') // '4000000000'
+
+arr = [12, '13', new BigNumber(14)]
+BigNumber.max.apply(null, arr) // '14'
+
+
+
+ minimum.min(n...) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the minimum of the arguments. +
+The return value is always exact and unrounded.
+x = new BigNumber('3257869345.0378653')
+BigNumber.minimum(4e9, x, '123456789.9') // '123456789.9'
+
+arr = [2, new BigNumber(-14), '-15.9999', -12]
+BigNumber.min.apply(null, arr) // '-15.9999'
+
+
+
+
+ random.random([dp]) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+ dp: number: integer, 0 to 1e+9 inclusive
+ Returns a new BigNumber with a pseudo-random value equal to or greater than 0 and
+ less than 1.
+
+ The return value will have dp decimal places (or less if trailing zeros are
+ produced).
+ If dp is omitted then the number of decimal places will default to the current
+ DECIMAL_PLACES setting.
+
+ Depending on the value of this BigNumber constructor's
+ CRYPTO setting and the support for the
+ crypto object in the host environment, the random digits of the return value are
+ generated by either Math.random (fastest), crypto.getRandomValues
+ (Web Cryptography API in recent browsers) or crypto.randomBytes (Node.js).
+
+ To be able to set CRYPTO to true when using
+ Node.js, the crypto object must be available globally:
+
global.crypto = require('crypto')
+
+ If CRYPTO is true, i.e. one of the
+ crypto methods is to be used, the value of a returned BigNumber should be
+ cryptographically-secure and statistically indistinguishable from a random value.
+
+ Throws if dp is invalid. See Errors.
+
BigNumber.config({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 10 })
+BigNumber.random() // '0.4117936847'
+BigNumber.random(20) // '0.78193327636914089009'
+
+
+
+ sum.sum(n...) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
Returns a BigNumber whose value is the sum of the arguments.
+The return value is always exact and unrounded.
+x = new BigNumber('3257869345.0378653')
+BigNumber.sum(4e9, x, '123456789.9') // '7381326134.9378653'
+
+arr = [2, new BigNumber(14), '15.9999', 12]
+BigNumber.sum.apply(null, arr) // '43.9999'
+
+
+
+ Properties
+
+ The library's enumerated rounding modes are stored as properties of the constructor.
+ (They are not referenced internally by the library itself.)
+
+ Rounding modes 0 to 6 (inclusive) are the same as those of Java's
+ BigDecimal class.
+
| Property | +Value | +Description | +
|---|---|---|
| ROUND_UP | +0 | +Rounds away from zero | +
| ROUND_DOWN | +1 | +Rounds towards zero | +
| ROUND_CEIL | +2 | +Rounds towards Infinity |
+
| ROUND_FLOOR | +3 | +Rounds towards -Infinity |
+
| ROUND_HALF_UP | +4 | +
+ Rounds towards nearest neighbour. + If equidistant, rounds away from zero + |
+
| ROUND_HALF_DOWN | +5 | +
+ Rounds towards nearest neighbour. + If equidistant, rounds towards zero + |
+
| ROUND_HALF_EVEN | +6 | +
+ Rounds towards nearest neighbour. + If equidistant, rounds towards even neighbour + |
+
| ROUND_HALF_CEIL | +7 | +
+ Rounds towards nearest neighbour. + If equidistant, rounds towards Infinity
+ |
+
| ROUND_HALF_FLOOR | +8 | +
+ Rounds towards nearest neighbour. + If equidistant, rounds towards -Infinity
+ |
+
+BigNumber.config({ ROUNDING_MODE: BigNumber.ROUND_CEIL })
+BigNumber.config({ ROUNDING_MODE: 2 }) // equivalent
+
+ DEBUG
+undefined|false|true
+
+ If BigNumber.DEBUG is set true then an error will be thrown
+ if this BigNumber constructor receives an invalid value, such as
+ a value of type number with more than 15 significant digits.
+ See BigNumber.
+
+ An error will also be thrown if the isBigNumber
+ method receives a BigNumber that is not well-formed.
+ See isBigNumber.
+
BigNumber.DEBUG = true+ + +
INSTANCE
+ + +Methods
+The methods inherited by a BigNumber instance from its constructor's prototype object.
+A BigNumber is immutable in the sense that it is not changed by its methods.
+
+ The treatment of ±0, ±Infinity and NaN is
+ consistent with how JavaScript treats these values.
+
Many method names have a shorter alias.
+ + + +absoluteValue.abs() ⇒ BigNumber
+ + Returns a BigNumber whose value is the absolute value, i.e. the magnitude, of the value of + this BigNumber. +
+The return value is always exact and unrounded.
++x = new BigNumber(-0.8) +y = x.absoluteValue() // '0.8' +z = y.abs() // '0.8'+ + + +
+ comparedTo.comparedTo(n [, base]) ⇒ number
+
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
| Returns | |
|---|---|
1 |
+ If the value of this BigNumber is greater than the value of n |
+
-1 |
+ If the value of this BigNumber is less than the value of n |
+
0 |
+ If this BigNumber and n have the same value |
+
null |
+ If the value of either this BigNumber or n is NaN |
+
+x = new BigNumber(Infinity)
+y = new BigNumber(5)
+x.comparedTo(y) // 1
+x.comparedTo(x.minus(1)) // 0
+y.comparedTo(NaN) // null
+y.comparedTo('110', 2) // -1
+
+
+
+
+ decimalPlaces.dp([dp [, rm]]) ⇒ BigNumber|number
+
+
+ dp: number: integer, 0 to 1e+9 inclusive
+ rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive
+
+ If dp is a number, returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber
+ rounded by rounding mode rm to a maximum of dp decimal places.
+
+ If dp is omitted, or is null or undefined, the return
+ value is the number of decimal places of the value of this BigNumber, or null if
+ the value of this BigNumber is ±Infinity or NaN.
+
+ If rm is omitted, or is null or undefined,
+ ROUNDING_MODE is used.
+
+ Throws if dp or rm is invalid. See Errors.
+
+x = new BigNumber(1234.56)
+x.decimalPlaces(1) // '1234.6'
+x.dp() // 2
+x.decimalPlaces(2) // '1234.56'
+x.dp(10) // '1234.56'
+x.decimalPlaces(0, 1) // '1234'
+x.dp(0, 6) // '1235'
+x.decimalPlaces(1, 1) // '1234.5'
+x.dp(1, BigNumber.ROUND_HALF_EVEN) // '1234.6'
+x // '1234.56'
+y = new BigNumber('9.9e-101')
+y.dp() // 102
+
+
+
+ dividedBy.div(n [, base]) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber divided by
+ n, rounded according to the current
+ DECIMAL_PLACES and
+ ROUNDING_MODE settings.
+
+x = new BigNumber(355) +y = new BigNumber(113) +x.dividedBy(y) // '3.14159292035398230088' +x.div(5) // '71' +x.div(47, 16) // '5'+ + + +
+ dividedToIntegerBy.idiv(n [, base]) ⇒
+ BigNumber
+
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the integer part of dividing the value of this BigNumber by
+ n.
+
+x = new BigNumber(5)
+y = new BigNumber(3)
+x.dividedToIntegerBy(y) // '1'
+x.idiv(0.7) // '7'
+x.idiv('0.f', 16) // '5'
+
+
+
+
+ exponentiatedBy.pow(n [, m]) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber: integer
+ m: number|string|BigNumber
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber exponentiated by
+ n, i.e. raised to the power n, and optionally modulo a modulus
+ m.
+
+ Throws if n is not an integer. See Errors.
+
+ If n is negative the result is rounded according to the current
+ DECIMAL_PLACES and
+ ROUNDING_MODE settings.
+
+ As the number of digits of the result of the power operation can grow so large so quickly,
+ e.g. 123.45610000 has over 50000 digits, the number of significant
+ digits calculated is limited to the value of the
+ POW_PRECISION setting (unless a modulus
+ m is specified).
+
+ By default POW_PRECISION is set to 0.
+ This means that an unlimited number of significant digits will be calculated, and that the
+ method's performance will decrease dramatically for larger exponents.
+
+ If m is specified and the value of m, n and this
+ BigNumber are integers, and n is positive, then a fast modular exponentiation
+ algorithm is used, otherwise the operation will be performed as
+ x.exponentiatedBy(n).modulo(m) with a
+ POW_PRECISION of 0.
+
+Math.pow(0.7, 2) // 0.48999999999999994 +x = new BigNumber(0.7) +x.exponentiatedBy(2) // '0.49' +BigNumber(3).pow(-2) // '0.11111111111111111111'+ + + +
+ integerValue.integerValue([rm]) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+
+ rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber rounded to an integer using
+ rounding mode rm.
+
+ If rm is omitted, or is null or undefined,
+ ROUNDING_MODE is used.
+
+ Throws if rm is invalid. See Errors.
+
+x = new BigNumber(123.456) +x.integerValue() // '123' +x.integerValue(BigNumber.ROUND_CEIL) // '124' +y = new BigNumber(-12.7) +y.integerValue() // '-13' +y.integerValue(BigNumber.ROUND_DOWN) // '-12'+
+ The following is an example of how to add a prototype method that emulates JavaScript's
+ Math.round function. Math.ceil, Math.floor and
+ Math.trunc can be emulated in the same way with
+ BigNumber.ROUND_CEIL, BigNumber.ROUND_FLOOR and
+ BigNumber.ROUND_DOWN respectively.
+
+BigNumber.prototype.round = function (n) {
+ return n.integerValue(BigNumber.ROUND_HALF_CEIL);
+};
+x.round() // '123'
+
+
+
+ isEqualTo.eq(n [, base]) ⇒ boolean
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is equal to the value of
+ n, otherwise returns false.
+ As with JavaScript, NaN does not equal NaN.
+
Note: This method uses the comparedTo method internally.
+0 === 1e-324 // true
+x = new BigNumber(0)
+x.isEqualTo('1e-324') // false
+BigNumber(-0).eq(x) // true ( -0 === 0 )
+BigNumber(255).eq('ff', 16) // true
+
+y = new BigNumber(NaN)
+y.isEqualTo(NaN) // false
+
+
+
+ isFinite.isFinite() ⇒ boolean
+
+ Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is a finite number, otherwise
+ returns false.
+
+ The only possible non-finite values of a BigNumber are NaN, Infinity
+ and -Infinity.
+
+x = new BigNumber(1) +x.isFinite() // true +y = new BigNumber(Infinity) +y.isFinite() // false+
+ Note: The native method isFinite() can be used if
+ n <= Number.MAX_VALUE.
+
isGreaterThan.gt(n [, base]) ⇒ boolean
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is greater than the value of
+ n, otherwise returns false.
+
Note: This method uses the comparedTo method internally.
+0.1 > (0.3 - 0.2) // true +x = new BigNumber(0.1) +x.isGreaterThan(BigNumber(0.3).minus(0.2)) // false +BigNumber(0).gt(x) // false +BigNumber(11, 3).gt(11.1, 2) // true+ + + +
+ isGreaterThanOrEqualTo.gte(n [, base]) ⇒ boolean
+
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is greater than or equal to the value
+ of n, otherwise returns false.
+
Note: This method uses the comparedTo method internally.
+(0.3 - 0.2) >= 0.1 // false
+x = new BigNumber(0.3).minus(0.2)
+x.isGreaterThanOrEqualTo(0.1) // true
+BigNumber(1).gte(x) // true
+BigNumber(10, 18).gte('i', 36) // true
+
+
+
+ isInteger.isInteger() ⇒ boolean
+
+ Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is an integer, otherwise returns
+ false.
+
+x = new BigNumber(1) +x.isInteger() // true +y = new BigNumber(123.456) +y.isInteger() // false+ + + +
isLessThan.lt(n [, base]) ⇒ boolean
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is less than the value of
+ n, otherwise returns false.
+
Note: This method uses the comparedTo method internally.
+(0.3 - 0.2) < 0.1 // true +x = new BigNumber(0.3).minus(0.2) +x.isLessThan(0.1) // false +BigNumber(0).lt(x) // true +BigNumber(11.1, 2).lt(11, 3) // true+ + + +
+ isLessThanOrEqualTo.lte(n [, base]) ⇒ boolean
+
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is less than or equal to the value of
+ n, otherwise returns false.
+
Note: This method uses the comparedTo method internally.
+0.1 <= (0.3 - 0.2) // false
+x = new BigNumber(0.1)
+x.isLessThanOrEqualTo(BigNumber(0.3).minus(0.2)) // true
+BigNumber(-1).lte(x) // true
+BigNumber(10, 18).lte('i', 36) // true
+
+
+
+ isNaN.isNaN() ⇒ boolean
+
+ Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is NaN, otherwise
+ returns false.
+
+x = new BigNumber(NaN)
+x.isNaN() // true
+y = new BigNumber('Infinity')
+y.isNaN() // false
+ Note: The native method isNaN() can also be used.
isNegative.isNegative() ⇒ boolean
+
+ Returns true if the sign of this BigNumber is negative, otherwise returns
+ false.
+
+x = new BigNumber(-0) +x.isNegative() // true +y = new BigNumber(2) +y.isNegative() // false+
Note: n < 0 can be used if n <= -Number.MIN_VALUE.
isPositive.isPositive() ⇒ boolean
+
+ Returns true if the sign of this BigNumber is positive, otherwise returns
+ false.
+
+x = new BigNumber(-0) +x.isPositive() // false +y = new BigNumber(2) +y.isPositive() // true+ + + +
isZero.isZero() ⇒ boolean
+
+ Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is zero or minus zero, otherwise
+ returns false.
+
+x = new BigNumber(-0) +x.isZero() && x.isNegative() // true +y = new BigNumber(Infinity) +y.isZero() // false+
Note: n == 0 can be used if n >= Number.MIN_VALUE.
+ minus.minus(n [, base]) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber minus n.
The return value is always exact and unrounded.
++0.3 - 0.1 // 0.19999999999999998 +x = new BigNumber(0.3) +x.minus(0.1) // '0.2' +x.minus(0.6, 20) // '0'+ + + +
modulo.mod(n [, base]) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber modulo n, i.e.
+ the integer remainder of dividing this BigNumber by n.
+
+ The value returned, and in particular its sign, is dependent on the value of the
+ MODULO_MODE setting of this BigNumber constructor.
+ If it is 1 (default value), the result will have the same sign as this BigNumber,
+ and it will match that of Javascript's % operator (within the limits of double
+ precision) and BigDecimal's remainder method.
+
The return value is always exact and unrounded.
+
+ See MODULO_MODE for a description of the other
+ modulo modes.
+
+1 % 0.9 // 0.09999999999999998
+x = new BigNumber(1)
+x.modulo(0.9) // '0.1'
+y = new BigNumber(33)
+y.mod('a', 33) // '3'
+
+
+
+
+ multipliedBy.times(n [, base]) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber multiplied by n.
+
The return value is always exact and unrounded.
+
+0.6 * 3 // 1.7999999999999998
+x = new BigNumber(0.6)
+y = x.multipliedBy(3) // '1.8'
+BigNumber('7e+500').times(y) // '1.26e+501'
+x.multipliedBy('-a', 16) // '-6'
+
+
+
+ negated.negated() ⇒ BigNumber
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber negated, i.e. multiplied by
+ -1.
+
+x = new BigNumber(1.8) +x.negated() // '-1.8' +y = new BigNumber(-1.3) +y.negated() // '1.3'+ + + +
plus.plus(n [, base]) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber plus n.
The return value is always exact and unrounded.
+
+0.1 + 0.2 // 0.30000000000000004
+x = new BigNumber(0.1)
+y = x.plus(0.2) // '0.3'
+BigNumber(0.7).plus(x).plus(y) // '1'
+x.plus('0.1', 8) // '0.225'
+
+
+
+
+ precision.sd([d [, rm]]) ⇒ BigNumber|number
+
+
+ d: number|boolean: integer, 1 to 1e+9
+ inclusive, or true or false
+ rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive.
+
+ If d is a number, returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber
+ rounded to a precision of d significant digits using rounding mode
+ rm.
+
+ If d is omitted or is null or undefined, the return
+ value is the number of significant digits of the value of this BigNumber, or null
+ if the value of this BigNumber is ±Infinity or NaN.
+ If d is true then any trailing zeros of the integer
+ part of a number are counted as significant digits, otherwise they are not.
+
+ If rm is omitted or is null or undefined,
+ ROUNDING_MODE will be used.
+
+ Throws if d or rm is invalid. See Errors.
+
+x = new BigNumber(9876.54321) +x.precision(6) // '9876.54' +x.sd() // 9 +x.precision(6, BigNumber.ROUND_UP) // '9876.55' +x.sd(2) // '9900' +x.precision(2, 1) // '9800' +x // '9876.54321' +y = new BigNumber(987000) +y.precision() // 3 +y.sd(true) // 6+ + + +
shiftedBy.shiftedBy(n) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+ n: number: integer,
+ -9007199254740991 to 9007199254740991 inclusive
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber shifted by n
+ places.
+
+ The shift is of the decimal point, i.e. of powers of ten, and is to the left if n
+ is negative or to the right if n is positive.
+
The return value is always exact and unrounded.
+
+ Throws if n is invalid. See Errors.
+
+x = new BigNumber(1.23) +x.shiftedBy(3) // '1230' +x.shiftedBy(-3) // '0.00123'+ + + +
squareRoot.sqrt() ⇒ BigNumber
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the square root of the value of this BigNumber,
+ rounded according to the current
+ DECIMAL_PLACES and
+ ROUNDING_MODE settings.
+
+ The return value will be correctly rounded, i.e. rounded as if the result was first calculated + to an infinite number of correct digits before rounding. +
++x = new BigNumber(16) +x.squareRoot() // '4' +y = new BigNumber(3) +y.sqrt() // '1.73205080756887729353'+ + + +
+ toExponential.toExponential([dp [, rm]]) ⇒ string
+
+
+ dp: number: integer, 0 to 1e+9 inclusive
+ rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive
+
+ Returns a string representing the value of this BigNumber in exponential notation rounded
+ using rounding mode rm to dp decimal places, i.e with one digit
+ before the decimal point and dp digits after it.
+
+ If the value of this BigNumber in exponential notation has fewer than dp fraction
+ digits, the return value will be appended with zeros accordingly.
+
+ If dp is omitted, or is null or undefined, the number
+ of digits after the decimal point defaults to the minimum number of digits necessary to
+ represent the value exactly.
+ If rm is omitted or is null or undefined,
+ ROUNDING_MODE is used.
+
+ Throws if dp or rm is invalid. See Errors.
+
+x = 45.6 +y = new BigNumber(x) +x.toExponential() // '4.56e+1' +y.toExponential() // '4.56e+1' +x.toExponential(0) // '5e+1' +y.toExponential(0) // '5e+1' +x.toExponential(1) // '4.6e+1' +y.toExponential(1) // '4.6e+1' +y.toExponential(1, 1) // '4.5e+1' (ROUND_DOWN) +x.toExponential(3) // '4.560e+1' +y.toExponential(3) // '4.560e+1'+ + + +
+ toFixed.toFixed([dp [, rm]]) ⇒ string
+
+
+ dp: number: integer, 0 to 1e+9 inclusive
+ rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive
+
+ Returns a string representing the value of this BigNumber in normal (fixed-point) notation
+ rounded to dp decimal places using rounding mode rm.
+
+ If the value of this BigNumber in normal notation has fewer than dp fraction
+ digits, the return value will be appended with zeros accordingly.
+
+ Unlike Number.prototype.toFixed, which returns exponential notation if a number
+ is greater or equal to 1021, this method will always return normal
+ notation.
+
+ If dp is omitted or is null or undefined, the return
+ value will be unrounded and in normal notation. This is also unlike
+ Number.prototype.toFixed, which returns the value to zero decimal places.
+ It is useful when fixed-point notation is required and the current
+ EXPONENTIAL_AT setting causes
+ toString to return exponential notation.
+ If rm is omitted or is null or undefined,
+ ROUNDING_MODE is used.
+
+ Throws if dp or rm is invalid. See Errors.
+
+x = 3.456 +y = new BigNumber(x) +x.toFixed() // '3' +y.toFixed() // '3.456' +y.toFixed(0) // '3' +x.toFixed(2) // '3.46' +y.toFixed(2) // '3.46' +y.toFixed(2, 1) // '3.45' (ROUND_DOWN) +x.toFixed(5) // '3.45600' +y.toFixed(5) // '3.45600'+ + + +
+ toFormat.toFormat([dp [, rm[, format]]]) ⇒ string
+
+
+ dp: number: integer, 0 to 1e+9 inclusive
+ rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive
+ format: object: see FORMAT
+
+
+ Returns a string representing the value of this BigNumber in normal (fixed-point) notation
+ rounded to dp decimal places using rounding mode rm, and formatted
+ according to the properties of the format object.
+
+ See FORMAT and the examples below for the properties of the
+ format object, their types, and their usage. A formatting object may contain
+ some or all of the recognised properties.
+
+ If dp is omitted or is null or undefined, then the
+ return value is not rounded to a fixed number of decimal places.
+ If rm is omitted or is null or undefined,
+ ROUNDING_MODE is used.
+ If format is omitted or is null or undefined, the
+ FORMAT object is used.
+
+ Throws if dp, rm or format is invalid. See
+ Errors.
+
+fmt = {
+ prefix = '',
+ decimalSeparator: '.',
+ groupSeparator: ',',
+ groupSize: 3,
+ secondaryGroupSize: 0,
+ fractionGroupSeparator: ' ',
+ fractionGroupSize: 0,
+ suffix = ''
+}
+
+x = new BigNumber('123456789.123456789')
+
+// Set the global formatting options
+BigNumber.config({ FORMAT: fmt })
+
+x.toFormat() // '123,456,789.123456789'
+x.toFormat(3) // '123,456,789.123'
+
+// If a reference to the object assigned to FORMAT has been retained,
+// the format properties can be changed directly
+fmt.groupSeparator = ' '
+fmt.fractionGroupSize = 5
+x.toFormat() // '123 456 789.12345 6789'
+
+// Alternatively, pass the formatting options as an argument
+fmt = {
+ prefix: '=> ',
+ decimalSeparator: ',',
+ groupSeparator: '.',
+ groupSize: 3,
+ secondaryGroupSize: 2
+}
+
+x.toFormat() // '123 456 789.12345 6789'
+x.toFormat(fmt) // '=> 12.34.56.789,123456789'
+x.toFormat(2, fmt) // '=> 12.34.56.789,12'
+x.toFormat(3, BigNumber.ROUND_UP, fmt) // '=> 12.34.56.789,124'
+
+
+
+
+ toFraction.toFraction([maximum_denominator])
+ ⇒ [BigNumber, BigNumber]
+
+
+ maximum_denominator:
+ number|string|BigNumber: integer >= 1 and <=
+ Infinity
+
+ Returns an array of two BigNumbers representing the value of this BigNumber as a simple
+ fraction with an integer numerator and an integer denominator. The denominator will be a
+ positive non-zero value less than or equal to maximum_denominator.
+
+ If a maximum_denominator is not specified, or is null or
+ undefined, the denominator will be the lowest value necessary to represent the
+ number exactly.
+
+ Throws if maximum_denominator is invalid. See Errors.
+
+x = new BigNumber(1.75)
+x.toFraction() // '7, 4'
+
+pi = new BigNumber('3.14159265358')
+pi.toFraction() // '157079632679,50000000000'
+pi.toFraction(100000) // '312689, 99532'
+pi.toFraction(10000) // '355, 113'
+pi.toFraction(100) // '311, 99'
+pi.toFraction(10) // '22, 7'
+pi.toFraction(1) // '3, 1'
+
+
+
+ toJSON.toJSON() ⇒ string
+ As valueOf.
+x = new BigNumber('177.7e+457')
+y = new BigNumber(235.4325)
+z = new BigNumber('0.0098074')
+
+// Serialize an array of three BigNumbers
+str = JSON.stringify( [x, y, z] )
+// "["1.777e+459","235.4325","0.0098074"]"
+
+// Return an array of three BigNumbers
+JSON.parse(str, function (key, val) {
+ return key === '' ? val : new BigNumber(val)
+})
+
+
+
+ toNumber.toNumber() ⇒ number
+ Returns the value of this BigNumber as a JavaScript number primitive.
++ This method is identical to using type coercion with the unary plus operator. +
+
+x = new BigNumber(456.789)
+x.toNumber() // 456.789
++x // 456.789
+
+y = new BigNumber('45987349857634085409857349856430985')
+y.toNumber() // 4.598734985763409e+34
+
+z = new BigNumber(-0)
+1 / z.toNumber() // -Infinity
+1 / +z // -Infinity
+
+
+
+
+ toPrecision.toPrecision([sd [, rm]]) ⇒ string
+
+
+ sd: number: integer, 1 to 1e+9 inclusive
+ rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive
+
+ Returns a string representing the value of this BigNumber rounded to sd
+ significant digits using rounding mode rm.
+
+ If sd is less than the number of digits necessary to represent the integer part
+ of the value in normal (fixed-point) notation, then exponential notation is used.
+
+ If sd is omitted, or is null or undefined, then the
+ return value is the same as n.toString().
+ If rm is omitted or is null or undefined,
+ ROUNDING_MODE is used.
+
+ Throws if sd or rm is invalid. See Errors.
+
+x = 45.6 +y = new BigNumber(x) +x.toPrecision() // '45.6' +y.toPrecision() // '45.6' +x.toPrecision(1) // '5e+1' +y.toPrecision(1) // '5e+1' +y.toPrecision(2, 0) // '4.6e+1' (ROUND_UP) +y.toPrecision(2, 1) // '4.5e+1' (ROUND_DOWN) +x.toPrecision(5) // '45.600' +y.toPrecision(5) // '45.600'+ + + +
toString.toString([base]) ⇒ string
+
+ base: number: integer, 2 to ALPHABET.length
+ inclusive (see ALPHABET).
+
+ Returns a string representing the value of this BigNumber in the specified base, or base
+ 10 if base is omitted or is null or
+ undefined.
+
+ For bases above 10, and using the default base conversion alphabet
+ (see ALPHABET), values from 10 to
+ 35 are represented by a-z
+ (as with Number.prototype.toString).
+
+ If a base is specified the value is rounded according to the current
+ DECIMAL_PLACES
+ and ROUNDING_MODE settings.
+
+ If a base is not specified, and this BigNumber has a positive
+ exponent that is equal to or greater than the positive component of the
+ current EXPONENTIAL_AT setting,
+ or a negative exponent equal to or less than the negative component of the
+ setting, then exponential notation is returned.
+
If base is null or undefined it is ignored.
+ Throws if base is invalid. See Errors.
+
+x = new BigNumber(750000)
+x.toString() // '750000'
+BigNumber.config({ EXPONENTIAL_AT: 5 })
+x.toString() // '7.5e+5'
+
+y = new BigNumber(362.875)
+y.toString(2) // '101101010.111'
+y.toString(9) // '442.77777777777777777778'
+y.toString(32) // 'ba.s'
+
+BigNumber.config({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 4 });
+z = new BigNumber('1.23456789')
+z.toString() // '1.23456789'
+z.toString(10) // '1.2346'
+
+
+
+ valueOf.valueOf() ⇒ string
+
+ As toString, but does not accept a base argument and includes
+ the minus sign for negative zero.
+
+x = new BigNumber('-0')
+x.toString() // '0'
+x.valueOf() // '-0'
+y = new BigNumber('1.777e+457')
+y.valueOf() // '1.777e+457'
+
+
+
+ Properties
+The properties of a BigNumber instance:
+| Property | +Description | +Type | +Value | +
|---|---|---|---|
| c | +coefficient* | +number[] |
+ Array of base 1e14 numbers |
+
| e | +exponent | +number | +Integer, -1000000000 to 1000000000 inclusive |
+
| s | +sign | +number | +-1 or 1 |
+
*significand
+
+ The value of any of the c, e and s properties may also
+ be null.
+
+ The above properties are best considered to be read-only. In early versions of this library it + was okay to change the exponent of a BigNumber by writing to its exponent property directly, + but this is no longer reliable as the value of the first element of the coefficient array is + now dependent on the exponent. +
++ Note that, as with JavaScript numbers, the original exponent and fractional trailing zeros are + not necessarily preserved. +
+x = new BigNumber(0.123) // '0.123'
+x.toExponential() // '1.23e-1'
+x.c // '1,2,3'
+x.e // -1
+x.s // 1
+
+y = new Number(-123.4567000e+2) // '-12345.67'
+y.toExponential() // '-1.234567e+4'
+z = new BigNumber('-123.4567000e+2') // '-12345.67'
+z.toExponential() // '-1.234567e+4'
+z.c // '1,2,3,4,5,6,7'
+z.e // 4
+z.s // -1
+
+
+
+ Zero, NaN and Infinity
+
+ The table below shows how ±0, NaN and
+ ±Infinity are stored.
+
| + | c | +e | +s | +
|---|---|---|---|
| ±0 | +[0] |
+ 0 |
+ ±1 |
+
| NaN | +null |
+ null |
+ null |
+
| ±Infinity | +null |
+ null |
+ ±1 |
+
+x = new Number(-0) // 0 +1 / x == -Infinity // true + +y = new BigNumber(-0) // '0' +y.c // '0' ( [0].toString() ) +y.e // 0 +y.s // -1+ + + +
Errors
+The table below shows the errors that are thrown.
+
+ The errors are generic Error objects whose message begins
+ '[BigNumber Error]'.
+
| Method | +Throws | +
|---|---|
+ BigNumber+ comparedTo+ dividedBy+ dividedToIntegerBy+ isEqualTo+ isGreaterThan+ isGreaterThanOrEqualTo+ isLessThan+ isLessThanOrEqualTo+ minus+ modulo+ plus+ multipliedBy
+ |
+ Base not a primitive number | +
| Base not an integer | +|
| Base out of range | +|
| Number primitive has more than 15 significant digits* | +|
| Not a base... number* | +|
| Not a number* | +|
clone |
+ Object expected | +
config |
+ Object expected | +
DECIMAL_PLACES not a primitive number |
+ |
DECIMAL_PLACES not an integer |
+ |
DECIMAL_PLACES out of range |
+ |
ROUNDING_MODE not a primitive number |
+ |
ROUNDING_MODE not an integer |
+ |
ROUNDING_MODE out of range |
+ |
EXPONENTIAL_AT not a primitive number |
+ |
EXPONENTIAL_AT not an integer |
+ |
EXPONENTIAL_AT out of range |
+ |
RANGE not a primitive number |
+ |
RANGE not an integer |
+ |
RANGE cannot be zero |
+ |
RANGE cannot be zero |
+ |
CRYPTO not true or false |
+ |
crypto unavailable |
+ |
MODULO_MODE not a primitive number |
+ |
MODULO_MODE not an integer |
+ |
MODULO_MODE out of range |
+ |
POW_PRECISION not a primitive number |
+ |
POW_PRECISION not an integer |
+ |
POW_PRECISION out of range |
+ |
FORMAT not an object |
+ |
ALPHABET invalid |
+ |
+ decimalPlaces+ precision+ random+ shiftedBy+ toExponential+ toFixed+ toFormat+ toPrecision
+ |
+ Argument not a primitive number | +
| Argument not an integer | +|
| Argument out of range | +|
+ decimalPlaces+ precision
+ |
+ Argument not true or false | +
exponentiatedBy |
+ Argument not an integer | +
isBigNumber |
+ Invalid BigNumber* | +
+ minimum+ maximum
+ |
+ Not a number* | +
+ random
+ |
+ crypto unavailable | +
+ toFormat
+ |
+ Argument not an object | +
toFraction |
+ Argument not an integer | +
| Argument out of range | +|
toString |
+ Base not a primitive number | +
| Base not an integer | +|
| Base out of range | +
*Only thrown if BigNumber.DEBUG is true.
To determine if an exception is a BigNumber Error:
+
+try {
+ // ...
+} catch (e) {
+ if (e instanceof Error && e.message.indexOf('[BigNumber Error]') === 0) {
+ // ...
+ }
+}
+
+
+
+ Type coercion
+
+ To prevent the accidental use of a BigNumber in primitive number operations, or the
+ accidental addition of a BigNumber to a string, the valueOf method can be safely
+ overwritten as shown below.
+
+ The valueOf method is the same as the
+ toJSON method, and both are the same as the
+ toString method except they do not take a base
+ argument and they include the minus sign for negative zero.
+
+BigNumber.prototype.valueOf = function () {
+ throw Error('valueOf called!')
+}
+
+x = new BigNumber(1)
+x / 2 // '[BigNumber Error] valueOf called!'
+x + 'abc' // '[BigNumber Error] valueOf called!'
+
+
+
+
+ FAQ
+ +Why are trailing fractional zeros removed from BigNumbers?
++ Some arbitrary-precision libraries retain trailing fractional zeros as they can indicate the + precision of a value. This can be useful but the results of arithmetic operations can be + misleading. +
+
+x = new BigDecimal("1.0")
+y = new BigDecimal("1.1000")
+z = x.add(y) // 2.1000
+
+x = new BigDecimal("1.20")
+y = new BigDecimal("3.45000")
+z = x.multiply(y) // 4.1400000
+ + To specify the precision of a value is to specify that the value lies + within a certain range. +
+
+ In the first example, x has a value of 1.0. The trailing zero shows
+ the precision of the value, implying that it is in the range 0.95 to
+ 1.05. Similarly, the precision indicated by the trailing zeros of y
+ indicates that the value is in the range 1.09995 to 1.10005.
+
+ If we add the two lowest values in the ranges we have, 0.95 + 1.09995 = 2.04995,
+ and if we add the two highest values we have, 1.05 + 1.10005 = 2.15005, so the
+ range of the result of the addition implied by the precision of its operands is
+ 2.04995 to 2.15005.
+
+ The result given by BigDecimal of 2.1000 however, indicates that the value is in
+ the range 2.09995 to 2.10005 and therefore the precision implied by
+ its trailing zeros may be misleading.
+
+ In the second example, the true range is 4.122744 to 4.157256 yet
+ the BigDecimal answer of 4.1400000 indicates a range of 4.13999995
+ to 4.14000005. Again, the precision implied by the trailing zeros may be
+ misleading.
+
+ This library, like binary floating point and most calculators, does not retain trailing
+ fractional zeros. Instead, the toExponential, toFixed and
+ toPrecision methods enable trailing zeros to be added if and when required.
+
Hello world!
'); +}); + +// 让服务器监听8080端口: +server.listen(8080); + +console.log('Server is running at http://127.0.0.1:8080/'); + + +``` + +## 搭建一个web服务器,针对不同的参数,给予不同的回应,把html文件用异步方式去读取,返回.再去试下用orm框架去操作数据给不同参数返回不同的数据. + diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,http\346\250\241\345\235\227/html/mb.html" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,http\346\250\241\345\235\227/html/mb.html" new file mode 100644 index 0000000..ffe56f5 --- /dev/null +++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,http\346\250\241\345\235\227/html/mb.html" @@ -0,0 +1,13 @@ + + + + + + +请你吃大面包,很大哦~
+ +
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,http\346\250\241\345\235\227/html/milk.html" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,http\346\250\241\345\235\227/html/milk.html"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..79ca60a
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,http\346\250\241\345\235\227/html/milk.html"
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,http\346\250\241\345\235\227/html/milk.html" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,http\346\250\241\345\235\227/html/milk.html"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..79ca60a
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,http\346\250\241\345\235\227/html/milk.html"
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ 请你喝纯牛奶,超级纯的哦~
+ +
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,http\346\250\241\345\235\227/zy.js" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,http\346\250\241\345\235\227/zy.js"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..3e4c347
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,http\346\250\241\345\235\227/zy.js"
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
+//## 搭建一个web服务器,针对不同的参数,给予不同的回应,把html文件用异步方式去读取,返回.再去试下用orm框架去操作数据给不同参数返回不同的数据.
+//访问链接http://127.0.0.1:8080/food?name=milk
+
+let fs = require('fs');
+let http=require('http');
+let server=http.createServer(async function(request,response){
+
+ console.log(request.method+':'+request.url);
+
+ response.writeHead(200,{'Content_Type':'text/html;charset=utf_8'});
+
+ if(request.url.indexOf("/food")>-1){
+ let value=hanshu.chuliurl(request.url);
+ let bf=hanshu.readfilefanfa(value);
+ response.end(bf);
+
+ }
+})
+// 让服务器监听8080端口:端口不能随意写,2000以上的随你写
+server.listen(8080);
+
+console.log('Server is running at http://127.0.0.1:8080/');
+
+let hanshu={
+ readfilefanfa:function(value){
+ let bf=fs.readFileSync("./html/"+value+".html");
+ return bf;
+ },
+ chuliurl:function(url){
+ let arrs = url.split("=");
+ let value=arrs[1];
+ return value;
+ },
+}
\ No newline at end of file
--
Gitee
From 89c664ce4e3a492ec622f514ecd96016986e80fd Mon Sep 17 00:00:00 2001
From: =?UTF-8?q?=E4=BD=95=E5=BB=BA=E6=81=92?= <431765163@qq.com>
Date: Thu, 2 Mar 2023 17:44:49 +0800
Subject: [PATCH 3/5] 1
---
.../node_express\346\241\206\346\236\2661.md" | 64 +
.../node_modules/.bin/mime" | 12 +
.../node_modules/.bin/mime.cmd" | 17 +
.../node_modules/.bin/mime.ps1" | 28 +
.../node_modules/.package-lock.json" | 638 ++
.../node_modules/accepts/HISTORY.md" | 243 +
.../node_modules/accepts/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/accepts/README.md" | 140 +
.../node_modules/accepts/index.js" | 238 +
.../node_modules/accepts/package.json" | 47 +
.../node_modules/array-flatten/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/array-flatten/README.md" | 43 +
.../array-flatten/array-flatten.js" | 64 +
.../node_modules/array-flatten/package.json" | 39 +
.../node_modules/bignumber.js/CHANGELOG.md" | 266 +
.../node_modules/bignumber.js/LICENCE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/bignumber.js/README.md" | 268 +
.../node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.d.ts" | 1829 ++++
.../node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.js" | 2902 ++++++
.../bignumber.js/bignumber.min.js" | 1 +
.../bignumber.js/bignumber.min.js.map" | 1 +
.../node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.mjs" | 2888 ++++++
.../node_modules/bignumber.js/doc/API.html" | 2237 +++++
.../node_modules/bignumber.js/package.json" | 40 +
.../node_modules/body-parser/HISTORY.md" | 657 ++
.../node_modules/body-parser/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/body-parser/README.md" | 464 +
.../node_modules/body-parser/SECURITY.md" | 25 +
.../node_modules/body-parser/index.js" | 156 +
.../node_modules/body-parser/lib/read.js" | 205 +
.../body-parser/lib/types/json.js" | 236 +
.../body-parser/lib/types/raw.js" | 101 +
.../body-parser/lib/types/text.js" | 121 +
.../body-parser/lib/types/urlencoded.js" | 284 +
.../node_modules/body-parser/package.json" | 56 +
.../node_modules/bytes/History.md" | 97 +
.../node_modules/bytes/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/bytes/Readme.md" | 152 +
.../node_modules/bytes/index.js" | 170 +
.../node_modules/bytes/package.json" | 42 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/.eslintignore" | 1 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/.eslintrc" | 17 +
.../call-bind/.github/FUNDING.yml" | 12 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/.nycrc" | 13 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/CHANGELOG.md" | 42 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/README.md" | 2 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/callBound.js" | 15 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/index.js" | 47 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/package.json" | 80 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/test/callBound.js" | 55 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/test/index.js" | 66 +
.../content-disposition/HISTORY.md" | 60 +
.../node_modules/content-disposition/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../content-disposition/README.md" | 142 +
.../content-disposition/index.js" | 458 +
.../content-disposition/package.json" | 44 +
.../node_modules/content-type/HISTORY.md" | 29 +
.../node_modules/content-type/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/content-type/README.md" | 94 +
.../node_modules/content-type/index.js" | 225 +
.../node_modules/content-type/package.json" | 42 +
.../node_modules/cookie-signature/.npmignore" | 4 +
.../node_modules/cookie-signature/History.md" | 38 +
.../node_modules/cookie-signature/Readme.md" | 42 +
.../node_modules/cookie-signature/index.js" | 51 +
.../cookie-signature/package.json" | 18 +
.../node_modules/cookie/HISTORY.md" | 142 +
.../node_modules/cookie/LICENSE" | 24 +
.../node_modules/cookie/README.md" | 302 +
.../node_modules/cookie/SECURITY.md" | 25 +
.../node_modules/cookie/index.js" | 270 +
.../node_modules/cookie/package.json" | 44 +
.../node_modules/core-util-is/LICENSE" | 19 +
.../node_modules/core-util-is/README.md" | 3 +
.../node_modules/core-util-is/lib/util.js" | 107 +
.../node_modules/core-util-is/package.json" | 38 +
.../node_modules/debug/.coveralls.yml" | 1 +
.../node_modules/debug/.eslintrc" | 11 +
.../node_modules/debug/.npmignore" | 9 +
.../node_modules/debug/.travis.yml" | 14 +
.../node_modules/debug/CHANGELOG.md" | 362 +
.../node_modules/debug/LICENSE" | 19 +
.../node_modules/debug/Makefile" | 50 +
.../node_modules/debug/README.md" | 312 +
.../node_modules/debug/component.json" | 19 +
.../node_modules/debug/karma.conf.js" | 70 +
.../node_modules/debug/node.js" | 1 +
.../node_modules/debug/package.json" | 49 +
.../node_modules/debug/src/browser.js" | 185 +
.../node_modules/debug/src/debug.js" | 202 +
.../node_modules/debug/src/index.js" | 10 +
.../node_modules/debug/src/inspector-log.js" | 15 +
.../node_modules/debug/src/node.js" | 248 +
.../node_modules/depd/History.md" | 103 +
.../node_modules/depd/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/depd/Readme.md" | 280 +
.../node_modules/depd/index.js" | 538 ++
.../node_modules/depd/lib/browser/index.js" | 77 +
.../node_modules/depd/package.json" | 45 +
.../node_modules/destroy/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/destroy/README.md" | 63 +
.../node_modules/destroy/index.js" | 209 +
.../node_modules/destroy/package.json" | 48 +
.../node_modules/ee-first/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/ee-first/README.md" | 80 +
.../node_modules/ee-first/index.js" | 95 +
.../node_modules/ee-first/package.json" | 29 +
.../node_modules/encodeurl/HISTORY.md" | 14 +
.../node_modules/encodeurl/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/encodeurl/README.md" | 128 +
.../node_modules/encodeurl/index.js" | 60 +
.../node_modules/encodeurl/package.json" | 40 +
.../node_modules/escape-html/LICENSE" | 24 +
.../node_modules/escape-html/Readme.md" | 43 +
.../node_modules/escape-html/index.js" | 78 +
.../node_modules/escape-html/package.json" | 24 +
.../node_modules/etag/HISTORY.md" | 83 +
.../node_modules/etag/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/etag/README.md" | 159 +
.../node_modules/etag/index.js" | 131 +
.../node_modules/etag/package.json" | 47 +
.../node_modules/express/History.md" | 3588 +++++++
.../node_modules/express/LICENSE" | 24 +
.../node_modules/express/Readme.md" | 166 +
.../node_modules/express/index.js" | 11 +
.../node_modules/express/lib/application.js" | 661 ++
.../node_modules/express/lib/express.js" | 116 +
.../express/lib/middleware/init.js" | 43 +
.../express/lib/middleware/query.js" | 47 +
.../node_modules/express/lib/request.js" | 525 +
.../node_modules/express/lib/response.js" | 1169 +++
.../node_modules/express/lib/router/index.js" | 673 ++
.../node_modules/express/lib/router/layer.js" | 181 +
.../node_modules/express/lib/router/route.js" | 225 +
.../node_modules/express/lib/utils.js" | 304 +
.../node_modules/express/lib/view.js" | 182 +
.../node_modules/express/package.json" | 99 +
.../node_modules/finalhandler/HISTORY.md" | 195 +
.../node_modules/finalhandler/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/finalhandler/README.md" | 147 +
.../node_modules/finalhandler/SECURITY.md" | 25 +
.../node_modules/finalhandler/index.js" | 336 +
.../node_modules/finalhandler/package.json" | 46 +
.../node_modules/forwarded/HISTORY.md" | 21 +
.../node_modules/forwarded/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/forwarded/README.md" | 57 +
.../node_modules/forwarded/index.js" | 90 +
.../node_modules/forwarded/package.json" | 45 +
.../node_modules/fresh/HISTORY.md" | 70 +
.../node_modules/fresh/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/fresh/README.md" | 119 +
.../node_modules/fresh/index.js" | 137 +
.../node_modules/fresh/package.json" | 46 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/.editorconfig" | 20 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/.eslintrc" | 15 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/.jscs.json" | 176 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/.npmignore" | 22 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/.travis.yml" | 168 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/LICENSE" | 20 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/README.md" | 48 +
.../function-bind/implementation.js" | 52 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/index.js" | 5 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/package.json" | 63 +
.../function-bind/test/.eslintrc" | 9 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/test/index.js" | 252 +
.../node_modules/get-intrinsic/.eslintrc" | 38 +
.../get-intrinsic/.github/FUNDING.yml" | 12 +
.../node_modules/get-intrinsic/.nycrc" | 9 +
.../node_modules/get-intrinsic/CHANGELOG.md" | 110 +
.../node_modules/get-intrinsic/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/get-intrinsic/README.md" | 71 +
.../node_modules/get-intrinsic/index.js" | 344 +
.../node_modules/get-intrinsic/package.json" | 92 +
.../get-intrinsic/test/GetIntrinsic.js" | 274 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/.eslintrc" | 11 +
.../has-symbols/.github/FUNDING.yml" | 12 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/.nycrc" | 9 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/CHANGELOG.md" | 75 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/README.md" | 46 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/index.js" | 13 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/package.json" | 101 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/shams.js" | 42 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/test/index.js" | 22 +
.../has-symbols/test/shams/core-js.js" | 28 +
.../test/shams/get-own-property-symbols.js" | 28 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/test/tests.js" | 56 +
.../node_modules/has/LICENSE-MIT" | 22 +
.../node_modules/has/README.md" | 18 +
.../node_modules/has/package.json" | 48 +
.../node_modules/has/src/index.js" | 5 +
.../node_modules/has/test/index.js" | 10 +
.../node_modules/http-errors/HISTORY.md" | 180 +
.../node_modules/http-errors/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/http-errors/README.md" | 169 +
.../node_modules/http-errors/index.js" | 289 +
.../node_modules/http-errors/package.json" | 50 +
.../node_modules/iconv-lite/Changelog.md" | 162 +
.../node_modules/iconv-lite/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/iconv-lite/README.md" | 156 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/dbcs-codec.js" | 555 ++
.../iconv-lite/encodings/dbcs-data.js" | 176 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/index.js" | 22 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/internal.js" | 188 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/sbcs-codec.js" | 72 +
.../encodings/sbcs-data-generated.js" | 451 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/sbcs-data.js" | 174 +
.../encodings/tables/big5-added.json" | 122 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/tables/cp936.json" | 264 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/tables/cp949.json" | 273 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/tables/cp950.json" | 177 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/tables/eucjp.json" | 182 +
.../encodings/tables/gb18030-ranges.json" | 1 +
.../encodings/tables/gbk-added.json" | 55 +
.../encodings/tables/shiftjis.json" | 125 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/utf16.js" | 177 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/utf7.js" | 290 +
.../iconv-lite/lib/bom-handling.js" | 52 +
.../iconv-lite/lib/extend-node.js" | 217 +
.../node_modules/iconv-lite/lib/index.d.ts" | 24 +
.../node_modules/iconv-lite/lib/index.js" | 153 +
.../node_modules/iconv-lite/lib/streams.js" | 121 +
.../node_modules/iconv-lite/package.json" | 46 +
.../node_modules/inherits/LICENSE" | 16 +
.../node_modules/inherits/README.md" | 42 +
.../node_modules/inherits/inherits.js" | 9 +
.../inherits/inherits_browser.js" | 27 +
.../node_modules/inherits/package.json" | 29 +
.../node_modules/ipaddr.js/LICENSE" | 19 +
.../node_modules/ipaddr.js/README.md" | 233 +
.../node_modules/ipaddr.js/ipaddr.min.js" | 1 +
.../node_modules/ipaddr.js/lib/ipaddr.js" | 673 ++
.../ipaddr.js/lib/ipaddr.js.d.ts" | 68 +
.../node_modules/ipaddr.js/package.json" | 35 +
.../node_modules/isarray/.npmignore" | 1 +
.../node_modules/isarray/.travis.yml" | 4 +
.../node_modules/isarray/Makefile" | 6 +
.../node_modules/isarray/README.md" | 60 +
.../node_modules/isarray/component.json" | 19 +
.../node_modules/isarray/index.js" | 5 +
.../node_modules/isarray/package.json" | 45 +
.../node_modules/isarray/test.js" | 20 +
.../node_modules/media-typer/HISTORY.md" | 22 +
.../node_modules/media-typer/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/media-typer/README.md" | 81 +
.../node_modules/media-typer/index.js" | 270 +
.../node_modules/media-typer/package.json" | 26 +
.../merge-descriptors/HISTORY.md" | 21 +
.../node_modules/merge-descriptors/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/merge-descriptors/README.md" | 48 +
.../node_modules/merge-descriptors/index.js" | 60 +
.../merge-descriptors/package.json" | 32 +
.../node_modules/methods/HISTORY.md" | 29 +
.../node_modules/methods/LICENSE" | 24 +
.../node_modules/methods/README.md" | 51 +
.../node_modules/methods/index.js" | 69 +
.../node_modules/methods/package.json" | 36 +
.../node_modules/mime-db/HISTORY.md" | 507 +
.../node_modules/mime-db/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/mime-db/README.md" | 100 +
.../node_modules/mime-db/db.json" | 8519 +++++++++++++++++
.../node_modules/mime-db/index.js" | 12 +
.../node_modules/mime-db/package.json" | 60 +
.../node_modules/mime-types/HISTORY.md" | 397 +
.../node_modules/mime-types/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/mime-types/README.md" | 113 +
.../node_modules/mime-types/index.js" | 188 +
.../node_modules/mime-types/package.json" | 44 +
.../node_modules/mime/.npmignore" | 0
.../node_modules/mime/CHANGELOG.md" | 164 +
.../node_modules/mime/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/mime/README.md" | 90 +
.../node_modules/mime/cli.js" | 8 +
.../node_modules/mime/mime.js" | 108 +
.../node_modules/mime/package.json" | 44 +
.../node_modules/mime/src/build.js" | 53 +
.../node_modules/mime/src/test.js" | 60 +
.../node_modules/mime/types.json" | 1 +
.../node_modules/ms/index.js" | 152 +
.../node_modules/ms/license.md" | 21 +
.../node_modules/ms/package.json" | 37 +
.../node_modules/ms/readme.md" | 51 +
.../node_modules/mysql/Changes.md" | 569 ++
.../node_modules/mysql/License" | 19 +
.../node_modules/mysql/Readme.md" | 1548 +++
.../node_modules/mysql/index.js" | 161 +
.../node_modules/mysql/lib/Connection.js" | 529 +
.../mysql/lib/ConnectionConfig.js" | 209 +
.../node_modules/mysql/lib/Pool.js" | 294 +
.../node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolCluster.js" | 288 +
.../node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolConfig.js" | 32 +
.../node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolConnection.js" | 65 +
.../node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolNamespace.js" | 136 +
.../node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolSelector.js" | 31 +
.../node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/Auth.js" | 168 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/BufferList.js" | 25 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/PacketHeader.js" | 5 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/PacketWriter.js" | 211 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/Parser.js" | 491 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/Protocol.js" | 463 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/ResultSet.js" | 7 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/SqlString.js" | 1 +
.../node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/Timer.js" | 33 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/constants/charsets.js" | 262 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/constants/client.js" | 26 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/constants/errors.js" | 2476 +++++
.../lib/protocol/constants/field_flags.js" | 18 +
.../lib/protocol/constants/server_status.js" | 39 +
.../lib/protocol/constants/ssl_profiles.js" | 1480 +++
.../mysql/lib/protocol/constants/types.js" | 72 +
.../packets/AuthSwitchRequestPacket.js" | 20 +
.../packets/AuthSwitchResponsePacket.js" | 14 +
.../packets/ClientAuthenticationPacket.js" | 54 +
.../protocol/packets/ComChangeUserPacket.js" | 26 +
.../lib/protocol/packets/ComPingPacket.js" | 12 +
.../lib/protocol/packets/ComQueryPacket.js" | 15 +
.../lib/protocol/packets/ComQuitPacket.js" | 12 +
.../protocol/packets/ComStatisticsPacket.js" | 12 +
.../lib/protocol/packets/EmptyPacket.js" | 9 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/packets/EofPacket.js" | 25 +
.../lib/protocol/packets/ErrorPacket.js" | 35 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/packets/Field.js" | 26 +
.../lib/protocol/packets/FieldPacket.js" | 93 +
.../packets/HandshakeInitializationPacket.js" | 103 +
.../protocol/packets/LocalDataFilePacket.js" | 15 +
.../packets/LocalInfileRequestPacket.js" | 21 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/packets/OkPacket.js" | 44 +
.../protocol/packets/OldPasswordPacket.js" | 14 +
.../packets/ResultSetHeaderPacket.js" | 14 +
.../lib/protocol/packets/RowDataPacket.js" | 130 +
.../lib/protocol/packets/SSLRequestPacket.js" | 27 +
.../lib/protocol/packets/StatisticsPacket.js" | 20 +
.../protocol/packets/UseOldPasswordPacket.js" | 14 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/packets/index.js" | 23 +
.../lib/protocol/sequences/ChangeUser.js" | 67 +
.../lib/protocol/sequences/Handshake.js" | 126 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Ping.js" | 19 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Query.js" | 228 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Quit.js" | 40 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Sequence.js" | 125 +
.../lib/protocol/sequences/Statistics.js" | 30 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/index.js" | 7 +
.../mysql/node_modules/safe-buffer/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../mysql/node_modules/safe-buffer/README.md" | 584 ++
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/index.d.ts" | 187 +
.../mysql/node_modules/safe-buffer/index.js" | 62 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/package.json" | 37 +
.../node_modules/mysql/package.json" | 46 +
.../node_modules/negotiator/HISTORY.md" | 108 +
.../node_modules/negotiator/LICENSE" | 24 +
.../node_modules/negotiator/README.md" | 203 +
.../node_modules/negotiator/index.js" | 82 +
.../node_modules/negotiator/lib/charset.js" | 169 +
.../node_modules/negotiator/lib/encoding.js" | 184 +
.../node_modules/negotiator/lib/language.js" | 179 +
.../node_modules/negotiator/lib/mediaType.js" | 294 +
.../node_modules/negotiator/package.json" | 42 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/.eslintrc" | 53 +
.../object-inspect/.github/FUNDING.yml" | 12 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/.nycrc" | 13 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/CHANGELOG.md" | 370 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../object-inspect/example/all.js" | 23 +
.../object-inspect/example/circular.js" | 6 +
.../object-inspect/example/fn.js" | 5 +
.../object-inspect/example/inspect.js" | 10 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/index.js" | 516 +
.../object-inspect/package-support.json" | 20 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/package.json" | 97 +
.../object-inspect/readme.markdown" | 86 +
.../object-inspect/test-core-js.js" | 26 +
.../object-inspect/test/bigint.js" | 58 +
.../object-inspect/test/browser/dom.js" | 15 +
.../object-inspect/test/circular.js" | 16 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/test/deep.js" | 12 +
.../object-inspect/test/element.js" | 53 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/test/err.js" | 48 +
.../object-inspect/test/fakes.js" | 29 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/test/fn.js" | 76 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/test/has.js" | 15 +
.../object-inspect/test/holes.js" | 15 +
.../object-inspect/test/indent-option.js" | 271 +
.../object-inspect/test/inspect.js" | 139 +
.../object-inspect/test/lowbyte.js" | 12 +
.../object-inspect/test/number.js" | 58 +
.../object-inspect/test/quoteStyle.js" | 17 +
.../object-inspect/test/toStringTag.js" | 40 +
.../object-inspect/test/undef.js" | 12 +
.../object-inspect/test/values.js" | 211 +
.../object-inspect/util.inspect.js" | 1 +
.../node_modules/on-finished/HISTORY.md" | 98 +
.../node_modules/on-finished/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/on-finished/README.md" | 162 +
.../node_modules/on-finished/index.js" | 234 +
.../node_modules/on-finished/package.json" | 39 +
.../node_modules/parseurl/HISTORY.md" | 58 +
.../node_modules/parseurl/LICENSE" | 24 +
.../node_modules/parseurl/README.md" | 133 +
.../node_modules/parseurl/index.js" | 158 +
.../node_modules/parseurl/package.json" | 40 +
.../node_modules/path-to-regexp/History.md" | 36 +
.../node_modules/path-to-regexp/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/path-to-regexp/Readme.md" | 35 +
.../node_modules/path-to-regexp/index.js" | 129 +
.../node_modules/path-to-regexp/package.json" | 30 +
.../process-nextick-args/index.js" | 45 +
.../process-nextick-args/license.md" | 19 +
.../process-nextick-args/package.json" | 25 +
.../process-nextick-args/readme.md" | 18 +
.../node_modules/proxy-addr/HISTORY.md" | 161 +
.../node_modules/proxy-addr/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/proxy-addr/README.md" | 139 +
.../node_modules/proxy-addr/index.js" | 327 +
.../node_modules/proxy-addr/package.json" | 47 +
.../node_modules/qs/.editorconfig" | 43 +
.../node_modules/qs/.eslintrc" | 38 +
.../node_modules/qs/.github/FUNDING.yml" | 12 +
.../node_modules/qs/.nycrc" | 13 +
.../node_modules/qs/CHANGELOG.md" | 546 ++
.../node_modules/qs/LICENSE.md" | 29 +
.../node_modules/qs/README.md" | 625 ++
.../node_modules/qs/dist/qs.js" | 2054 ++++
.../node_modules/qs/lib/formats.js" | 23 +
.../node_modules/qs/lib/index.js" | 11 +
.../node_modules/qs/lib/parse.js" | 263 +
.../node_modules/qs/lib/stringify.js" | 326 +
.../node_modules/qs/lib/utils.js" | 252 +
.../node_modules/qs/package.json" | 77 +
.../node_modules/qs/test/parse.js" | 855 ++
.../node_modules/qs/test/stringify.js" | 909 ++
.../node_modules/qs/test/utils.js" | 136 +
.../node_modules/range-parser/HISTORY.md" | 56 +
.../node_modules/range-parser/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/range-parser/README.md" | 84 +
.../node_modules/range-parser/index.js" | 162 +
.../node_modules/range-parser/package.json" | 44 +
.../node_modules/raw-body/HISTORY.md" | 303 +
.../node_modules/raw-body/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/raw-body/README.md" | 223 +
.../node_modules/raw-body/SECURITY.md" | 24 +
.../node_modules/raw-body/index.d.ts" | 87 +
.../node_modules/raw-body/index.js" | 329 +
.../node_modules/raw-body/package.json" | 49 +
.../node_modules/readable-stream/.travis.yml" | 34 +
.../readable-stream/CONTRIBUTING.md" | 38 +
.../readable-stream/GOVERNANCE.md" | 136 +
.../node_modules/readable-stream/LICENSE" | 47 +
.../node_modules/readable-stream/README.md" | 58 +
.../doc/wg-meetings/2015-01-30.md" | 60 +
.../readable-stream/duplex-browser.js" | 1 +
.../node_modules/readable-stream/duplex.js" | 1 +
.../readable-stream/lib/_stream_duplex.js" | 131 +
.../lib/_stream_passthrough.js" | 47 +
.../readable-stream/lib/_stream_readable.js" | 1019 ++
.../readable-stream/lib/_stream_transform.js" | 214 +
.../readable-stream/lib/_stream_writable.js" | 687 ++
.../lib/internal/streams/BufferList.js" | 79 +
.../lib/internal/streams/destroy.js" | 74 +
.../lib/internal/streams/stream-browser.js" | 1 +
.../lib/internal/streams/stream.js" | 1 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/README.md" | 584 ++
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/index.d.ts" | 187 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/index.js" | 62 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/package.json" | 37 +
.../readable-stream/package.json" | 52 +
.../readable-stream/passthrough.js" | 1 +
.../readable-stream/readable-browser.js" | 7 +
.../node_modules/readable-stream/readable.js" | 19 +
.../readable-stream/transform.js" | 1 +
.../readable-stream/writable-browser.js" | 1 +
.../node_modules/readable-stream/writable.js" | 8 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/README.md" | 584 ++
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/index.d.ts" | 187 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/index.js" | 65 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/package.json" | 51 +
.../node_modules/safer-buffer/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../safer-buffer/Porting-Buffer.md" | 268 +
.../node_modules/safer-buffer/Readme.md" | 156 +
.../node_modules/safer-buffer/dangerous.js" | 58 +
.../node_modules/safer-buffer/package.json" | 34 +
.../node_modules/safer-buffer/safer.js" | 77 +
.../node_modules/safer-buffer/tests.js" | 406 +
.../node_modules/send/HISTORY.md" | 521 +
.../node_modules/send/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/send/README.md" | 327 +
.../node_modules/send/SECURITY.md" | 24 +
.../node_modules/send/index.js" | 1143 +++
.../send/node_modules/ms/index.js" | 162 +
.../send/node_modules/ms/license.md" | 21 +
.../send/node_modules/ms/package.json" | 38 +
.../send/node_modules/ms/readme.md" | 59 +
.../node_modules/send/package.json" | 62 +
.../node_modules/serve-static/HISTORY.md" | 471 +
.../node_modules/serve-static/LICENSE" | 25 +
.../node_modules/serve-static/README.md" | 257 +
.../node_modules/serve-static/index.js" | 210 +
.../node_modules/serve-static/package.json" | 42 +
.../node_modules/setprototypeof/LICENSE" | 13 +
.../node_modules/setprototypeof/README.md" | 31 +
.../node_modules/setprototypeof/index.d.ts" | 2 +
.../node_modules/setprototypeof/index.js" | 17 +
.../node_modules/setprototypeof/package.json" | 38 +
.../setprototypeof/test/index.js" | 24 +
.../node_modules/side-channel/.eslintignore" | 1 +
.../node_modules/side-channel/.eslintrc" | 11 +
.../side-channel/.github/FUNDING.yml" | 12 +
.../node_modules/side-channel/.nycrc" | 13 +
.../node_modules/side-channel/CHANGELOG.md" | 65 +
.../node_modules/side-channel/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/side-channel/README.md" | 2 +
.../node_modules/side-channel/index.js" | 124 +
.../node_modules/side-channel/package.json" | 67 +
.../node_modules/side-channel/test/index.js" | 78 +
.../node_modules/sqlstring/HISTORY.md" | 43 +
.../node_modules/sqlstring/LICENSE" | 19 +
.../node_modules/sqlstring/README.md" | 206 +
.../node_modules/sqlstring/index.js" | 1 +
.../node_modules/sqlstring/lib/SqlString.js" | 237 +
.../node_modules/sqlstring/package.json" | 47 +
.../node_modules/statuses/HISTORY.md" | 82 +
.../node_modules/statuses/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/statuses/README.md" | 136 +
.../node_modules/statuses/codes.json" | 65 +
.../node_modules/statuses/index.js" | 146 +
.../node_modules/statuses/package.json" | 49 +
.../node_modules/string_decoder/.travis.yml" | 50 +
.../node_modules/string_decoder/LICENSE" | 48 +
.../node_modules/string_decoder/README.md" | 47 +
.../string_decoder/lib/string_decoder.js" | 296 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/README.md" | 584 ++
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/index.d.ts" | 187 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/index.js" | 62 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/package.json" | 37 +
.../node_modules/string_decoder/package.json" | 31 +
.../node_modules/toidentifier/HISTORY.md" | 9 +
.../node_modules/toidentifier/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/toidentifier/README.md" | 61 +
.../node_modules/toidentifier/index.js" | 32 +
.../node_modules/toidentifier/package.json" | 38 +
.../node_modules/type-is/HISTORY.md" | 259 +
.../node_modules/type-is/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/type-is/README.md" | 170 +
.../node_modules/type-is/index.js" | 266 +
.../node_modules/type-is/package.json" | 45 +
.../node_modules/unpipe/HISTORY.md" | 4 +
.../node_modules/unpipe/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/unpipe/README.md" | 43 +
.../node_modules/unpipe/index.js" | 69 +
.../node_modules/unpipe/package.json" | 27 +
.../node_modules/util-deprecate/History.md" | 16 +
.../node_modules/util-deprecate/LICENSE" | 24 +
.../node_modules/util-deprecate/README.md" | 53 +
.../node_modules/util-deprecate/browser.js" | 67 +
.../node_modules/util-deprecate/node.js" | 6 +
.../node_modules/util-deprecate/package.json" | 27 +
.../node_modules/utils-merge/.npmignore" | 9 +
.../node_modules/utils-merge/LICENSE" | 20 +
.../node_modules/utils-merge/README.md" | 34 +
.../node_modules/utils-merge/index.js" | 23 +
.../node_modules/utils-merge/package.json" | 40 +
.../node_modules/vary/HISTORY.md" | 39 +
.../node_modules/vary/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/vary/README.md" | 101 +
.../node_modules/vary/index.js" | 149 +
.../node_modules/vary/package.json" | 43 +
.../package-lock.json" | 644 ++
.../package.json" | 6 +
.../show.html" | 91 +
.../zy.js" | 30 +
573 files changed, 90985 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_express\346\241\206\346\236\2661.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime.cmd"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime.ps1"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.package-lock.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/array-flatten/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/array-flatten/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/array-flatten/array-flatten.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/array-flatten/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/CHANGELOG.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/LICENCE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.d.ts"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.min.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.min.js.map"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.mjs"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/doc/API.html"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/SECURITY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/lib/read.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/lib/types/json.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/lib/types/raw.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/lib/types/text.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/lib/types/urlencoded.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bytes/History.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bytes/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bytes/Readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bytes/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bytes/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/.eslintignore"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/.eslintrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/.github/FUNDING.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/.nycrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/CHANGELOG.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/callBound.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/test/callBound.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/test/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-disposition/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-disposition/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-disposition/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-disposition/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-disposition/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-type/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-type/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-type/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-type/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-type/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie-signature/.npmignore"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie-signature/History.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie-signature/Readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie-signature/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie-signature/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/SECURITY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/core-util-is/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/core-util-is/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/core-util-is/lib/util.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/core-util-is/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/.coveralls.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/.eslintrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/.npmignore"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/.travis.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/CHANGELOG.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/Makefile"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/component.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/karma.conf.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/node.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/src/browser.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/src/debug.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/src/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/src/inspector-log.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/src/node.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/depd/History.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/depd/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/depd/Readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/depd/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/depd/lib/browser/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/depd/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/destroy/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/destroy/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/destroy/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/destroy/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ee-first/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ee-first/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ee-first/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ee-first/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/encodeurl/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/encodeurl/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/encodeurl/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/encodeurl/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/encodeurl/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/escape-html/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/escape-html/Readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/escape-html/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/escape-html/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/etag/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/etag/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/etag/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/etag/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/etag/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/History.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/Readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/application.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/express.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/middleware/init.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/middleware/query.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/request.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/response.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/router/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/router/layer.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/router/route.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/utils.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/view.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/finalhandler/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/finalhandler/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/finalhandler/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/finalhandler/SECURITY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/finalhandler/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/finalhandler/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/forwarded/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/forwarded/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/forwarded/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/forwarded/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/forwarded/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/fresh/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/fresh/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/fresh/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/fresh/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/fresh/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/.editorconfig"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/.eslintrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/.jscs.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/.npmignore"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/.travis.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/implementation.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/test/.eslintrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/test/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/get-intrinsic/.eslintrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/get-intrinsic/.github/FUNDING.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/get-intrinsic/.nycrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/get-intrinsic/CHANGELOG.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/get-intrinsic/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/get-intrinsic/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/get-intrinsic/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/get-intrinsic/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/get-intrinsic/test/GetIntrinsic.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/.eslintrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/.github/FUNDING.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/.nycrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/CHANGELOG.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/shams.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/test/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/test/shams/core-js.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/test/shams/get-own-property-symbols.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/test/tests.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has/LICENSE-MIT"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has/src/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has/test/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/http-errors/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/http-errors/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/http-errors/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/http-errors/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/http-errors/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/Changelog.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/dbcs-codec.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/dbcs-data.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/internal.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/sbcs-codec.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/sbcs-data-generated.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/sbcs-data.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/tables/big5-added.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/tables/cp936.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/tables/cp949.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/tables/cp950.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/tables/eucjp.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/tables/gb18030-ranges.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/tables/gbk-added.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/tables/shiftjis.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/utf16.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/utf7.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/lib/bom-handling.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/lib/extend-node.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/lib/index.d.ts"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/lib/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/lib/streams.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/inherits/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/inherits/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/inherits/inherits.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/inherits/inherits_browser.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/inherits/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ipaddr.js/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ipaddr.js/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ipaddr.js/ipaddr.min.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ipaddr.js/lib/ipaddr.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ipaddr.js/lib/ipaddr.js.d.ts"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ipaddr.js/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/isarray/.npmignore"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/isarray/.travis.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/isarray/Makefile"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/isarray/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/isarray/component.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/isarray/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/isarray/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/isarray/test.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/media-typer/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/media-typer/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/media-typer/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/media-typer/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/media-typer/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/merge-descriptors/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/merge-descriptors/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/merge-descriptors/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/merge-descriptors/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/merge-descriptors/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/methods/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/methods/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/methods/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/methods/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/methods/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-db/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-db/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-db/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-db/db.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-db/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-db/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-types/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-types/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-types/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-types/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-types/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/.npmignore"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/CHANGELOG.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/cli.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/mime.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/src/build.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/src/test.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/types.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ms/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ms/license.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ms/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ms/readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/Changes.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/License"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/Readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/Connection.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/ConnectionConfig.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/Pool.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolCluster.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolConfig.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolConnection.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolNamespace.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolSelector.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/Auth.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/BufferList.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/PacketHeader.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/PacketWriter.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/Parser.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/Protocol.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/ResultSet.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/SqlString.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/Timer.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/constants/charsets.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/constants/client.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/constants/errors.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/constants/field_flags.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/constants/server_status.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/constants/ssl_profiles.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/constants/types.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/AuthSwitchRequestPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/AuthSwitchResponsePacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/ClientAuthenticationPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/ComChangeUserPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/ComPingPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/ComQueryPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/ComQuitPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/ComStatisticsPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/EmptyPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/EofPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/ErrorPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/Field.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/FieldPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/HandshakeInitializationPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/LocalDataFilePacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/LocalInfileRequestPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/OkPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/OldPasswordPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/ResultSetHeaderPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/RowDataPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/SSLRequestPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/StatisticsPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/UseOldPasswordPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/ChangeUser.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Handshake.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Ping.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Query.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Quit.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Sequence.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Statistics.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/node_modules/safe-buffer/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/node_modules/safe-buffer/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/node_modules/safe-buffer/index.d.ts"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/node_modules/safe-buffer/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/node_modules/safe-buffer/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/negotiator/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/negotiator/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/negotiator/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/negotiator/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/negotiator/lib/charset.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/negotiator/lib/encoding.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/negotiator/lib/language.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/negotiator/lib/mediaType.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/negotiator/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/.eslintrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/.github/FUNDING.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/.nycrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/CHANGELOG.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/example/all.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/example/circular.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/example/fn.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/example/inspect.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/package-support.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/readme.markdown"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test-core-js.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/bigint.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/browser/dom.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/circular.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/deep.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/element.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/err.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/fakes.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/fn.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/has.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/holes.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/indent-option.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/inspect.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/lowbyte.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/number.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/quoteStyle.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/toStringTag.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/undef.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/values.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/util.inspect.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/on-finished/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/on-finished/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/on-finished/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/on-finished/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/on-finished/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/parseurl/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/parseurl/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/parseurl/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/parseurl/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/parseurl/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/path-to-regexp/History.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/path-to-regexp/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/path-to-regexp/Readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/path-to-regexp/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/path-to-regexp/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/process-nextick-args/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/process-nextick-args/license.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/process-nextick-args/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/process-nextick-args/readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/proxy-addr/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/proxy-addr/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/proxy-addr/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/proxy-addr/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/proxy-addr/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/.editorconfig"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/.eslintrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/.github/FUNDING.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/.nycrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/CHANGELOG.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/LICENSE.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/dist/qs.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/lib/formats.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/lib/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/lib/parse.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/lib/stringify.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/lib/utils.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/test/parse.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/test/stringify.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/test/utils.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/range-parser/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/range-parser/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/range-parser/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/range-parser/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/range-parser/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/raw-body/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/raw-body/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/raw-body/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/raw-body/SECURITY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/raw-body/index.d.ts"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/raw-body/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/raw-body/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/.travis.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/CONTRIBUTING.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/GOVERNANCE.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/doc/wg-meetings/2015-01-30.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/duplex-browser.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/duplex.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/lib/_stream_duplex.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/lib/_stream_passthrough.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/lib/_stream_readable.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/lib/_stream_transform.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/lib/_stream_writable.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/lib/internal/streams/BufferList.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/lib/internal/streams/destroy.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/lib/internal/streams/stream-browser.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/lib/internal/streams/stream.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/node_modules/safe-buffer/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/node_modules/safe-buffer/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/node_modules/safe-buffer/index.d.ts"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/node_modules/safe-buffer/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/node_modules/safe-buffer/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/passthrough.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/readable-browser.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/readable.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/transform.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/writable-browser.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/writable.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safe-buffer/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safe-buffer/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safe-buffer/index.d.ts"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safe-buffer/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safe-buffer/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safer-buffer/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safer-buffer/Porting-Buffer.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safer-buffer/Readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safer-buffer/dangerous.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safer-buffer/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safer-buffer/safer.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safer-buffer/tests.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/SECURITY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/node_modules/ms/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/node_modules/ms/license.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/node_modules/ms/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/node_modules/ms/readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/serve-static/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/serve-static/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/serve-static/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/serve-static/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/serve-static/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/setprototypeof/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/setprototypeof/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/setprototypeof/index.d.ts"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/setprototypeof/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/setprototypeof/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/setprototypeof/test/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/.eslintignore"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/.eslintrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/.github/FUNDING.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/.nycrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/CHANGELOG.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/test/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/sqlstring/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/sqlstring/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/sqlstring/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/sqlstring/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/sqlstring/lib/SqlString.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/sqlstring/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/statuses/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/statuses/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/statuses/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/statuses/codes.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/statuses/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/statuses/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/.travis.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/lib/string_decoder.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/node_modules/safe-buffer/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/node_modules/safe-buffer/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/node_modules/safe-buffer/index.d.ts"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/node_modules/safe-buffer/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/node_modules/safe-buffer/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/toidentifier/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/toidentifier/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/toidentifier/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/toidentifier/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/toidentifier/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/type-is/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/type-is/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/type-is/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/type-is/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/type-is/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/unpipe/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/unpipe/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/unpipe/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/unpipe/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/unpipe/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/util-deprecate/History.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/util-deprecate/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/util-deprecate/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/util-deprecate/browser.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/util-deprecate/node.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/util-deprecate/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/utils-merge/.npmignore"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/utils-merge/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/utils-merge/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/utils-merge/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/utils-merge/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/vary/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/vary/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/vary/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/vary/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/vary/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/package-lock.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/show.html"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/zy.js"
diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_express\346\241\206\346\236\2661.md" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_express\346\241\206\346\236\2661.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..21ea167
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_express\346\241\206\346\236\2661.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+## node 的框架
+
+### 初始Express
+
+1.1 Express介绍
+Express是目前流行的基于Node.js运行环境的Web应用程序开发框架,它简洁且灵活,为Web应用程序提供了强大的功能。Express提供了一个轻量级模块,类似于jQuery(封装的工具库),它把Node.js的HTTP模块的功能封装在一个简单易用的接口中,用于扩展HTTP模块的功能,能够轻松地处理服务器的路由、响应、Cookie和HTTP请求的状态。
+
+Express的优势:
+(1)简洁的路由定义方式。
+(2)简化HTTP请求参数的处理。
+(3)提供中间件机制控制HTTP请求。
+(4)拥有大量第三方中间件。
+(5)支持多种模版引擎
+
+### 安装express 框架
+
+```js
+
+// 项目初始化
+npm init -y
+// 安装
+npm install express --save
+
+// 查看版本
+
+npm list express
+
+
+```
+
+## 利用Express搭建Web服务器
+
+利用Express搭建Web服务器的基本步骤:
+
+#### 引入express模块;
+#### 调用express()方法创建服务器对象;
+#### 定义路由;
+#### 调用listen()方法监听端口
+
+
+来个例子
+
+```js
+
+// 引入express模块
+const express = require("express");
+// 创建Web服务器对象
+const app = express();
+// 定义GET路由,接收/处理客户端的GET请求
+app.get("/", (req, res) => {
+ // 对客户端做出响应,send()方法会根据内容的类型自动设置请求头
+ res.end("hello express");
+})
+// 监听3000端口
+app.listen(3000);
+
+```
+#### 理解 app 是啥,req,res 是啥.怎么接收参数,怎么回应参数.
+
+## 作业:利用express 想想怎么结合数据库,去实现学生(贪吃蛇的排名列表),能把学生的分数,班级
+## 在班上排名显示出来,还能实现分页
+
+
+
diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0a62a1b
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime"
@@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
+#!/bin/sh
+basedir=$(dirname "$(echo "$0" | sed -e 's,\\,/,g')")
+
+case `uname` in
+ *CYGWIN*|*MINGW*|*MSYS*) basedir=`cygpath -w "$basedir"`;;
+esac
+
+if [ -x "$basedir/node" ]; then
+ exec "$basedir/node" "$basedir/../mime/cli.js" "$@"
+else
+ exec node "$basedir/../mime/cli.js" "$@"
+fi
diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime.cmd" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime.cmd"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..54491f1
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime.cmd"
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+@ECHO off
+GOTO start
+:find_dp0
+SET dp0=%~dp0
+EXIT /b
+:start
+SETLOCAL
+CALL :find_dp0
+
+IF EXIST "%dp0%\node.exe" (
+ SET "_prog=%dp0%\node.exe"
+) ELSE (
+ SET "_prog=node"
+ SET PATHEXT=%PATHEXT:;.JS;=;%
+)
+
+endLocal & goto #_undefined_# 2>NUL || title %COMSPEC% & "%_prog%" "%dp0%\..\mime\cli.js" %*
diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime.ps1" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime.ps1"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..2222f40
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime.ps1"
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+#!/usr/bin/env pwsh
+$basedir=Split-Path $MyInvocation.MyCommand.Definition -Parent
+
+$exe=""
+if ($PSVersionTable.PSVersion -lt "6.0" -or $IsWindows) {
+ # Fix case when both the Windows and Linux builds of Node
+ # are installed in the same directory
+ $exe=".exe"
+}
+$ret=0
+if (Test-Path "$basedir/node$exe") {
+ # Support pipeline input
+ if ($MyInvocation.ExpectingInput) {
+ $input | & "$basedir/node$exe" "$basedir/../mime/cli.js" $args
+ } else {
+ & "$basedir/node$exe" "$basedir/../mime/cli.js" $args
+ }
+ $ret=$LASTEXITCODE
+} else {
+ # Support pipeline input
+ if ($MyInvocation.ExpectingInput) {
+ $input | & "node$exe" "$basedir/../mime/cli.js" $args
+ } else {
+ & "node$exe" "$basedir/../mime/cli.js" $args
+ }
+ $ret=$LASTEXITCODE
+}
+exit $ret
diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.package-lock.json" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.package-lock.json"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f25425c
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.package-lock.json"
@@ -0,0 +1,638 @@
+{
+ "name": "3.01,express 框架1",
+ "lockfileVersion": 3,
+ "requires": true,
+ "packages": {
+ "node_modules/accepts": {
+ "version": "1.3.8",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/accepts/-/accepts-1.3.8.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-PYAthTa2m2VKxuvSD3DPC/Gy+U+sOA1LAuT8mkmRuvw+NACSaeXEQ+NHcVF7rONl6qcaxV3Uuemwawk+7+SJLw==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "mime-types": "~2.1.34",
+ "negotiator": "0.6.3"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/array-flatten": {
+ "version": "1.1.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/array-flatten/-/array-flatten-1.1.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-PCVAQswWemu6UdxsDFFX/+gVeYqKAod3D3UVm91jHwynguOwAvYPhx8nNlM++NqRcK6CxxpUafjmhIdKiHibqg=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/bignumber.js": {
+ "version": "9.0.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/bignumber.js/-/bignumber.js-9.0.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-t/OYhhJ2SD+YGBQcjY8GzzDHEk9f3nerxjtfa6tlMXfe7frs/WozhvCNoGvpM0P3bNf3Gq5ZRMlGr5f3r4/N8A==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": "*"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/body-parser": {
+ "version": "1.20.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/body-parser/-/body-parser-1.20.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-jWi7abTbYwajOytWCQc37VulmWiRae5RyTpaCyDcS5/lMdtwSz5lOpDE67srw/HYe35f1z3fDQw+3txg7gNtWw==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "bytes": "3.1.2",
+ "content-type": "~1.0.4",
+ "debug": "2.6.9",
+ "depd": "2.0.0",
+ "destroy": "1.2.0",
+ "http-errors": "2.0.0",
+ "iconv-lite": "0.4.24",
+ "on-finished": "2.4.1",
+ "qs": "6.11.0",
+ "raw-body": "2.5.1",
+ "type-is": "~1.6.18",
+ "unpipe": "1.0.0"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8",
+ "npm": "1.2.8000 || >= 1.4.16"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/bytes": {
+ "version": "3.1.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/bytes/-/bytes-3.1.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-/Nf7TyzTx6S3yRJObOAV7956r8cr2+Oj8AC5dt8wSP3BQAoeX58NoHyCU8P8zGkNXStjTSi6fzO6F0pBdcYbEg==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/call-bind": {
+ "version": "1.0.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/call-bind/-/call-bind-1.0.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-7O+FbCihrB5WGbFYesctwmTKae6rOiIzmz1icreWJ+0aA7LJfuqhEso2T9ncpcFtzMQtzXf2QGGueWJGTYsqrA==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "function-bind": "^1.1.1",
+ "get-intrinsic": "^1.0.2"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/content-disposition": {
+ "version": "0.5.4",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/content-disposition/-/content-disposition-0.5.4.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-FveZTNuGw04cxlAiWbzi6zTAL/lhehaWbTtgluJh4/E95DqMwTmha3KZN1aAWA8cFIhHzMZUvLevkw5Rqk+tSQ==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "safe-buffer": "5.2.1"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/content-type": {
+ "version": "1.0.5",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/content-type/-/content-type-1.0.5.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-nTjqfcBFEipKdXCv4YDQWCfmcLZKm81ldF0pAopTvyrFGVbcR6P/VAAd5G7N+0tTr8QqiU0tFadD6FK4NtJwOA==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/cookie": {
+ "version": "0.5.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/cookie/-/cookie-0.5.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-YZ3GUyn/o8gfKJlnlX7g7xq4gyO6OSuhGPKaaGssGB2qgDUS0gPgtTvoyZLTt9Ab6dC4hfc9dV5arkvc/OCmrw==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/cookie-signature": {
+ "version": "1.0.6",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/cookie-signature/-/cookie-signature-1.0.6.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-QADzlaHc8icV8I7vbaJXJwod9HWYp8uCqf1xa4OfNu1T7JVxQIrUgOWtHdNDtPiywmFbiS12VjotIXLrKM3orQ=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/core-util-is": {
+ "version": "1.0.3",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/core-util-is/-/core-util-is-1.0.3.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-ZQBvi1DcpJ4GDqanjucZ2Hj3wEO5pZDS89BWbkcrvdxksJorwUDDZamX9ldFkp9aw2lmBDLgkObEA4DWNJ9FYQ=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/debug": {
+ "version": "2.6.9",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/debug/-/debug-2.6.9.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-bC7ElrdJaJnPbAP+1EotYvqZsb3ecl5wi6Bfi6BJTUcNowp6cvspg0jXznRTKDjm/E7AdgFBVeAPVMNcKGsHMA==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "ms": "2.0.0"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/depd": {
+ "version": "2.0.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/depd/-/depd-2.0.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-g7nH6P6dyDioJogAAGprGpCtVImJhpPk/roCzdb3fIh61/s/nPsfR6onyMwkCAR/OlC3yBC0lESvUoQEAssIrw==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/destroy": {
+ "version": "1.2.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/destroy/-/destroy-1.2.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-2sJGJTaXIIaR1w4iJSNoN0hnMY7Gpc/n8D4qSCJw8QqFWXf7cuAgnEHxBpweaVcPevC2l3KpjYCx3NypQQgaJg==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8",
+ "npm": "1.2.8000 || >= 1.4.16"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/ee-first": {
+ "version": "1.1.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/ee-first/-/ee-first-1.1.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-WMwm9LhRUo+WUaRN+vRuETqG89IgZphVSNkdFgeb6sS/E4OrDIN7t48CAewSHXc6C8lefD8KKfr5vY61brQlow=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/encodeurl": {
+ "version": "1.0.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/encodeurl/-/encodeurl-1.0.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-TPJXq8JqFaVYm2CWmPvnP2Iyo4ZSM7/QKcSmuMLDObfpH5fi7RUGmd/rTDf+rut/saiDiQEeVTNgAmJEdAOx0w==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/escape-html": {
+ "version": "1.0.3",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/escape-html/-/escape-html-1.0.3.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-NiSupZ4OeuGwr68lGIeym/ksIZMJodUGOSCZ/FSnTxcrekbvqrgdUxlJOMpijaKZVjAJrWrGs/6Jy8OMuyj9ow=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/etag": {
+ "version": "1.8.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/etag/-/etag-1.8.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-aIL5Fx7mawVa300al2BnEE4iNvo1qETxLrPI/o05L7z6go7fCw1J6EQmbK4FmJ2AS7kgVF/KEZWufBfdClMcPg==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/express": {
+ "version": "4.18.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/express/-/express-4.18.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-5/PsL6iGPdfQ/lKM1UuielYgv3BUoJfz1aUwU9vHZ+J7gyvwdQXFEBIEIaxeGf0GIcreATNyBExtalisDbuMqQ==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "accepts": "~1.3.8",
+ "array-flatten": "1.1.1",
+ "body-parser": "1.20.1",
+ "content-disposition": "0.5.4",
+ "content-type": "~1.0.4",
+ "cookie": "0.5.0",
+ "cookie-signature": "1.0.6",
+ "debug": "2.6.9",
+ "depd": "2.0.0",
+ "encodeurl": "~1.0.2",
+ "escape-html": "~1.0.3",
+ "etag": "~1.8.1",
+ "finalhandler": "1.2.0",
+ "fresh": "0.5.2",
+ "http-errors": "2.0.0",
+ "merge-descriptors": "1.0.1",
+ "methods": "~1.1.2",
+ "on-finished": "2.4.1",
+ "parseurl": "~1.3.3",
+ "path-to-regexp": "0.1.7",
+ "proxy-addr": "~2.0.7",
+ "qs": "6.11.0",
+ "range-parser": "~1.2.1",
+ "safe-buffer": "5.2.1",
+ "send": "0.18.0",
+ "serve-static": "1.15.0",
+ "setprototypeof": "1.2.0",
+ "statuses": "2.0.1",
+ "type-is": "~1.6.18",
+ "utils-merge": "1.0.1",
+ "vary": "~1.1.2"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.10.0"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/finalhandler": {
+ "version": "1.2.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/finalhandler/-/finalhandler-1.2.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-5uXcUVftlQMFnWC9qu/svkWv3GTd2PfUhK/3PLkYNAe7FbqJMt3515HaxE6eRL74GdsriiwujiawdaB1BpEISg==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "debug": "2.6.9",
+ "encodeurl": "~1.0.2",
+ "escape-html": "~1.0.3",
+ "on-finished": "2.4.1",
+ "parseurl": "~1.3.3",
+ "statuses": "2.0.1",
+ "unpipe": "~1.0.0"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/forwarded": {
+ "version": "0.2.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/forwarded/-/forwarded-0.2.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-buRG0fpBtRHSTCOASe6hD258tEubFoRLb4ZNA6NxMVHNw2gOcwHo9wyablzMzOA5z9xA9L1KNjk/Nt6MT9aYow==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/fresh": {
+ "version": "0.5.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/fresh/-/fresh-0.5.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-zJ2mQYM18rEFOudeV4GShTGIQ7RbzA7ozbU9I/XBpm7kqgMywgmylMwXHxZJmkVoYkna9d2pVXVXPdYTP9ej8Q==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/function-bind": {
+ "version": "1.1.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/function-bind/-/function-bind-1.1.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-yIovAzMX49sF8Yl58fSCWJ5svSLuaibPxXQJFLmBObTuCr0Mf1KiPopGM9NiFjiYBCbfaa2Fh6breQ6ANVTI0A=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/get-intrinsic": {
+ "version": "1.2.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/get-intrinsic/-/get-intrinsic-1.2.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-L049y6nFOuom5wGyRc3/gdTLO94dySVKRACj1RmJZBQXlbTMhtNIgkWkUHq+jYmZvKf14EW1EoJnnjbmoHij0Q==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "function-bind": "^1.1.1",
+ "has": "^1.0.3",
+ "has-symbols": "^1.0.3"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/has": {
+ "version": "1.0.3",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/has/-/has-1.0.3.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-f2dvO0VU6Oej7RkWJGrehjbzMAjFp5/VKPp5tTpWIV4JHHZK1/BxbFRtf/siA2SWTe09caDmVtYYzWEIbBS4zw==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "function-bind": "^1.1.1"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.4.0"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/has-symbols": {
+ "version": "1.0.3",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/has-symbols/-/has-symbols-1.0.3.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-l3LCuF6MgDNwTDKkdYGEihYjt5pRPbEg46rtlmnSPlUbgmB8LOIrKJbYYFBSbnPaJexMKtiPO8hmeRjRz2Td+A==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.4"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/http-errors": {
+ "version": "2.0.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/http-errors/-/http-errors-2.0.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-FtwrG/euBzaEjYeRqOgly7G0qviiXoJWnvEH2Z1plBdXgbyjv34pHTSb9zoeHMyDy33+DWy5Wt9Wo+TURtOYSQ==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "depd": "2.0.0",
+ "inherits": "2.0.4",
+ "setprototypeof": "1.2.0",
+ "statuses": "2.0.1",
+ "toidentifier": "1.0.1"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/iconv-lite": {
+ "version": "0.4.24",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/iconv-lite/-/iconv-lite-0.4.24.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-v3MXnZAcvnywkTUEZomIActle7RXXeedOR31wwl7VlyoXO4Qi9arvSenNQWne1TcRwhCL1HwLI21bEqdpj8/rA==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "safer-buffer": ">= 2.1.2 < 3"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">=0.10.0"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/inherits": {
+ "version": "2.0.4",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/inherits/-/inherits-2.0.4.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-k/vGaX4/Yla3WzyMCvTQOXYeIHvqOKtnqBduzTHpzpQZzAskKMhZ2K+EnBiSM9zGSoIFeMpXKxa4dYeZIQqewQ=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/ipaddr.js": {
+ "version": "1.9.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/ipaddr.js/-/ipaddr.js-1.9.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-0KI/607xoxSToH7GjN1FfSbLoU0+btTicjsQSWQlh/hZykN8KpmMf7uYwPW3R+akZ6R/w18ZlXSHBYXiYUPO3g==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.10"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/isarray": {
+ "version": "1.0.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/isarray/-/isarray-1.0.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-VLghIWNM6ELQzo7zwmcg0NmTVyWKYjvIeM83yjp0wRDTmUnrM678fQbcKBo6n2CJEF0szoG//ytg+TKla89ALQ=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/media-typer": {
+ "version": "0.3.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/media-typer/-/media-typer-0.3.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-dq+qelQ9akHpcOl/gUVRTxVIOkAJ1wR3QAvb4RsVjS8oVoFjDGTc679wJYmUmknUF5HwMLOgb5O+a3KxfWapPQ==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/merge-descriptors": {
+ "version": "1.0.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/merge-descriptors/-/merge-descriptors-1.0.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-cCi6g3/Zr1iqQi6ySbseM1Xvooa98N0w31jzUYrXPX2xqObmFGHJ0tQ5u74H3mVh7wLouTseZyYIq39g8cNp1w=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/methods": {
+ "version": "1.1.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/methods/-/methods-1.1.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-iclAHeNqNm68zFtnZ0e+1L2yUIdvzNoauKU4WBA3VvH/vPFieF7qfRlwUZU+DA9P9bPXIS90ulxoUoCH23sV2w==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/mime": {
+ "version": "1.6.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/mime/-/mime-1.6.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-x0Vn8spI+wuJ1O6S7gnbaQg8Pxh4NNHb7KSINmEWKiPE4RKOplvijn+NkmYmmRgP68mc70j2EbeTFRsrswaQeg==",
+ "bin": {
+ "mime": "cli.js"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">=4"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/mime-db": {
+ "version": "1.52.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/mime-db/-/mime-db-1.52.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-sPU4uV7dYlvtWJxwwxHD0PuihVNiE7TyAbQ5SWxDCB9mUYvOgroQOwYQQOKPJ8CIbE+1ETVlOoK1UC2nU3gYvg==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/mime-types": {
+ "version": "2.1.35",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/mime-types/-/mime-types-2.1.35.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-ZDY+bPm5zTTF+YpCrAU9nK0UgICYPT0QtT1NZWFv4s++TNkcgVaT0g6+4R2uI4MjQjzysHB1zxuWL50hzaeXiw==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "mime-db": "1.52.0"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/ms": {
+ "version": "2.0.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/ms/-/ms-2.0.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-Tpp60P6IUJDTuOq/5Z8cdskzJujfwqfOTkrwIwj7IRISpnkJnT6SyJ4PCPnGMoFjC9ddhal5KVIYtAt97ix05A=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/mysql": {
+ "version": "2.18.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/mysql/-/mysql-2.18.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-Bca+gk2YWmqp2Uf6k5NFEurwY/0td0cpebAucFpY/3jhrwrVGuxU2uQFCHjU19SJfje0yQvi+rVWdq78hR5lig==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "bignumber.js": "9.0.0",
+ "readable-stream": "2.3.7",
+ "safe-buffer": "5.1.2",
+ "sqlstring": "2.3.1"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/mysql/node_modules/safe-buffer": {
+ "version": "5.1.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/safe-buffer/-/safe-buffer-5.1.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-Gd2UZBJDkXlY7GbJxfsE8/nvKkUEU1G38c1siN6QP6a9PT9MmHB8GnpscSmMJSoF8LOIrt8ud/wPtojys4G6+g=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/negotiator": {
+ "version": "0.6.3",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/negotiator/-/negotiator-0.6.3.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-+EUsqGPLsM+j/zdChZjsnX51g4XrHFOIXwfnCVPGlQk/k5giakcKsuxCObBRu6DSm9opw/O6slWbJdghQM4bBg==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/object-inspect": {
+ "version": "1.12.3",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/object-inspect/-/object-inspect-1.12.3.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-geUvdk7c+eizMNUDkRpW1wJwgfOiOeHbxBR/hLXK1aT6zmVSO0jsQcs7fj6MGw89jC/cjGfLcNOrtMYtGqm81g=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/on-finished": {
+ "version": "2.4.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/on-finished/-/on-finished-2.4.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-oVlzkg3ENAhCk2zdv7IJwd/QUD4z2RxRwpkcGY8psCVcCYZNq4wYnVWALHM+brtuJjePWiYF/ClmuDr8Ch5+kg==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "ee-first": "1.1.1"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/parseurl": {
+ "version": "1.3.3",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/parseurl/-/parseurl-1.3.3.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-CiyeOxFT/JZyN5m0z9PfXw4SCBJ6Sygz1Dpl0wqjlhDEGGBP1GnsUVEL0p63hoG1fcj3fHynXi9NYO4nWOL+qQ==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/path-to-regexp": {
+ "version": "0.1.7",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/path-to-regexp/-/path-to-regexp-0.1.7.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-5DFkuoqlv1uYQKxy8omFBeJPQcdoE07Kv2sferDCrAq1ohOU+MSDswDIbnx3YAM60qIOnYa53wBhXW0EbMonrQ=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/process-nextick-args": {
+ "version": "2.0.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/process-nextick-args/-/process-nextick-args-2.0.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-3ouUOpQhtgrbOa17J7+uxOTpITYWaGP7/AhoR3+A+/1e9skrzelGi/dXzEYyvbxubEF6Wn2ypscTKiKJFFn1ag=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/proxy-addr": {
+ "version": "2.0.7",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/proxy-addr/-/proxy-addr-2.0.7.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-llQsMLSUDUPT44jdrU/O37qlnifitDP+ZwrmmZcoSKyLKvtZxpyV0n2/bD/N4tBAAZ/gJEdZU7KMraoK1+XYAg==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "forwarded": "0.2.0",
+ "ipaddr.js": "1.9.1"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.10"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/qs": {
+ "version": "6.11.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/qs/-/qs-6.11.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-MvjoMCJwEarSbUYk5O+nmoSzSutSsTwF85zcHPQ9OrlFoZOYIjaqBAJIqIXjptyD5vThxGq52Xu/MaJzRkIk4Q==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "side-channel": "^1.0.4"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">=0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/range-parser": {
+ "version": "1.2.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/range-parser/-/range-parser-1.2.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-Hrgsx+orqoygnmhFbKaHE6c296J+HTAQXoxEF6gNupROmmGJRoyzfG3ccAveqCBrwr/2yxQ5BVd/GTl5agOwSg==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/raw-body": {
+ "version": "2.5.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/raw-body/-/raw-body-2.5.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-qqJBtEyVgS0ZmPGdCFPWJ3FreoqvG4MVQln/kCgF7Olq95IbOp0/BWyMwbdtn4VTvkM8Y7khCQ2Xgk/tcrCXig==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "bytes": "3.1.2",
+ "http-errors": "2.0.0",
+ "iconv-lite": "0.4.24",
+ "unpipe": "1.0.0"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/readable-stream": {
+ "version": "2.3.7",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/readable-stream/-/readable-stream-2.3.7.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-Ebho8K4jIbHAxnuxi7o42OrZgF/ZTNcsZj6nRKyUmkhLFq8CHItp/fy6hQZuZmP/n3yZ9VBUbp4zz/mX8hmYPw==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "core-util-is": "~1.0.0",
+ "inherits": "~2.0.3",
+ "isarray": "~1.0.0",
+ "process-nextick-args": "~2.0.0",
+ "safe-buffer": "~5.1.1",
+ "string_decoder": "~1.1.1",
+ "util-deprecate": "~1.0.1"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/readable-stream/node_modules/safe-buffer": {
+ "version": "5.1.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/safe-buffer/-/safe-buffer-5.1.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-Gd2UZBJDkXlY7GbJxfsE8/nvKkUEU1G38c1siN6QP6a9PT9MmHB8GnpscSmMJSoF8LOIrt8ud/wPtojys4G6+g=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/safe-buffer": {
+ "version": "5.2.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/safe-buffer/-/safe-buffer-5.2.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-rp3So07KcdmmKbGvgaNxQSJr7bGVSVk5S9Eq1F+ppbRo70+YeaDxkw5Dd8NPN+GD6bjnYm2VuPuCXmpuYvmCXQ=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/safer-buffer": {
+ "version": "2.1.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/safer-buffer/-/safer-buffer-2.1.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-YZo3K82SD7Riyi0E1EQPojLz7kpepnSQI9IyPbHHg1XXXevb5dJI7tpyN2ADxGcQbHG7vcyRHk0cbwqcQriUtg=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/send": {
+ "version": "0.18.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/send/-/send-0.18.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-qqWzuOjSFOuqPjFe4NOsMLafToQQwBSOEpS+FwEt3A2V3vKubTquT3vmLTQpFgMXp8AlFWFuP1qKaJZOtPpVXg==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "debug": "2.6.9",
+ "depd": "2.0.0",
+ "destroy": "1.2.0",
+ "encodeurl": "~1.0.2",
+ "escape-html": "~1.0.3",
+ "etag": "~1.8.1",
+ "fresh": "0.5.2",
+ "http-errors": "2.0.0",
+ "mime": "1.6.0",
+ "ms": "2.1.3",
+ "on-finished": "2.4.1",
+ "range-parser": "~1.2.1",
+ "statuses": "2.0.1"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8.0"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/send/node_modules/ms": {
+ "version": "2.1.3",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/ms/-/ms-2.1.3.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-6FlzubTLZG3J2a/NVCAleEhjzq5oxgHyaCU9yYXvcLsvoVaHJq/s5xXI6/XXP6tz7R9xAOtHnSO/tXtF3WRTlA=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/serve-static": {
+ "version": "1.15.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/serve-static/-/serve-static-1.15.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-XGuRDNjXUijsUL0vl6nSD7cwURuzEgglbOaFuZM9g3kwDXOWVTck0jLzjPzGD+TazWbboZYu52/9/XPdUgne9g==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "encodeurl": "~1.0.2",
+ "escape-html": "~1.0.3",
+ "parseurl": "~1.3.3",
+ "send": "0.18.0"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8.0"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/setprototypeof": {
+ "version": "1.2.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/setprototypeof/-/setprototypeof-1.2.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-E5LDX7Wrp85Kil5bhZv46j8jOeboKq5JMmYM3gVGdGH8xFpPWXUMsNrlODCrkoxMEeNi/XZIwuRvY4XNwYMJpw=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/side-channel": {
+ "version": "1.0.4",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/side-channel/-/side-channel-1.0.4.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-q5XPytqFEIKHkGdiMIrY10mvLRvnQh42/+GoBlFW3b2LXLE2xxJpZFdm94we0BaoV3RwJyGqg5wS7epxTv0Zvw==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "call-bind": "^1.0.0",
+ "get-intrinsic": "^1.0.2",
+ "object-inspect": "^1.9.0"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/sqlstring": {
+ "version": "2.3.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/sqlstring/-/sqlstring-2.3.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-ooAzh/7dxIG5+uDik1z/Rd1vli0+38izZhGzSa34FwR7IbelPWCCKSNIl8jlL/F7ERvy8CB2jNeM1E9i9mXMAQ==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/statuses": {
+ "version": "2.0.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/statuses/-/statuses-2.0.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-RwNA9Z/7PrK06rYLIzFMlaF+l73iwpzsqRIFgbMLbTcLD6cOao82TaWefPXQvB2fOC4AjuYSEndS7N/mTCbkdQ==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/string_decoder": {
+ "version": "1.1.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/string_decoder/-/string_decoder-1.1.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-n/ShnvDi6FHbbVfviro+WojiFzv+s8MPMHBczVePfUpDJLwoLT0ht1l4YwBCbi8pJAveEEdnkHyPyTP/mzRfwg==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "safe-buffer": "~5.1.0"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/string_decoder/node_modules/safe-buffer": {
+ "version": "5.1.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/safe-buffer/-/safe-buffer-5.1.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-Gd2UZBJDkXlY7GbJxfsE8/nvKkUEU1G38c1siN6QP6a9PT9MmHB8GnpscSmMJSoF8LOIrt8ud/wPtojys4G6+g=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/toidentifier": {
+ "version": "1.0.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/toidentifier/-/toidentifier-1.0.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-o5sSPKEkg/DIQNmH43V0/uerLrpzVedkUh8tGNvaeXpfpuwjKenlSox/2O/BTlZUtEe+JG7s5YhEz608PlAHRA==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">=0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/type-is": {
+ "version": "1.6.18",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/type-is/-/type-is-1.6.18.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-TkRKr9sUTxEH8MdfuCSP7VizJyzRNMjj2J2do2Jr3Kym598JVdEksuzPQCnlFPW4ky9Q+iA+ma9BGm06XQBy8g==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "media-typer": "0.3.0",
+ "mime-types": "~2.1.24"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/unpipe": {
+ "version": "1.0.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/unpipe/-/unpipe-1.0.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-pjy2bYhSsufwWlKwPc+l3cN7+wuJlK6uz0YdJEOlQDbl6jo/YlPi4mb8agUkVC8BF7V8NuzeyPNqRksA3hztKQ==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/util-deprecate": {
+ "version": "1.0.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/util-deprecate/-/util-deprecate-1.0.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-EPD5q1uXyFxJpCrLnCc1nHnq3gOa6DZBocAIiI2TaSCA7VCJ1UJDMagCzIkXNsUYfD1daK//LTEQ8xiIbrHtcw=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/utils-merge": {
+ "version": "1.0.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/utils-merge/-/utils-merge-1.0.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-pMZTvIkT1d+TFGvDOqodOclx0QWkkgi6Tdoa8gC8ffGAAqz9pzPTZWAybbsHHoED/ztMtkv/VoYTYyShUn81hA==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.4.0"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/vary": {
+ "version": "1.1.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/vary/-/vary-1.1.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-BNGbWLfd0eUPabhkXUVm0j8uuvREyTh5ovRa/dyow/BqAbZJyC+5fU+IzQOzmAKzYqYRAISoRhdQr3eIZ/PXqg==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/HISTORY.md" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/HISTORY.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..cb5990c
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/HISTORY.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,243 @@
+1.3.8 / 2022-02-02
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.34
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.51.0
+ * deps: negotiator@0.6.3
+
+1.3.7 / 2019-04-29
+==================
+
+ * deps: negotiator@0.6.2
+ - Fix sorting charset, encoding, and language with extra parameters
+
+1.3.6 / 2019-04-28
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.24
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.40.0
+
+1.3.5 / 2018-02-28
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.18
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.33.0
+
+1.3.4 / 2017-08-22
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.16
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.29.0
+
+1.3.3 / 2016-05-02
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.11
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.23.0
+ * deps: negotiator@0.6.1
+ - perf: improve `Accept` parsing speed
+ - perf: improve `Accept-Charset` parsing speed
+ - perf: improve `Accept-Encoding` parsing speed
+ - perf: improve `Accept-Language` parsing speed
+
+1.3.2 / 2016-03-08
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.10
+ - Fix extension of `application/dash+xml`
+ - Update primary extension for `audio/mp4`
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.22.0
+
+1.3.1 / 2016-01-19
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.9
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.21.0
+
+1.3.0 / 2015-09-29
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.7
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.19.0
+ * deps: negotiator@0.6.0
+ - Fix including type extensions in parameters in `Accept` parsing
+ - Fix parsing `Accept` parameters with quoted equals
+ - Fix parsing `Accept` parameters with quoted semicolons
+ - Lazy-load modules from main entry point
+ - perf: delay type concatenation until needed
+ - perf: enable strict mode
+ - perf: hoist regular expressions
+ - perf: remove closures getting spec properties
+ - perf: remove a closure from media type parsing
+ - perf: remove property delete from media type parsing
+
+1.2.13 / 2015-09-06
+===================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.6
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.18.0
+
+1.2.12 / 2015-07-30
+===================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.4
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.16.0
+
+1.2.11 / 2015-07-16
+===================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.3
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.15.0
+
+1.2.10 / 2015-07-01
+===================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.2
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.14.0
+
+1.2.9 / 2015-06-08
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.1
+ - perf: fix deopt during mapping
+
+1.2.8 / 2015-06-07
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.0
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.13.0
+ * perf: avoid argument reassignment & argument slice
+ * perf: avoid negotiator recursive construction
+ * perf: enable strict mode
+ * perf: remove unnecessary bitwise operator
+
+1.2.7 / 2015-05-10
+==================
+
+ * deps: negotiator@0.5.3
+ - Fix media type parameter matching to be case-insensitive
+
+1.2.6 / 2015-05-07
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.0.11
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.9.1
+ * deps: negotiator@0.5.2
+ - Fix comparing media types with quoted values
+ - Fix splitting media types with quoted commas
+
+1.2.5 / 2015-03-13
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.0.10
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.8.0
+
+1.2.4 / 2015-02-14
+==================
+
+ * Support Node.js 0.6
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.0.9
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.7.0
+ * deps: negotiator@0.5.1
+ - Fix preference sorting to be stable for long acceptable lists
+
+1.2.3 / 2015-01-31
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.0.8
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.6.0
+
+1.2.2 / 2014-12-30
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.0.7
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.5.0
+
+1.2.1 / 2014-12-30
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.0.5
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.3.1
+
+1.2.0 / 2014-12-19
+==================
+
+ * deps: negotiator@0.5.0
+ - Fix list return order when large accepted list
+ - Fix missing identity encoding when q=0 exists
+ - Remove dynamic building of Negotiator class
+
+1.1.4 / 2014-12-10
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.0.4
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.3.0
+
+1.1.3 / 2014-11-09
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.0.3
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.2.0
+
+1.1.2 / 2014-10-14
+==================
+
+ * deps: negotiator@0.4.9
+ - Fix error when media type has invalid parameter
+
+1.1.1 / 2014-09-28
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.0.2
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.1.0
+ * deps: negotiator@0.4.8
+ - Fix all negotiations to be case-insensitive
+ - Stable sort preferences of same quality according to client order
+
+1.1.0 / 2014-09-02
+==================
+
+ * update `mime-types`
+
+1.0.7 / 2014-07-04
+==================
+
+ * Fix wrong type returned from `type` when match after unknown extension
+
+1.0.6 / 2014-06-24
+==================
+
+ * deps: negotiator@0.4.7
+
+1.0.5 / 2014-06-20
+==================
+
+ * fix crash when unknown extension given
+
+1.0.4 / 2014-06-19
+==================
+
+ * use `mime-types`
+
+1.0.3 / 2014-06-11
+==================
+
+ * deps: negotiator@0.4.6
+ - Order by specificity when quality is the same
+
+1.0.2 / 2014-05-29
+==================
+
+ * Fix interpretation when header not in request
+ * deps: pin negotiator@0.4.5
+
+1.0.1 / 2014-01-18
+==================
+
+ * Identity encoding isn't always acceptable
+ * deps: negotiator@~0.4.0
+
+1.0.0 / 2013-12-27
+==================
+
+ * Genesis
diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/LICENSE" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/LICENSE"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0616607
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/LICENSE"
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+(The MIT License)
+
+Copyright (c) 2014 Jonathan Ong
+
+
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,http\346\250\241\345\235\227/zy.js" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,http\346\250\241\345\235\227/zy.js"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..3e4c347
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,http\346\250\241\345\235\227/zy.js"
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
+//## 搭建一个web服务器,针对不同的参数,给予不同的回应,把html文件用异步方式去读取,返回.再去试下用orm框架去操作数据给不同参数返回不同的数据.
+//访问链接http://127.0.0.1:8080/food?name=milk
+
+let fs = require('fs');
+let http=require('http');
+let server=http.createServer(async function(request,response){
+
+ console.log(request.method+':'+request.url);
+
+ response.writeHead(200,{'Content_Type':'text/html;charset=utf_8'});
+
+ if(request.url.indexOf("/food")>-1){
+ let value=hanshu.chuliurl(request.url);
+ let bf=hanshu.readfilefanfa(value);
+ response.end(bf);
+
+ }
+})
+// 让服务器监听8080端口:端口不能随意写,2000以上的随你写
+server.listen(8080);
+
+console.log('Server is running at http://127.0.0.1:8080/');
+
+let hanshu={
+ readfilefanfa:function(value){
+ let bf=fs.readFileSync("./html/"+value+".html");
+ return bf;
+ },
+ chuliurl:function(url){
+ let arrs = url.split("=");
+ let value=arrs[1];
+ return value;
+ },
+}
\ No newline at end of file
--
Gitee
From 89c664ce4e3a492ec622f514ecd96016986e80fd Mon Sep 17 00:00:00 2001
From: =?UTF-8?q?=E4=BD=95=E5=BB=BA=E6=81=92?= <431765163@qq.com>
Date: Thu, 2 Mar 2023 17:44:49 +0800
Subject: [PATCH 3/5] 1
---
.../node_express\346\241\206\346\236\2661.md" | 64 +
.../node_modules/.bin/mime" | 12 +
.../node_modules/.bin/mime.cmd" | 17 +
.../node_modules/.bin/mime.ps1" | 28 +
.../node_modules/.package-lock.json" | 638 ++
.../node_modules/accepts/HISTORY.md" | 243 +
.../node_modules/accepts/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/accepts/README.md" | 140 +
.../node_modules/accepts/index.js" | 238 +
.../node_modules/accepts/package.json" | 47 +
.../node_modules/array-flatten/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/array-flatten/README.md" | 43 +
.../array-flatten/array-flatten.js" | 64 +
.../node_modules/array-flatten/package.json" | 39 +
.../node_modules/bignumber.js/CHANGELOG.md" | 266 +
.../node_modules/bignumber.js/LICENCE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/bignumber.js/README.md" | 268 +
.../node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.d.ts" | 1829 ++++
.../node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.js" | 2902 ++++++
.../bignumber.js/bignumber.min.js" | 1 +
.../bignumber.js/bignumber.min.js.map" | 1 +
.../node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.mjs" | 2888 ++++++
.../node_modules/bignumber.js/doc/API.html" | 2237 +++++
.../node_modules/bignumber.js/package.json" | 40 +
.../node_modules/body-parser/HISTORY.md" | 657 ++
.../node_modules/body-parser/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/body-parser/README.md" | 464 +
.../node_modules/body-parser/SECURITY.md" | 25 +
.../node_modules/body-parser/index.js" | 156 +
.../node_modules/body-parser/lib/read.js" | 205 +
.../body-parser/lib/types/json.js" | 236 +
.../body-parser/lib/types/raw.js" | 101 +
.../body-parser/lib/types/text.js" | 121 +
.../body-parser/lib/types/urlencoded.js" | 284 +
.../node_modules/body-parser/package.json" | 56 +
.../node_modules/bytes/History.md" | 97 +
.../node_modules/bytes/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/bytes/Readme.md" | 152 +
.../node_modules/bytes/index.js" | 170 +
.../node_modules/bytes/package.json" | 42 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/.eslintignore" | 1 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/.eslintrc" | 17 +
.../call-bind/.github/FUNDING.yml" | 12 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/.nycrc" | 13 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/CHANGELOG.md" | 42 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/README.md" | 2 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/callBound.js" | 15 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/index.js" | 47 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/package.json" | 80 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/test/callBound.js" | 55 +
.../node_modules/call-bind/test/index.js" | 66 +
.../content-disposition/HISTORY.md" | 60 +
.../node_modules/content-disposition/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../content-disposition/README.md" | 142 +
.../content-disposition/index.js" | 458 +
.../content-disposition/package.json" | 44 +
.../node_modules/content-type/HISTORY.md" | 29 +
.../node_modules/content-type/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/content-type/README.md" | 94 +
.../node_modules/content-type/index.js" | 225 +
.../node_modules/content-type/package.json" | 42 +
.../node_modules/cookie-signature/.npmignore" | 4 +
.../node_modules/cookie-signature/History.md" | 38 +
.../node_modules/cookie-signature/Readme.md" | 42 +
.../node_modules/cookie-signature/index.js" | 51 +
.../cookie-signature/package.json" | 18 +
.../node_modules/cookie/HISTORY.md" | 142 +
.../node_modules/cookie/LICENSE" | 24 +
.../node_modules/cookie/README.md" | 302 +
.../node_modules/cookie/SECURITY.md" | 25 +
.../node_modules/cookie/index.js" | 270 +
.../node_modules/cookie/package.json" | 44 +
.../node_modules/core-util-is/LICENSE" | 19 +
.../node_modules/core-util-is/README.md" | 3 +
.../node_modules/core-util-is/lib/util.js" | 107 +
.../node_modules/core-util-is/package.json" | 38 +
.../node_modules/debug/.coveralls.yml" | 1 +
.../node_modules/debug/.eslintrc" | 11 +
.../node_modules/debug/.npmignore" | 9 +
.../node_modules/debug/.travis.yml" | 14 +
.../node_modules/debug/CHANGELOG.md" | 362 +
.../node_modules/debug/LICENSE" | 19 +
.../node_modules/debug/Makefile" | 50 +
.../node_modules/debug/README.md" | 312 +
.../node_modules/debug/component.json" | 19 +
.../node_modules/debug/karma.conf.js" | 70 +
.../node_modules/debug/node.js" | 1 +
.../node_modules/debug/package.json" | 49 +
.../node_modules/debug/src/browser.js" | 185 +
.../node_modules/debug/src/debug.js" | 202 +
.../node_modules/debug/src/index.js" | 10 +
.../node_modules/debug/src/inspector-log.js" | 15 +
.../node_modules/debug/src/node.js" | 248 +
.../node_modules/depd/History.md" | 103 +
.../node_modules/depd/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/depd/Readme.md" | 280 +
.../node_modules/depd/index.js" | 538 ++
.../node_modules/depd/lib/browser/index.js" | 77 +
.../node_modules/depd/package.json" | 45 +
.../node_modules/destroy/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/destroy/README.md" | 63 +
.../node_modules/destroy/index.js" | 209 +
.../node_modules/destroy/package.json" | 48 +
.../node_modules/ee-first/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/ee-first/README.md" | 80 +
.../node_modules/ee-first/index.js" | 95 +
.../node_modules/ee-first/package.json" | 29 +
.../node_modules/encodeurl/HISTORY.md" | 14 +
.../node_modules/encodeurl/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/encodeurl/README.md" | 128 +
.../node_modules/encodeurl/index.js" | 60 +
.../node_modules/encodeurl/package.json" | 40 +
.../node_modules/escape-html/LICENSE" | 24 +
.../node_modules/escape-html/Readme.md" | 43 +
.../node_modules/escape-html/index.js" | 78 +
.../node_modules/escape-html/package.json" | 24 +
.../node_modules/etag/HISTORY.md" | 83 +
.../node_modules/etag/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/etag/README.md" | 159 +
.../node_modules/etag/index.js" | 131 +
.../node_modules/etag/package.json" | 47 +
.../node_modules/express/History.md" | 3588 +++++++
.../node_modules/express/LICENSE" | 24 +
.../node_modules/express/Readme.md" | 166 +
.../node_modules/express/index.js" | 11 +
.../node_modules/express/lib/application.js" | 661 ++
.../node_modules/express/lib/express.js" | 116 +
.../express/lib/middleware/init.js" | 43 +
.../express/lib/middleware/query.js" | 47 +
.../node_modules/express/lib/request.js" | 525 +
.../node_modules/express/lib/response.js" | 1169 +++
.../node_modules/express/lib/router/index.js" | 673 ++
.../node_modules/express/lib/router/layer.js" | 181 +
.../node_modules/express/lib/router/route.js" | 225 +
.../node_modules/express/lib/utils.js" | 304 +
.../node_modules/express/lib/view.js" | 182 +
.../node_modules/express/package.json" | 99 +
.../node_modules/finalhandler/HISTORY.md" | 195 +
.../node_modules/finalhandler/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/finalhandler/README.md" | 147 +
.../node_modules/finalhandler/SECURITY.md" | 25 +
.../node_modules/finalhandler/index.js" | 336 +
.../node_modules/finalhandler/package.json" | 46 +
.../node_modules/forwarded/HISTORY.md" | 21 +
.../node_modules/forwarded/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/forwarded/README.md" | 57 +
.../node_modules/forwarded/index.js" | 90 +
.../node_modules/forwarded/package.json" | 45 +
.../node_modules/fresh/HISTORY.md" | 70 +
.../node_modules/fresh/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/fresh/README.md" | 119 +
.../node_modules/fresh/index.js" | 137 +
.../node_modules/fresh/package.json" | 46 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/.editorconfig" | 20 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/.eslintrc" | 15 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/.jscs.json" | 176 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/.npmignore" | 22 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/.travis.yml" | 168 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/LICENSE" | 20 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/README.md" | 48 +
.../function-bind/implementation.js" | 52 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/index.js" | 5 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/package.json" | 63 +
.../function-bind/test/.eslintrc" | 9 +
.../node_modules/function-bind/test/index.js" | 252 +
.../node_modules/get-intrinsic/.eslintrc" | 38 +
.../get-intrinsic/.github/FUNDING.yml" | 12 +
.../node_modules/get-intrinsic/.nycrc" | 9 +
.../node_modules/get-intrinsic/CHANGELOG.md" | 110 +
.../node_modules/get-intrinsic/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/get-intrinsic/README.md" | 71 +
.../node_modules/get-intrinsic/index.js" | 344 +
.../node_modules/get-intrinsic/package.json" | 92 +
.../get-intrinsic/test/GetIntrinsic.js" | 274 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/.eslintrc" | 11 +
.../has-symbols/.github/FUNDING.yml" | 12 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/.nycrc" | 9 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/CHANGELOG.md" | 75 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/README.md" | 46 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/index.js" | 13 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/package.json" | 101 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/shams.js" | 42 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/test/index.js" | 22 +
.../has-symbols/test/shams/core-js.js" | 28 +
.../test/shams/get-own-property-symbols.js" | 28 +
.../node_modules/has-symbols/test/tests.js" | 56 +
.../node_modules/has/LICENSE-MIT" | 22 +
.../node_modules/has/README.md" | 18 +
.../node_modules/has/package.json" | 48 +
.../node_modules/has/src/index.js" | 5 +
.../node_modules/has/test/index.js" | 10 +
.../node_modules/http-errors/HISTORY.md" | 180 +
.../node_modules/http-errors/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/http-errors/README.md" | 169 +
.../node_modules/http-errors/index.js" | 289 +
.../node_modules/http-errors/package.json" | 50 +
.../node_modules/iconv-lite/Changelog.md" | 162 +
.../node_modules/iconv-lite/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/iconv-lite/README.md" | 156 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/dbcs-codec.js" | 555 ++
.../iconv-lite/encodings/dbcs-data.js" | 176 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/index.js" | 22 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/internal.js" | 188 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/sbcs-codec.js" | 72 +
.../encodings/sbcs-data-generated.js" | 451 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/sbcs-data.js" | 174 +
.../encodings/tables/big5-added.json" | 122 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/tables/cp936.json" | 264 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/tables/cp949.json" | 273 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/tables/cp950.json" | 177 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/tables/eucjp.json" | 182 +
.../encodings/tables/gb18030-ranges.json" | 1 +
.../encodings/tables/gbk-added.json" | 55 +
.../encodings/tables/shiftjis.json" | 125 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/utf16.js" | 177 +
.../iconv-lite/encodings/utf7.js" | 290 +
.../iconv-lite/lib/bom-handling.js" | 52 +
.../iconv-lite/lib/extend-node.js" | 217 +
.../node_modules/iconv-lite/lib/index.d.ts" | 24 +
.../node_modules/iconv-lite/lib/index.js" | 153 +
.../node_modules/iconv-lite/lib/streams.js" | 121 +
.../node_modules/iconv-lite/package.json" | 46 +
.../node_modules/inherits/LICENSE" | 16 +
.../node_modules/inherits/README.md" | 42 +
.../node_modules/inherits/inherits.js" | 9 +
.../inherits/inherits_browser.js" | 27 +
.../node_modules/inherits/package.json" | 29 +
.../node_modules/ipaddr.js/LICENSE" | 19 +
.../node_modules/ipaddr.js/README.md" | 233 +
.../node_modules/ipaddr.js/ipaddr.min.js" | 1 +
.../node_modules/ipaddr.js/lib/ipaddr.js" | 673 ++
.../ipaddr.js/lib/ipaddr.js.d.ts" | 68 +
.../node_modules/ipaddr.js/package.json" | 35 +
.../node_modules/isarray/.npmignore" | 1 +
.../node_modules/isarray/.travis.yml" | 4 +
.../node_modules/isarray/Makefile" | 6 +
.../node_modules/isarray/README.md" | 60 +
.../node_modules/isarray/component.json" | 19 +
.../node_modules/isarray/index.js" | 5 +
.../node_modules/isarray/package.json" | 45 +
.../node_modules/isarray/test.js" | 20 +
.../node_modules/media-typer/HISTORY.md" | 22 +
.../node_modules/media-typer/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/media-typer/README.md" | 81 +
.../node_modules/media-typer/index.js" | 270 +
.../node_modules/media-typer/package.json" | 26 +
.../merge-descriptors/HISTORY.md" | 21 +
.../node_modules/merge-descriptors/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/merge-descriptors/README.md" | 48 +
.../node_modules/merge-descriptors/index.js" | 60 +
.../merge-descriptors/package.json" | 32 +
.../node_modules/methods/HISTORY.md" | 29 +
.../node_modules/methods/LICENSE" | 24 +
.../node_modules/methods/README.md" | 51 +
.../node_modules/methods/index.js" | 69 +
.../node_modules/methods/package.json" | 36 +
.../node_modules/mime-db/HISTORY.md" | 507 +
.../node_modules/mime-db/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/mime-db/README.md" | 100 +
.../node_modules/mime-db/db.json" | 8519 +++++++++++++++++
.../node_modules/mime-db/index.js" | 12 +
.../node_modules/mime-db/package.json" | 60 +
.../node_modules/mime-types/HISTORY.md" | 397 +
.../node_modules/mime-types/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/mime-types/README.md" | 113 +
.../node_modules/mime-types/index.js" | 188 +
.../node_modules/mime-types/package.json" | 44 +
.../node_modules/mime/.npmignore" | 0
.../node_modules/mime/CHANGELOG.md" | 164 +
.../node_modules/mime/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/mime/README.md" | 90 +
.../node_modules/mime/cli.js" | 8 +
.../node_modules/mime/mime.js" | 108 +
.../node_modules/mime/package.json" | 44 +
.../node_modules/mime/src/build.js" | 53 +
.../node_modules/mime/src/test.js" | 60 +
.../node_modules/mime/types.json" | 1 +
.../node_modules/ms/index.js" | 152 +
.../node_modules/ms/license.md" | 21 +
.../node_modules/ms/package.json" | 37 +
.../node_modules/ms/readme.md" | 51 +
.../node_modules/mysql/Changes.md" | 569 ++
.../node_modules/mysql/License" | 19 +
.../node_modules/mysql/Readme.md" | 1548 +++
.../node_modules/mysql/index.js" | 161 +
.../node_modules/mysql/lib/Connection.js" | 529 +
.../mysql/lib/ConnectionConfig.js" | 209 +
.../node_modules/mysql/lib/Pool.js" | 294 +
.../node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolCluster.js" | 288 +
.../node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolConfig.js" | 32 +
.../node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolConnection.js" | 65 +
.../node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolNamespace.js" | 136 +
.../node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolSelector.js" | 31 +
.../node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/Auth.js" | 168 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/BufferList.js" | 25 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/PacketHeader.js" | 5 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/PacketWriter.js" | 211 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/Parser.js" | 491 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/Protocol.js" | 463 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/ResultSet.js" | 7 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/SqlString.js" | 1 +
.../node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/Timer.js" | 33 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/constants/charsets.js" | 262 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/constants/client.js" | 26 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/constants/errors.js" | 2476 +++++
.../lib/protocol/constants/field_flags.js" | 18 +
.../lib/protocol/constants/server_status.js" | 39 +
.../lib/protocol/constants/ssl_profiles.js" | 1480 +++
.../mysql/lib/protocol/constants/types.js" | 72 +
.../packets/AuthSwitchRequestPacket.js" | 20 +
.../packets/AuthSwitchResponsePacket.js" | 14 +
.../packets/ClientAuthenticationPacket.js" | 54 +
.../protocol/packets/ComChangeUserPacket.js" | 26 +
.../lib/protocol/packets/ComPingPacket.js" | 12 +
.../lib/protocol/packets/ComQueryPacket.js" | 15 +
.../lib/protocol/packets/ComQuitPacket.js" | 12 +
.../protocol/packets/ComStatisticsPacket.js" | 12 +
.../lib/protocol/packets/EmptyPacket.js" | 9 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/packets/EofPacket.js" | 25 +
.../lib/protocol/packets/ErrorPacket.js" | 35 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/packets/Field.js" | 26 +
.../lib/protocol/packets/FieldPacket.js" | 93 +
.../packets/HandshakeInitializationPacket.js" | 103 +
.../protocol/packets/LocalDataFilePacket.js" | 15 +
.../packets/LocalInfileRequestPacket.js" | 21 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/packets/OkPacket.js" | 44 +
.../protocol/packets/OldPasswordPacket.js" | 14 +
.../packets/ResultSetHeaderPacket.js" | 14 +
.../lib/protocol/packets/RowDataPacket.js" | 130 +
.../lib/protocol/packets/SSLRequestPacket.js" | 27 +
.../lib/protocol/packets/StatisticsPacket.js" | 20 +
.../protocol/packets/UseOldPasswordPacket.js" | 14 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/packets/index.js" | 23 +
.../lib/protocol/sequences/ChangeUser.js" | 67 +
.../lib/protocol/sequences/Handshake.js" | 126 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Ping.js" | 19 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Query.js" | 228 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Quit.js" | 40 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Sequence.js" | 125 +
.../lib/protocol/sequences/Statistics.js" | 30 +
.../mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/index.js" | 7 +
.../mysql/node_modules/safe-buffer/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../mysql/node_modules/safe-buffer/README.md" | 584 ++
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/index.d.ts" | 187 +
.../mysql/node_modules/safe-buffer/index.js" | 62 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/package.json" | 37 +
.../node_modules/mysql/package.json" | 46 +
.../node_modules/negotiator/HISTORY.md" | 108 +
.../node_modules/negotiator/LICENSE" | 24 +
.../node_modules/negotiator/README.md" | 203 +
.../node_modules/negotiator/index.js" | 82 +
.../node_modules/negotiator/lib/charset.js" | 169 +
.../node_modules/negotiator/lib/encoding.js" | 184 +
.../node_modules/negotiator/lib/language.js" | 179 +
.../node_modules/negotiator/lib/mediaType.js" | 294 +
.../node_modules/negotiator/package.json" | 42 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/.eslintrc" | 53 +
.../object-inspect/.github/FUNDING.yml" | 12 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/.nycrc" | 13 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/CHANGELOG.md" | 370 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../object-inspect/example/all.js" | 23 +
.../object-inspect/example/circular.js" | 6 +
.../object-inspect/example/fn.js" | 5 +
.../object-inspect/example/inspect.js" | 10 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/index.js" | 516 +
.../object-inspect/package-support.json" | 20 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/package.json" | 97 +
.../object-inspect/readme.markdown" | 86 +
.../object-inspect/test-core-js.js" | 26 +
.../object-inspect/test/bigint.js" | 58 +
.../object-inspect/test/browser/dom.js" | 15 +
.../object-inspect/test/circular.js" | 16 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/test/deep.js" | 12 +
.../object-inspect/test/element.js" | 53 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/test/err.js" | 48 +
.../object-inspect/test/fakes.js" | 29 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/test/fn.js" | 76 +
.../node_modules/object-inspect/test/has.js" | 15 +
.../object-inspect/test/holes.js" | 15 +
.../object-inspect/test/indent-option.js" | 271 +
.../object-inspect/test/inspect.js" | 139 +
.../object-inspect/test/lowbyte.js" | 12 +
.../object-inspect/test/number.js" | 58 +
.../object-inspect/test/quoteStyle.js" | 17 +
.../object-inspect/test/toStringTag.js" | 40 +
.../object-inspect/test/undef.js" | 12 +
.../object-inspect/test/values.js" | 211 +
.../object-inspect/util.inspect.js" | 1 +
.../node_modules/on-finished/HISTORY.md" | 98 +
.../node_modules/on-finished/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/on-finished/README.md" | 162 +
.../node_modules/on-finished/index.js" | 234 +
.../node_modules/on-finished/package.json" | 39 +
.../node_modules/parseurl/HISTORY.md" | 58 +
.../node_modules/parseurl/LICENSE" | 24 +
.../node_modules/parseurl/README.md" | 133 +
.../node_modules/parseurl/index.js" | 158 +
.../node_modules/parseurl/package.json" | 40 +
.../node_modules/path-to-regexp/History.md" | 36 +
.../node_modules/path-to-regexp/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/path-to-regexp/Readme.md" | 35 +
.../node_modules/path-to-regexp/index.js" | 129 +
.../node_modules/path-to-regexp/package.json" | 30 +
.../process-nextick-args/index.js" | 45 +
.../process-nextick-args/license.md" | 19 +
.../process-nextick-args/package.json" | 25 +
.../process-nextick-args/readme.md" | 18 +
.../node_modules/proxy-addr/HISTORY.md" | 161 +
.../node_modules/proxy-addr/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/proxy-addr/README.md" | 139 +
.../node_modules/proxy-addr/index.js" | 327 +
.../node_modules/proxy-addr/package.json" | 47 +
.../node_modules/qs/.editorconfig" | 43 +
.../node_modules/qs/.eslintrc" | 38 +
.../node_modules/qs/.github/FUNDING.yml" | 12 +
.../node_modules/qs/.nycrc" | 13 +
.../node_modules/qs/CHANGELOG.md" | 546 ++
.../node_modules/qs/LICENSE.md" | 29 +
.../node_modules/qs/README.md" | 625 ++
.../node_modules/qs/dist/qs.js" | 2054 ++++
.../node_modules/qs/lib/formats.js" | 23 +
.../node_modules/qs/lib/index.js" | 11 +
.../node_modules/qs/lib/parse.js" | 263 +
.../node_modules/qs/lib/stringify.js" | 326 +
.../node_modules/qs/lib/utils.js" | 252 +
.../node_modules/qs/package.json" | 77 +
.../node_modules/qs/test/parse.js" | 855 ++
.../node_modules/qs/test/stringify.js" | 909 ++
.../node_modules/qs/test/utils.js" | 136 +
.../node_modules/range-parser/HISTORY.md" | 56 +
.../node_modules/range-parser/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/range-parser/README.md" | 84 +
.../node_modules/range-parser/index.js" | 162 +
.../node_modules/range-parser/package.json" | 44 +
.../node_modules/raw-body/HISTORY.md" | 303 +
.../node_modules/raw-body/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/raw-body/README.md" | 223 +
.../node_modules/raw-body/SECURITY.md" | 24 +
.../node_modules/raw-body/index.d.ts" | 87 +
.../node_modules/raw-body/index.js" | 329 +
.../node_modules/raw-body/package.json" | 49 +
.../node_modules/readable-stream/.travis.yml" | 34 +
.../readable-stream/CONTRIBUTING.md" | 38 +
.../readable-stream/GOVERNANCE.md" | 136 +
.../node_modules/readable-stream/LICENSE" | 47 +
.../node_modules/readable-stream/README.md" | 58 +
.../doc/wg-meetings/2015-01-30.md" | 60 +
.../readable-stream/duplex-browser.js" | 1 +
.../node_modules/readable-stream/duplex.js" | 1 +
.../readable-stream/lib/_stream_duplex.js" | 131 +
.../lib/_stream_passthrough.js" | 47 +
.../readable-stream/lib/_stream_readable.js" | 1019 ++
.../readable-stream/lib/_stream_transform.js" | 214 +
.../readable-stream/lib/_stream_writable.js" | 687 ++
.../lib/internal/streams/BufferList.js" | 79 +
.../lib/internal/streams/destroy.js" | 74 +
.../lib/internal/streams/stream-browser.js" | 1 +
.../lib/internal/streams/stream.js" | 1 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/README.md" | 584 ++
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/index.d.ts" | 187 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/index.js" | 62 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/package.json" | 37 +
.../readable-stream/package.json" | 52 +
.../readable-stream/passthrough.js" | 1 +
.../readable-stream/readable-browser.js" | 7 +
.../node_modules/readable-stream/readable.js" | 19 +
.../readable-stream/transform.js" | 1 +
.../readable-stream/writable-browser.js" | 1 +
.../node_modules/readable-stream/writable.js" | 8 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/README.md" | 584 ++
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/index.d.ts" | 187 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/index.js" | 65 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/package.json" | 51 +
.../node_modules/safer-buffer/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../safer-buffer/Porting-Buffer.md" | 268 +
.../node_modules/safer-buffer/Readme.md" | 156 +
.../node_modules/safer-buffer/dangerous.js" | 58 +
.../node_modules/safer-buffer/package.json" | 34 +
.../node_modules/safer-buffer/safer.js" | 77 +
.../node_modules/safer-buffer/tests.js" | 406 +
.../node_modules/send/HISTORY.md" | 521 +
.../node_modules/send/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/send/README.md" | 327 +
.../node_modules/send/SECURITY.md" | 24 +
.../node_modules/send/index.js" | 1143 +++
.../send/node_modules/ms/index.js" | 162 +
.../send/node_modules/ms/license.md" | 21 +
.../send/node_modules/ms/package.json" | 38 +
.../send/node_modules/ms/readme.md" | 59 +
.../node_modules/send/package.json" | 62 +
.../node_modules/serve-static/HISTORY.md" | 471 +
.../node_modules/serve-static/LICENSE" | 25 +
.../node_modules/serve-static/README.md" | 257 +
.../node_modules/serve-static/index.js" | 210 +
.../node_modules/serve-static/package.json" | 42 +
.../node_modules/setprototypeof/LICENSE" | 13 +
.../node_modules/setprototypeof/README.md" | 31 +
.../node_modules/setprototypeof/index.d.ts" | 2 +
.../node_modules/setprototypeof/index.js" | 17 +
.../node_modules/setprototypeof/package.json" | 38 +
.../setprototypeof/test/index.js" | 24 +
.../node_modules/side-channel/.eslintignore" | 1 +
.../node_modules/side-channel/.eslintrc" | 11 +
.../side-channel/.github/FUNDING.yml" | 12 +
.../node_modules/side-channel/.nycrc" | 13 +
.../node_modules/side-channel/CHANGELOG.md" | 65 +
.../node_modules/side-channel/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/side-channel/README.md" | 2 +
.../node_modules/side-channel/index.js" | 124 +
.../node_modules/side-channel/package.json" | 67 +
.../node_modules/side-channel/test/index.js" | 78 +
.../node_modules/sqlstring/HISTORY.md" | 43 +
.../node_modules/sqlstring/LICENSE" | 19 +
.../node_modules/sqlstring/README.md" | 206 +
.../node_modules/sqlstring/index.js" | 1 +
.../node_modules/sqlstring/lib/SqlString.js" | 237 +
.../node_modules/sqlstring/package.json" | 47 +
.../node_modules/statuses/HISTORY.md" | 82 +
.../node_modules/statuses/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/statuses/README.md" | 136 +
.../node_modules/statuses/codes.json" | 65 +
.../node_modules/statuses/index.js" | 146 +
.../node_modules/statuses/package.json" | 49 +
.../node_modules/string_decoder/.travis.yml" | 50 +
.../node_modules/string_decoder/LICENSE" | 48 +
.../node_modules/string_decoder/README.md" | 47 +
.../string_decoder/lib/string_decoder.js" | 296 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/README.md" | 584 ++
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/index.d.ts" | 187 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/index.js" | 62 +
.../node_modules/safe-buffer/package.json" | 37 +
.../node_modules/string_decoder/package.json" | 31 +
.../node_modules/toidentifier/HISTORY.md" | 9 +
.../node_modules/toidentifier/LICENSE" | 21 +
.../node_modules/toidentifier/README.md" | 61 +
.../node_modules/toidentifier/index.js" | 32 +
.../node_modules/toidentifier/package.json" | 38 +
.../node_modules/type-is/HISTORY.md" | 259 +
.../node_modules/type-is/LICENSE" | 23 +
.../node_modules/type-is/README.md" | 170 +
.../node_modules/type-is/index.js" | 266 +
.../node_modules/type-is/package.json" | 45 +
.../node_modules/unpipe/HISTORY.md" | 4 +
.../node_modules/unpipe/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/unpipe/README.md" | 43 +
.../node_modules/unpipe/index.js" | 69 +
.../node_modules/unpipe/package.json" | 27 +
.../node_modules/util-deprecate/History.md" | 16 +
.../node_modules/util-deprecate/LICENSE" | 24 +
.../node_modules/util-deprecate/README.md" | 53 +
.../node_modules/util-deprecate/browser.js" | 67 +
.../node_modules/util-deprecate/node.js" | 6 +
.../node_modules/util-deprecate/package.json" | 27 +
.../node_modules/utils-merge/.npmignore" | 9 +
.../node_modules/utils-merge/LICENSE" | 20 +
.../node_modules/utils-merge/README.md" | 34 +
.../node_modules/utils-merge/index.js" | 23 +
.../node_modules/utils-merge/package.json" | 40 +
.../node_modules/vary/HISTORY.md" | 39 +
.../node_modules/vary/LICENSE" | 22 +
.../node_modules/vary/README.md" | 101 +
.../node_modules/vary/index.js" | 149 +
.../node_modules/vary/package.json" | 43 +
.../package-lock.json" | 644 ++
.../package.json" | 6 +
.../show.html" | 91 +
.../zy.js" | 30 +
573 files changed, 90985 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_express\346\241\206\346\236\2661.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime.cmd"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime.ps1"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.package-lock.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/array-flatten/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/array-flatten/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/array-flatten/array-flatten.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/array-flatten/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/CHANGELOG.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/LICENCE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.d.ts"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.min.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.min.js.map"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.mjs"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/doc/API.html"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/SECURITY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/lib/read.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/lib/types/json.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/lib/types/raw.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/lib/types/text.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/lib/types/urlencoded.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/body-parser/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bytes/History.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bytes/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bytes/Readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bytes/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bytes/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/.eslintignore"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/.eslintrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/.github/FUNDING.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/.nycrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/CHANGELOG.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/callBound.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/test/callBound.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/call-bind/test/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-disposition/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-disposition/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-disposition/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-disposition/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-disposition/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-type/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-type/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-type/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-type/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/content-type/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie-signature/.npmignore"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie-signature/History.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie-signature/Readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie-signature/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie-signature/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/SECURITY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/core-util-is/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/core-util-is/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/core-util-is/lib/util.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/core-util-is/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/.coveralls.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/.eslintrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/.npmignore"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/.travis.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/CHANGELOG.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/Makefile"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/component.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/karma.conf.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/node.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/src/browser.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/src/debug.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/src/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/src/inspector-log.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/debug/src/node.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/depd/History.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/depd/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/depd/Readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/depd/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/depd/lib/browser/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/depd/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/destroy/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/destroy/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/destroy/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/destroy/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ee-first/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ee-first/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ee-first/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ee-first/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/encodeurl/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/encodeurl/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/encodeurl/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/encodeurl/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/encodeurl/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/escape-html/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/escape-html/Readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/escape-html/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/escape-html/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/etag/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/etag/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/etag/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/etag/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/etag/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/History.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/Readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/application.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/express.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/middleware/init.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/middleware/query.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/request.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/response.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/router/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/router/layer.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/router/route.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/utils.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/lib/view.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/express/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/finalhandler/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/finalhandler/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/finalhandler/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/finalhandler/SECURITY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/finalhandler/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/finalhandler/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/forwarded/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/forwarded/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/forwarded/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/forwarded/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/forwarded/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/fresh/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/fresh/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/fresh/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/fresh/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/fresh/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/.editorconfig"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/.eslintrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/.jscs.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/.npmignore"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/.travis.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/implementation.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/test/.eslintrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/function-bind/test/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/get-intrinsic/.eslintrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/get-intrinsic/.github/FUNDING.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/get-intrinsic/.nycrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/get-intrinsic/CHANGELOG.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/get-intrinsic/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/get-intrinsic/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/get-intrinsic/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/get-intrinsic/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/get-intrinsic/test/GetIntrinsic.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/.eslintrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/.github/FUNDING.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/.nycrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/CHANGELOG.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/shams.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/test/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/test/shams/core-js.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/test/shams/get-own-property-symbols.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has-symbols/test/tests.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has/LICENSE-MIT"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has/src/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/has/test/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/http-errors/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/http-errors/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/http-errors/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/http-errors/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/http-errors/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/Changelog.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/dbcs-codec.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/dbcs-data.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/internal.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/sbcs-codec.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/sbcs-data-generated.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/sbcs-data.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/tables/big5-added.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/tables/cp936.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/tables/cp949.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/tables/cp950.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/tables/eucjp.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/tables/gb18030-ranges.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/tables/gbk-added.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/tables/shiftjis.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/utf16.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/encodings/utf7.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/lib/bom-handling.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/lib/extend-node.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/lib/index.d.ts"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/lib/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/lib/streams.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/iconv-lite/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/inherits/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/inherits/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/inherits/inherits.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/inherits/inherits_browser.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/inherits/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ipaddr.js/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ipaddr.js/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ipaddr.js/ipaddr.min.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ipaddr.js/lib/ipaddr.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ipaddr.js/lib/ipaddr.js.d.ts"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ipaddr.js/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/isarray/.npmignore"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/isarray/.travis.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/isarray/Makefile"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/isarray/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/isarray/component.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/isarray/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/isarray/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/isarray/test.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/media-typer/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/media-typer/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/media-typer/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/media-typer/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/media-typer/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/merge-descriptors/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/merge-descriptors/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/merge-descriptors/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/merge-descriptors/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/merge-descriptors/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/methods/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/methods/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/methods/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/methods/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/methods/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-db/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-db/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-db/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-db/db.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-db/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-db/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-types/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-types/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-types/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-types/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime-types/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/.npmignore"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/CHANGELOG.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/cli.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/mime.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/src/build.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/src/test.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mime/types.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ms/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ms/license.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ms/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/ms/readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/Changes.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/License"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/Readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/Connection.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/ConnectionConfig.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/Pool.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolCluster.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolConfig.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolConnection.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolNamespace.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/PoolSelector.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/Auth.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/BufferList.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/PacketHeader.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/PacketWriter.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/Parser.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/Protocol.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/ResultSet.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/SqlString.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/Timer.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/constants/charsets.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/constants/client.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/constants/errors.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/constants/field_flags.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/constants/server_status.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/constants/ssl_profiles.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/constants/types.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/AuthSwitchRequestPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/AuthSwitchResponsePacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/ClientAuthenticationPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/ComChangeUserPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/ComPingPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/ComQueryPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/ComQuitPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/ComStatisticsPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/EmptyPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/EofPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/ErrorPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/Field.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/FieldPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/HandshakeInitializationPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/LocalDataFilePacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/LocalInfileRequestPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/OkPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/OldPasswordPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/ResultSetHeaderPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/RowDataPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/SSLRequestPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/StatisticsPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/UseOldPasswordPacket.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/packets/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/ChangeUser.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Handshake.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Ping.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Query.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Quit.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Sequence.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/Statistics.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/lib/protocol/sequences/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/node_modules/safe-buffer/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/node_modules/safe-buffer/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/node_modules/safe-buffer/index.d.ts"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/node_modules/safe-buffer/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/node_modules/safe-buffer/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/mysql/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/negotiator/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/negotiator/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/negotiator/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/negotiator/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/negotiator/lib/charset.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/negotiator/lib/encoding.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/negotiator/lib/language.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/negotiator/lib/mediaType.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/negotiator/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/.eslintrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/.github/FUNDING.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/.nycrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/CHANGELOG.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/example/all.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/example/circular.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/example/fn.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/example/inspect.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/package-support.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/readme.markdown"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test-core-js.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/bigint.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/browser/dom.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/circular.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/deep.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/element.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/err.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/fakes.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/fn.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/has.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/holes.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/indent-option.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/inspect.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/lowbyte.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/number.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/quoteStyle.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/toStringTag.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/undef.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/test/values.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/object-inspect/util.inspect.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/on-finished/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/on-finished/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/on-finished/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/on-finished/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/on-finished/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/parseurl/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/parseurl/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/parseurl/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/parseurl/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/parseurl/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/path-to-regexp/History.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/path-to-regexp/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/path-to-regexp/Readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/path-to-regexp/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/path-to-regexp/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/process-nextick-args/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/process-nextick-args/license.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/process-nextick-args/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/process-nextick-args/readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/proxy-addr/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/proxy-addr/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/proxy-addr/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/proxy-addr/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/proxy-addr/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/.editorconfig"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/.eslintrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/.github/FUNDING.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/.nycrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/CHANGELOG.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/LICENSE.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/dist/qs.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/lib/formats.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/lib/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/lib/parse.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/lib/stringify.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/lib/utils.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/test/parse.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/test/stringify.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/qs/test/utils.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/range-parser/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/range-parser/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/range-parser/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/range-parser/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/range-parser/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/raw-body/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/raw-body/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/raw-body/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/raw-body/SECURITY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/raw-body/index.d.ts"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/raw-body/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/raw-body/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/.travis.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/CONTRIBUTING.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/GOVERNANCE.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/doc/wg-meetings/2015-01-30.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/duplex-browser.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/duplex.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/lib/_stream_duplex.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/lib/_stream_passthrough.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/lib/_stream_readable.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/lib/_stream_transform.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/lib/_stream_writable.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/lib/internal/streams/BufferList.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/lib/internal/streams/destroy.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/lib/internal/streams/stream-browser.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/lib/internal/streams/stream.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/node_modules/safe-buffer/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/node_modules/safe-buffer/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/node_modules/safe-buffer/index.d.ts"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/node_modules/safe-buffer/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/node_modules/safe-buffer/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/passthrough.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/readable-browser.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/readable.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/transform.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/writable-browser.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/readable-stream/writable.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safe-buffer/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safe-buffer/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safe-buffer/index.d.ts"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safe-buffer/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safe-buffer/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safer-buffer/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safer-buffer/Porting-Buffer.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safer-buffer/Readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safer-buffer/dangerous.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safer-buffer/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safer-buffer/safer.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/safer-buffer/tests.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/SECURITY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/node_modules/ms/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/node_modules/ms/license.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/node_modules/ms/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/node_modules/ms/readme.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/send/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/serve-static/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/serve-static/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/serve-static/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/serve-static/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/serve-static/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/setprototypeof/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/setprototypeof/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/setprototypeof/index.d.ts"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/setprototypeof/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/setprototypeof/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/setprototypeof/test/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/.eslintignore"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/.eslintrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/.github/FUNDING.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/.nycrc"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/CHANGELOG.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/side-channel/test/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/sqlstring/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/sqlstring/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/sqlstring/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/sqlstring/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/sqlstring/lib/SqlString.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/sqlstring/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/statuses/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/statuses/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/statuses/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/statuses/codes.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/statuses/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/statuses/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/.travis.yml"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/lib/string_decoder.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/node_modules/safe-buffer/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/node_modules/safe-buffer/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/node_modules/safe-buffer/index.d.ts"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/node_modules/safe-buffer/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/node_modules/safe-buffer/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/string_decoder/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/toidentifier/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/toidentifier/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/toidentifier/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/toidentifier/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/toidentifier/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/type-is/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/type-is/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/type-is/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/type-is/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/type-is/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/unpipe/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/unpipe/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/unpipe/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/unpipe/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/unpipe/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/util-deprecate/History.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/util-deprecate/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/util-deprecate/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/util-deprecate/browser.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/util-deprecate/node.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/util-deprecate/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/utils-merge/.npmignore"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/utils-merge/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/utils-merge/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/utils-merge/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/utils-merge/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/vary/HISTORY.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/vary/LICENSE"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/vary/README.md"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/vary/index.js"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/vary/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/package-lock.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/package.json"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/show.html"
create mode 100644 "\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/zy.js"
diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_express\346\241\206\346\236\2661.md" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_express\346\241\206\346\236\2661.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..21ea167
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_express\346\241\206\346\236\2661.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+## node 的框架
+
+### 初始Express
+
+1.1 Express介绍
+Express是目前流行的基于Node.js运行环境的Web应用程序开发框架,它简洁且灵活,为Web应用程序提供了强大的功能。Express提供了一个轻量级模块,类似于jQuery(封装的工具库),它把Node.js的HTTP模块的功能封装在一个简单易用的接口中,用于扩展HTTP模块的功能,能够轻松地处理服务器的路由、响应、Cookie和HTTP请求的状态。
+
+Express的优势:
+(1)简洁的路由定义方式。
+(2)简化HTTP请求参数的处理。
+(3)提供中间件机制控制HTTP请求。
+(4)拥有大量第三方中间件。
+(5)支持多种模版引擎
+
+### 安装express 框架
+
+```js
+
+// 项目初始化
+npm init -y
+// 安装
+npm install express --save
+
+// 查看版本
+
+npm list express
+
+
+```
+
+## 利用Express搭建Web服务器
+
+利用Express搭建Web服务器的基本步骤:
+
+#### 引入express模块;
+#### 调用express()方法创建服务器对象;
+#### 定义路由;
+#### 调用listen()方法监听端口
+
+
+来个例子
+
+```js
+
+// 引入express模块
+const express = require("express");
+// 创建Web服务器对象
+const app = express();
+// 定义GET路由,接收/处理客户端的GET请求
+app.get("/", (req, res) => {
+ // 对客户端做出响应,send()方法会根据内容的类型自动设置请求头
+ res.end("hello express");
+})
+// 监听3000端口
+app.listen(3000);
+
+```
+#### 理解 app 是啥,req,res 是啥.怎么接收参数,怎么回应参数.
+
+## 作业:利用express 想想怎么结合数据库,去实现学生(贪吃蛇的排名列表),能把学生的分数,班级
+## 在班上排名显示出来,还能实现分页
+
+
+
diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0a62a1b
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime"
@@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
+#!/bin/sh
+basedir=$(dirname "$(echo "$0" | sed -e 's,\\,/,g')")
+
+case `uname` in
+ *CYGWIN*|*MINGW*|*MSYS*) basedir=`cygpath -w "$basedir"`;;
+esac
+
+if [ -x "$basedir/node" ]; then
+ exec "$basedir/node" "$basedir/../mime/cli.js" "$@"
+else
+ exec node "$basedir/../mime/cli.js" "$@"
+fi
diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime.cmd" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime.cmd"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..54491f1
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime.cmd"
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+@ECHO off
+GOTO start
+:find_dp0
+SET dp0=%~dp0
+EXIT /b
+:start
+SETLOCAL
+CALL :find_dp0
+
+IF EXIST "%dp0%\node.exe" (
+ SET "_prog=%dp0%\node.exe"
+) ELSE (
+ SET "_prog=node"
+ SET PATHEXT=%PATHEXT:;.JS;=;%
+)
+
+endLocal & goto #_undefined_# 2>NUL || title %COMSPEC% & "%_prog%" "%dp0%\..\mime\cli.js" %*
diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime.ps1" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime.ps1"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..2222f40
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.bin/mime.ps1"
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+#!/usr/bin/env pwsh
+$basedir=Split-Path $MyInvocation.MyCommand.Definition -Parent
+
+$exe=""
+if ($PSVersionTable.PSVersion -lt "6.0" -or $IsWindows) {
+ # Fix case when both the Windows and Linux builds of Node
+ # are installed in the same directory
+ $exe=".exe"
+}
+$ret=0
+if (Test-Path "$basedir/node$exe") {
+ # Support pipeline input
+ if ($MyInvocation.ExpectingInput) {
+ $input | & "$basedir/node$exe" "$basedir/../mime/cli.js" $args
+ } else {
+ & "$basedir/node$exe" "$basedir/../mime/cli.js" $args
+ }
+ $ret=$LASTEXITCODE
+} else {
+ # Support pipeline input
+ if ($MyInvocation.ExpectingInput) {
+ $input | & "node$exe" "$basedir/../mime/cli.js" $args
+ } else {
+ & "node$exe" "$basedir/../mime/cli.js" $args
+ }
+ $ret=$LASTEXITCODE
+}
+exit $ret
diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.package-lock.json" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.package-lock.json"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f25425c
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/.package-lock.json"
@@ -0,0 +1,638 @@
+{
+ "name": "3.01,express 框架1",
+ "lockfileVersion": 3,
+ "requires": true,
+ "packages": {
+ "node_modules/accepts": {
+ "version": "1.3.8",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/accepts/-/accepts-1.3.8.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-PYAthTa2m2VKxuvSD3DPC/Gy+U+sOA1LAuT8mkmRuvw+NACSaeXEQ+NHcVF7rONl6qcaxV3Uuemwawk+7+SJLw==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "mime-types": "~2.1.34",
+ "negotiator": "0.6.3"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/array-flatten": {
+ "version": "1.1.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/array-flatten/-/array-flatten-1.1.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-PCVAQswWemu6UdxsDFFX/+gVeYqKAod3D3UVm91jHwynguOwAvYPhx8nNlM++NqRcK6CxxpUafjmhIdKiHibqg=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/bignumber.js": {
+ "version": "9.0.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/bignumber.js/-/bignumber.js-9.0.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-t/OYhhJ2SD+YGBQcjY8GzzDHEk9f3nerxjtfa6tlMXfe7frs/WozhvCNoGvpM0P3bNf3Gq5ZRMlGr5f3r4/N8A==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": "*"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/body-parser": {
+ "version": "1.20.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/body-parser/-/body-parser-1.20.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-jWi7abTbYwajOytWCQc37VulmWiRae5RyTpaCyDcS5/lMdtwSz5lOpDE67srw/HYe35f1z3fDQw+3txg7gNtWw==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "bytes": "3.1.2",
+ "content-type": "~1.0.4",
+ "debug": "2.6.9",
+ "depd": "2.0.0",
+ "destroy": "1.2.0",
+ "http-errors": "2.0.0",
+ "iconv-lite": "0.4.24",
+ "on-finished": "2.4.1",
+ "qs": "6.11.0",
+ "raw-body": "2.5.1",
+ "type-is": "~1.6.18",
+ "unpipe": "1.0.0"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8",
+ "npm": "1.2.8000 || >= 1.4.16"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/bytes": {
+ "version": "3.1.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/bytes/-/bytes-3.1.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-/Nf7TyzTx6S3yRJObOAV7956r8cr2+Oj8AC5dt8wSP3BQAoeX58NoHyCU8P8zGkNXStjTSi6fzO6F0pBdcYbEg==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/call-bind": {
+ "version": "1.0.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/call-bind/-/call-bind-1.0.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-7O+FbCihrB5WGbFYesctwmTKae6rOiIzmz1icreWJ+0aA7LJfuqhEso2T9ncpcFtzMQtzXf2QGGueWJGTYsqrA==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "function-bind": "^1.1.1",
+ "get-intrinsic": "^1.0.2"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/content-disposition": {
+ "version": "0.5.4",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/content-disposition/-/content-disposition-0.5.4.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-FveZTNuGw04cxlAiWbzi6zTAL/lhehaWbTtgluJh4/E95DqMwTmha3KZN1aAWA8cFIhHzMZUvLevkw5Rqk+tSQ==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "safe-buffer": "5.2.1"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/content-type": {
+ "version": "1.0.5",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/content-type/-/content-type-1.0.5.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-nTjqfcBFEipKdXCv4YDQWCfmcLZKm81ldF0pAopTvyrFGVbcR6P/VAAd5G7N+0tTr8QqiU0tFadD6FK4NtJwOA==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/cookie": {
+ "version": "0.5.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/cookie/-/cookie-0.5.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-YZ3GUyn/o8gfKJlnlX7g7xq4gyO6OSuhGPKaaGssGB2qgDUS0gPgtTvoyZLTt9Ab6dC4hfc9dV5arkvc/OCmrw==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/cookie-signature": {
+ "version": "1.0.6",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/cookie-signature/-/cookie-signature-1.0.6.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-QADzlaHc8icV8I7vbaJXJwod9HWYp8uCqf1xa4OfNu1T7JVxQIrUgOWtHdNDtPiywmFbiS12VjotIXLrKM3orQ=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/core-util-is": {
+ "version": "1.0.3",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/core-util-is/-/core-util-is-1.0.3.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-ZQBvi1DcpJ4GDqanjucZ2Hj3wEO5pZDS89BWbkcrvdxksJorwUDDZamX9ldFkp9aw2lmBDLgkObEA4DWNJ9FYQ=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/debug": {
+ "version": "2.6.9",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/debug/-/debug-2.6.9.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-bC7ElrdJaJnPbAP+1EotYvqZsb3ecl5wi6Bfi6BJTUcNowp6cvspg0jXznRTKDjm/E7AdgFBVeAPVMNcKGsHMA==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "ms": "2.0.0"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/depd": {
+ "version": "2.0.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/depd/-/depd-2.0.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-g7nH6P6dyDioJogAAGprGpCtVImJhpPk/roCzdb3fIh61/s/nPsfR6onyMwkCAR/OlC3yBC0lESvUoQEAssIrw==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/destroy": {
+ "version": "1.2.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/destroy/-/destroy-1.2.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-2sJGJTaXIIaR1w4iJSNoN0hnMY7Gpc/n8D4qSCJw8QqFWXf7cuAgnEHxBpweaVcPevC2l3KpjYCx3NypQQgaJg==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8",
+ "npm": "1.2.8000 || >= 1.4.16"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/ee-first": {
+ "version": "1.1.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/ee-first/-/ee-first-1.1.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-WMwm9LhRUo+WUaRN+vRuETqG89IgZphVSNkdFgeb6sS/E4OrDIN7t48CAewSHXc6C8lefD8KKfr5vY61brQlow=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/encodeurl": {
+ "version": "1.0.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/encodeurl/-/encodeurl-1.0.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-TPJXq8JqFaVYm2CWmPvnP2Iyo4ZSM7/QKcSmuMLDObfpH5fi7RUGmd/rTDf+rut/saiDiQEeVTNgAmJEdAOx0w==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/escape-html": {
+ "version": "1.0.3",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/escape-html/-/escape-html-1.0.3.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-NiSupZ4OeuGwr68lGIeym/ksIZMJodUGOSCZ/FSnTxcrekbvqrgdUxlJOMpijaKZVjAJrWrGs/6Jy8OMuyj9ow=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/etag": {
+ "version": "1.8.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/etag/-/etag-1.8.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-aIL5Fx7mawVa300al2BnEE4iNvo1qETxLrPI/o05L7z6go7fCw1J6EQmbK4FmJ2AS7kgVF/KEZWufBfdClMcPg==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/express": {
+ "version": "4.18.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/express/-/express-4.18.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-5/PsL6iGPdfQ/lKM1UuielYgv3BUoJfz1aUwU9vHZ+J7gyvwdQXFEBIEIaxeGf0GIcreATNyBExtalisDbuMqQ==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "accepts": "~1.3.8",
+ "array-flatten": "1.1.1",
+ "body-parser": "1.20.1",
+ "content-disposition": "0.5.4",
+ "content-type": "~1.0.4",
+ "cookie": "0.5.0",
+ "cookie-signature": "1.0.6",
+ "debug": "2.6.9",
+ "depd": "2.0.0",
+ "encodeurl": "~1.0.2",
+ "escape-html": "~1.0.3",
+ "etag": "~1.8.1",
+ "finalhandler": "1.2.0",
+ "fresh": "0.5.2",
+ "http-errors": "2.0.0",
+ "merge-descriptors": "1.0.1",
+ "methods": "~1.1.2",
+ "on-finished": "2.4.1",
+ "parseurl": "~1.3.3",
+ "path-to-regexp": "0.1.7",
+ "proxy-addr": "~2.0.7",
+ "qs": "6.11.0",
+ "range-parser": "~1.2.1",
+ "safe-buffer": "5.2.1",
+ "send": "0.18.0",
+ "serve-static": "1.15.0",
+ "setprototypeof": "1.2.0",
+ "statuses": "2.0.1",
+ "type-is": "~1.6.18",
+ "utils-merge": "1.0.1",
+ "vary": "~1.1.2"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.10.0"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/finalhandler": {
+ "version": "1.2.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/finalhandler/-/finalhandler-1.2.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-5uXcUVftlQMFnWC9qu/svkWv3GTd2PfUhK/3PLkYNAe7FbqJMt3515HaxE6eRL74GdsriiwujiawdaB1BpEISg==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "debug": "2.6.9",
+ "encodeurl": "~1.0.2",
+ "escape-html": "~1.0.3",
+ "on-finished": "2.4.1",
+ "parseurl": "~1.3.3",
+ "statuses": "2.0.1",
+ "unpipe": "~1.0.0"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/forwarded": {
+ "version": "0.2.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/forwarded/-/forwarded-0.2.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-buRG0fpBtRHSTCOASe6hD258tEubFoRLb4ZNA6NxMVHNw2gOcwHo9wyablzMzOA5z9xA9L1KNjk/Nt6MT9aYow==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/fresh": {
+ "version": "0.5.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/fresh/-/fresh-0.5.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-zJ2mQYM18rEFOudeV4GShTGIQ7RbzA7ozbU9I/XBpm7kqgMywgmylMwXHxZJmkVoYkna9d2pVXVXPdYTP9ej8Q==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/function-bind": {
+ "version": "1.1.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/function-bind/-/function-bind-1.1.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-yIovAzMX49sF8Yl58fSCWJ5svSLuaibPxXQJFLmBObTuCr0Mf1KiPopGM9NiFjiYBCbfaa2Fh6breQ6ANVTI0A=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/get-intrinsic": {
+ "version": "1.2.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/get-intrinsic/-/get-intrinsic-1.2.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-L049y6nFOuom5wGyRc3/gdTLO94dySVKRACj1RmJZBQXlbTMhtNIgkWkUHq+jYmZvKf14EW1EoJnnjbmoHij0Q==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "function-bind": "^1.1.1",
+ "has": "^1.0.3",
+ "has-symbols": "^1.0.3"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/has": {
+ "version": "1.0.3",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/has/-/has-1.0.3.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-f2dvO0VU6Oej7RkWJGrehjbzMAjFp5/VKPp5tTpWIV4JHHZK1/BxbFRtf/siA2SWTe09caDmVtYYzWEIbBS4zw==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "function-bind": "^1.1.1"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.4.0"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/has-symbols": {
+ "version": "1.0.3",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/has-symbols/-/has-symbols-1.0.3.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-l3LCuF6MgDNwTDKkdYGEihYjt5pRPbEg46rtlmnSPlUbgmB8LOIrKJbYYFBSbnPaJexMKtiPO8hmeRjRz2Td+A==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.4"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/http-errors": {
+ "version": "2.0.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/http-errors/-/http-errors-2.0.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-FtwrG/euBzaEjYeRqOgly7G0qviiXoJWnvEH2Z1plBdXgbyjv34pHTSb9zoeHMyDy33+DWy5Wt9Wo+TURtOYSQ==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "depd": "2.0.0",
+ "inherits": "2.0.4",
+ "setprototypeof": "1.2.0",
+ "statuses": "2.0.1",
+ "toidentifier": "1.0.1"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/iconv-lite": {
+ "version": "0.4.24",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/iconv-lite/-/iconv-lite-0.4.24.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-v3MXnZAcvnywkTUEZomIActle7RXXeedOR31wwl7VlyoXO4Qi9arvSenNQWne1TcRwhCL1HwLI21bEqdpj8/rA==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "safer-buffer": ">= 2.1.2 < 3"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">=0.10.0"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/inherits": {
+ "version": "2.0.4",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/inherits/-/inherits-2.0.4.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-k/vGaX4/Yla3WzyMCvTQOXYeIHvqOKtnqBduzTHpzpQZzAskKMhZ2K+EnBiSM9zGSoIFeMpXKxa4dYeZIQqewQ=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/ipaddr.js": {
+ "version": "1.9.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/ipaddr.js/-/ipaddr.js-1.9.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-0KI/607xoxSToH7GjN1FfSbLoU0+btTicjsQSWQlh/hZykN8KpmMf7uYwPW3R+akZ6R/w18ZlXSHBYXiYUPO3g==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.10"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/isarray": {
+ "version": "1.0.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/isarray/-/isarray-1.0.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-VLghIWNM6ELQzo7zwmcg0NmTVyWKYjvIeM83yjp0wRDTmUnrM678fQbcKBo6n2CJEF0szoG//ytg+TKla89ALQ=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/media-typer": {
+ "version": "0.3.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/media-typer/-/media-typer-0.3.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-dq+qelQ9akHpcOl/gUVRTxVIOkAJ1wR3QAvb4RsVjS8oVoFjDGTc679wJYmUmknUF5HwMLOgb5O+a3KxfWapPQ==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/merge-descriptors": {
+ "version": "1.0.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/merge-descriptors/-/merge-descriptors-1.0.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-cCi6g3/Zr1iqQi6ySbseM1Xvooa98N0w31jzUYrXPX2xqObmFGHJ0tQ5u74H3mVh7wLouTseZyYIq39g8cNp1w=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/methods": {
+ "version": "1.1.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/methods/-/methods-1.1.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-iclAHeNqNm68zFtnZ0e+1L2yUIdvzNoauKU4WBA3VvH/vPFieF7qfRlwUZU+DA9P9bPXIS90ulxoUoCH23sV2w==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/mime": {
+ "version": "1.6.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/mime/-/mime-1.6.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-x0Vn8spI+wuJ1O6S7gnbaQg8Pxh4NNHb7KSINmEWKiPE4RKOplvijn+NkmYmmRgP68mc70j2EbeTFRsrswaQeg==",
+ "bin": {
+ "mime": "cli.js"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">=4"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/mime-db": {
+ "version": "1.52.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/mime-db/-/mime-db-1.52.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-sPU4uV7dYlvtWJxwwxHD0PuihVNiE7TyAbQ5SWxDCB9mUYvOgroQOwYQQOKPJ8CIbE+1ETVlOoK1UC2nU3gYvg==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/mime-types": {
+ "version": "2.1.35",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/mime-types/-/mime-types-2.1.35.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-ZDY+bPm5zTTF+YpCrAU9nK0UgICYPT0QtT1NZWFv4s++TNkcgVaT0g6+4R2uI4MjQjzysHB1zxuWL50hzaeXiw==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "mime-db": "1.52.0"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/ms": {
+ "version": "2.0.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/ms/-/ms-2.0.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-Tpp60P6IUJDTuOq/5Z8cdskzJujfwqfOTkrwIwj7IRISpnkJnT6SyJ4PCPnGMoFjC9ddhal5KVIYtAt97ix05A=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/mysql": {
+ "version": "2.18.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/mysql/-/mysql-2.18.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-Bca+gk2YWmqp2Uf6k5NFEurwY/0td0cpebAucFpY/3jhrwrVGuxU2uQFCHjU19SJfje0yQvi+rVWdq78hR5lig==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "bignumber.js": "9.0.0",
+ "readable-stream": "2.3.7",
+ "safe-buffer": "5.1.2",
+ "sqlstring": "2.3.1"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/mysql/node_modules/safe-buffer": {
+ "version": "5.1.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/safe-buffer/-/safe-buffer-5.1.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-Gd2UZBJDkXlY7GbJxfsE8/nvKkUEU1G38c1siN6QP6a9PT9MmHB8GnpscSmMJSoF8LOIrt8ud/wPtojys4G6+g=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/negotiator": {
+ "version": "0.6.3",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/negotiator/-/negotiator-0.6.3.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-+EUsqGPLsM+j/zdChZjsnX51g4XrHFOIXwfnCVPGlQk/k5giakcKsuxCObBRu6DSm9opw/O6slWbJdghQM4bBg==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/object-inspect": {
+ "version": "1.12.3",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/object-inspect/-/object-inspect-1.12.3.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-geUvdk7c+eizMNUDkRpW1wJwgfOiOeHbxBR/hLXK1aT6zmVSO0jsQcs7fj6MGw89jC/cjGfLcNOrtMYtGqm81g=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/on-finished": {
+ "version": "2.4.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/on-finished/-/on-finished-2.4.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-oVlzkg3ENAhCk2zdv7IJwd/QUD4z2RxRwpkcGY8psCVcCYZNq4wYnVWALHM+brtuJjePWiYF/ClmuDr8Ch5+kg==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "ee-first": "1.1.1"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/parseurl": {
+ "version": "1.3.3",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/parseurl/-/parseurl-1.3.3.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-CiyeOxFT/JZyN5m0z9PfXw4SCBJ6Sygz1Dpl0wqjlhDEGGBP1GnsUVEL0p63hoG1fcj3fHynXi9NYO4nWOL+qQ==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/path-to-regexp": {
+ "version": "0.1.7",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/path-to-regexp/-/path-to-regexp-0.1.7.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-5DFkuoqlv1uYQKxy8omFBeJPQcdoE07Kv2sferDCrAq1ohOU+MSDswDIbnx3YAM60qIOnYa53wBhXW0EbMonrQ=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/process-nextick-args": {
+ "version": "2.0.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/process-nextick-args/-/process-nextick-args-2.0.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-3ouUOpQhtgrbOa17J7+uxOTpITYWaGP7/AhoR3+A+/1e9skrzelGi/dXzEYyvbxubEF6Wn2ypscTKiKJFFn1ag=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/proxy-addr": {
+ "version": "2.0.7",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/proxy-addr/-/proxy-addr-2.0.7.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-llQsMLSUDUPT44jdrU/O37qlnifitDP+ZwrmmZcoSKyLKvtZxpyV0n2/bD/N4tBAAZ/gJEdZU7KMraoK1+XYAg==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "forwarded": "0.2.0",
+ "ipaddr.js": "1.9.1"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.10"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/qs": {
+ "version": "6.11.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/qs/-/qs-6.11.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-MvjoMCJwEarSbUYk5O+nmoSzSutSsTwF85zcHPQ9OrlFoZOYIjaqBAJIqIXjptyD5vThxGq52Xu/MaJzRkIk4Q==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "side-channel": "^1.0.4"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">=0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/range-parser": {
+ "version": "1.2.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/range-parser/-/range-parser-1.2.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-Hrgsx+orqoygnmhFbKaHE6c296J+HTAQXoxEF6gNupROmmGJRoyzfG3ccAveqCBrwr/2yxQ5BVd/GTl5agOwSg==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/raw-body": {
+ "version": "2.5.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/raw-body/-/raw-body-2.5.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-qqJBtEyVgS0ZmPGdCFPWJ3FreoqvG4MVQln/kCgF7Olq95IbOp0/BWyMwbdtn4VTvkM8Y7khCQ2Xgk/tcrCXig==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "bytes": "3.1.2",
+ "http-errors": "2.0.0",
+ "iconv-lite": "0.4.24",
+ "unpipe": "1.0.0"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/readable-stream": {
+ "version": "2.3.7",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/readable-stream/-/readable-stream-2.3.7.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-Ebho8K4jIbHAxnuxi7o42OrZgF/ZTNcsZj6nRKyUmkhLFq8CHItp/fy6hQZuZmP/n3yZ9VBUbp4zz/mX8hmYPw==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "core-util-is": "~1.0.0",
+ "inherits": "~2.0.3",
+ "isarray": "~1.0.0",
+ "process-nextick-args": "~2.0.0",
+ "safe-buffer": "~5.1.1",
+ "string_decoder": "~1.1.1",
+ "util-deprecate": "~1.0.1"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/readable-stream/node_modules/safe-buffer": {
+ "version": "5.1.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/safe-buffer/-/safe-buffer-5.1.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-Gd2UZBJDkXlY7GbJxfsE8/nvKkUEU1G38c1siN6QP6a9PT9MmHB8GnpscSmMJSoF8LOIrt8ud/wPtojys4G6+g=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/safe-buffer": {
+ "version": "5.2.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/safe-buffer/-/safe-buffer-5.2.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-rp3So07KcdmmKbGvgaNxQSJr7bGVSVk5S9Eq1F+ppbRo70+YeaDxkw5Dd8NPN+GD6bjnYm2VuPuCXmpuYvmCXQ=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/safer-buffer": {
+ "version": "2.1.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/safer-buffer/-/safer-buffer-2.1.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-YZo3K82SD7Riyi0E1EQPojLz7kpepnSQI9IyPbHHg1XXXevb5dJI7tpyN2ADxGcQbHG7vcyRHk0cbwqcQriUtg=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/send": {
+ "version": "0.18.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/send/-/send-0.18.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-qqWzuOjSFOuqPjFe4NOsMLafToQQwBSOEpS+FwEt3A2V3vKubTquT3vmLTQpFgMXp8AlFWFuP1qKaJZOtPpVXg==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "debug": "2.6.9",
+ "depd": "2.0.0",
+ "destroy": "1.2.0",
+ "encodeurl": "~1.0.2",
+ "escape-html": "~1.0.3",
+ "etag": "~1.8.1",
+ "fresh": "0.5.2",
+ "http-errors": "2.0.0",
+ "mime": "1.6.0",
+ "ms": "2.1.3",
+ "on-finished": "2.4.1",
+ "range-parser": "~1.2.1",
+ "statuses": "2.0.1"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8.0"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/send/node_modules/ms": {
+ "version": "2.1.3",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/ms/-/ms-2.1.3.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-6FlzubTLZG3J2a/NVCAleEhjzq5oxgHyaCU9yYXvcLsvoVaHJq/s5xXI6/XXP6tz7R9xAOtHnSO/tXtF3WRTlA=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/serve-static": {
+ "version": "1.15.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/serve-static/-/serve-static-1.15.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-XGuRDNjXUijsUL0vl6nSD7cwURuzEgglbOaFuZM9g3kwDXOWVTck0jLzjPzGD+TazWbboZYu52/9/XPdUgne9g==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "encodeurl": "~1.0.2",
+ "escape-html": "~1.0.3",
+ "parseurl": "~1.3.3",
+ "send": "0.18.0"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8.0"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/setprototypeof": {
+ "version": "1.2.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/setprototypeof/-/setprototypeof-1.2.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-E5LDX7Wrp85Kil5bhZv46j8jOeboKq5JMmYM3gVGdGH8xFpPWXUMsNrlODCrkoxMEeNi/XZIwuRvY4XNwYMJpw=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/side-channel": {
+ "version": "1.0.4",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/side-channel/-/side-channel-1.0.4.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-q5XPytqFEIKHkGdiMIrY10mvLRvnQh42/+GoBlFW3b2LXLE2xxJpZFdm94we0BaoV3RwJyGqg5wS7epxTv0Zvw==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "call-bind": "^1.0.0",
+ "get-intrinsic": "^1.0.2",
+ "object-inspect": "^1.9.0"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/sqlstring": {
+ "version": "2.3.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/sqlstring/-/sqlstring-2.3.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-ooAzh/7dxIG5+uDik1z/Rd1vli0+38izZhGzSa34FwR7IbelPWCCKSNIl8jlL/F7ERvy8CB2jNeM1E9i9mXMAQ==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/statuses": {
+ "version": "2.0.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/statuses/-/statuses-2.0.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-RwNA9Z/7PrK06rYLIzFMlaF+l73iwpzsqRIFgbMLbTcLD6cOao82TaWefPXQvB2fOC4AjuYSEndS7N/mTCbkdQ==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/string_decoder": {
+ "version": "1.1.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/string_decoder/-/string_decoder-1.1.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-n/ShnvDi6FHbbVfviro+WojiFzv+s8MPMHBczVePfUpDJLwoLT0ht1l4YwBCbi8pJAveEEdnkHyPyTP/mzRfwg==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "safe-buffer": "~5.1.0"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/string_decoder/node_modules/safe-buffer": {
+ "version": "5.1.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/safe-buffer/-/safe-buffer-5.1.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-Gd2UZBJDkXlY7GbJxfsE8/nvKkUEU1G38c1siN6QP6a9PT9MmHB8GnpscSmMJSoF8LOIrt8ud/wPtojys4G6+g=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/toidentifier": {
+ "version": "1.0.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/toidentifier/-/toidentifier-1.0.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-o5sSPKEkg/DIQNmH43V0/uerLrpzVedkUh8tGNvaeXpfpuwjKenlSox/2O/BTlZUtEe+JG7s5YhEz608PlAHRA==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">=0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/type-is": {
+ "version": "1.6.18",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/type-is/-/type-is-1.6.18.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-TkRKr9sUTxEH8MdfuCSP7VizJyzRNMjj2J2do2Jr3Kym598JVdEksuzPQCnlFPW4ky9Q+iA+ma9BGm06XQBy8g==",
+ "dependencies": {
+ "media-typer": "0.3.0",
+ "mime-types": "~2.1.24"
+ },
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.6"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/unpipe": {
+ "version": "1.0.0",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/unpipe/-/unpipe-1.0.0.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-pjy2bYhSsufwWlKwPc+l3cN7+wuJlK6uz0YdJEOlQDbl6jo/YlPi4mb8agUkVC8BF7V8NuzeyPNqRksA3hztKQ==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/util-deprecate": {
+ "version": "1.0.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/util-deprecate/-/util-deprecate-1.0.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-EPD5q1uXyFxJpCrLnCc1nHnq3gOa6DZBocAIiI2TaSCA7VCJ1UJDMagCzIkXNsUYfD1daK//LTEQ8xiIbrHtcw=="
+ },
+ "node_modules/utils-merge": {
+ "version": "1.0.1",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/utils-merge/-/utils-merge-1.0.1.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-pMZTvIkT1d+TFGvDOqodOclx0QWkkgi6Tdoa8gC8ffGAAqz9pzPTZWAybbsHHoED/ztMtkv/VoYTYyShUn81hA==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.4.0"
+ }
+ },
+ "node_modules/vary": {
+ "version": "1.1.2",
+ "resolved": "https://registry.npmmirror.com/vary/-/vary-1.1.2.tgz",
+ "integrity": "sha512-BNGbWLfd0eUPabhkXUVm0j8uuvREyTh5ovRa/dyow/BqAbZJyC+5fU+IzQOzmAKzYqYRAISoRhdQr3eIZ/PXqg==",
+ "engines": {
+ "node": ">= 0.8"
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/HISTORY.md" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/HISTORY.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..cb5990c
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/HISTORY.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,243 @@
+1.3.8 / 2022-02-02
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.34
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.51.0
+ * deps: negotiator@0.6.3
+
+1.3.7 / 2019-04-29
+==================
+
+ * deps: negotiator@0.6.2
+ - Fix sorting charset, encoding, and language with extra parameters
+
+1.3.6 / 2019-04-28
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.24
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.40.0
+
+1.3.5 / 2018-02-28
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.18
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.33.0
+
+1.3.4 / 2017-08-22
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.16
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.29.0
+
+1.3.3 / 2016-05-02
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.11
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.23.0
+ * deps: negotiator@0.6.1
+ - perf: improve `Accept` parsing speed
+ - perf: improve `Accept-Charset` parsing speed
+ - perf: improve `Accept-Encoding` parsing speed
+ - perf: improve `Accept-Language` parsing speed
+
+1.3.2 / 2016-03-08
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.10
+ - Fix extension of `application/dash+xml`
+ - Update primary extension for `audio/mp4`
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.22.0
+
+1.3.1 / 2016-01-19
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.9
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.21.0
+
+1.3.0 / 2015-09-29
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.7
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.19.0
+ * deps: negotiator@0.6.0
+ - Fix including type extensions in parameters in `Accept` parsing
+ - Fix parsing `Accept` parameters with quoted equals
+ - Fix parsing `Accept` parameters with quoted semicolons
+ - Lazy-load modules from main entry point
+ - perf: delay type concatenation until needed
+ - perf: enable strict mode
+ - perf: hoist regular expressions
+ - perf: remove closures getting spec properties
+ - perf: remove a closure from media type parsing
+ - perf: remove property delete from media type parsing
+
+1.2.13 / 2015-09-06
+===================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.6
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.18.0
+
+1.2.12 / 2015-07-30
+===================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.4
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.16.0
+
+1.2.11 / 2015-07-16
+===================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.3
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.15.0
+
+1.2.10 / 2015-07-01
+===================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.2
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.14.0
+
+1.2.9 / 2015-06-08
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.1
+ - perf: fix deopt during mapping
+
+1.2.8 / 2015-06-07
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.1.0
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.13.0
+ * perf: avoid argument reassignment & argument slice
+ * perf: avoid negotiator recursive construction
+ * perf: enable strict mode
+ * perf: remove unnecessary bitwise operator
+
+1.2.7 / 2015-05-10
+==================
+
+ * deps: negotiator@0.5.3
+ - Fix media type parameter matching to be case-insensitive
+
+1.2.6 / 2015-05-07
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.0.11
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.9.1
+ * deps: negotiator@0.5.2
+ - Fix comparing media types with quoted values
+ - Fix splitting media types with quoted commas
+
+1.2.5 / 2015-03-13
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.0.10
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.8.0
+
+1.2.4 / 2015-02-14
+==================
+
+ * Support Node.js 0.6
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.0.9
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.7.0
+ * deps: negotiator@0.5.1
+ - Fix preference sorting to be stable for long acceptable lists
+
+1.2.3 / 2015-01-31
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.0.8
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.6.0
+
+1.2.2 / 2014-12-30
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.0.7
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.5.0
+
+1.2.1 / 2014-12-30
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.0.5
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.3.1
+
+1.2.0 / 2014-12-19
+==================
+
+ * deps: negotiator@0.5.0
+ - Fix list return order when large accepted list
+ - Fix missing identity encoding when q=0 exists
+ - Remove dynamic building of Negotiator class
+
+1.1.4 / 2014-12-10
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.0.4
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.3.0
+
+1.1.3 / 2014-11-09
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.0.3
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.2.0
+
+1.1.2 / 2014-10-14
+==================
+
+ * deps: negotiator@0.4.9
+ - Fix error when media type has invalid parameter
+
+1.1.1 / 2014-09-28
+==================
+
+ * deps: mime-types@~2.0.2
+ - deps: mime-db@~1.1.0
+ * deps: negotiator@0.4.8
+ - Fix all negotiations to be case-insensitive
+ - Stable sort preferences of same quality according to client order
+
+1.1.0 / 2014-09-02
+==================
+
+ * update `mime-types`
+
+1.0.7 / 2014-07-04
+==================
+
+ * Fix wrong type returned from `type` when match after unknown extension
+
+1.0.6 / 2014-06-24
+==================
+
+ * deps: negotiator@0.4.7
+
+1.0.5 / 2014-06-20
+==================
+
+ * fix crash when unknown extension given
+
+1.0.4 / 2014-06-19
+==================
+
+ * use `mime-types`
+
+1.0.3 / 2014-06-11
+==================
+
+ * deps: negotiator@0.4.6
+ - Order by specificity when quality is the same
+
+1.0.2 / 2014-05-29
+==================
+
+ * Fix interpretation when header not in request
+ * deps: pin negotiator@0.4.5
+
+1.0.1 / 2014-01-18
+==================
+
+ * Identity encoding isn't always acceptable
+ * deps: negotiator@~0.4.0
+
+1.0.0 / 2013-12-27
+==================
+
+ * Genesis
diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/LICENSE" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/LICENSE"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..0616607
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/accepts/LICENSE"
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+(The MIT License)
+
+Copyright (c) 2014 Jonathan Ong + +## Features + + - Integers and decimals + - Simple API but full-featured + - Faster, smaller, and perhaps easier to use than JavaScript versions of Java's BigDecimal + - 8 KB minified and gzipped + - Replicates the `toExponential`, `toFixed`, `toPrecision` and `toString` methods of JavaScript's Number type + - Includes a `toFraction` and a correctly-rounded `squareRoot` method + - Supports cryptographically-secure pseudo-random number generation + - No dependencies + - Wide platform compatibility: uses JavaScript 1.5 (ECMAScript 3) features only + - Comprehensive [documentation](http://mikemcl.github.io/bignumber.js/) and test set + +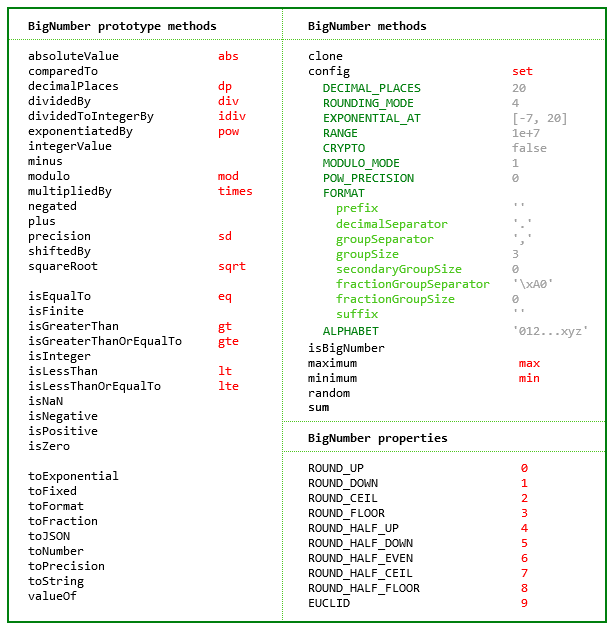 + +If a smaller and simpler library is required see [big.js](https://github.com/MikeMcl/big.js/). +It's less than half the size but only works with decimal numbers and only has half the methods. +It also does not allow `NaN` or `Infinity`, or have the configuration options of this library. + +See also [decimal.js](https://github.com/MikeMcl/decimal.js/), which among other things adds support for non-integer powers, and performs all operations to a specified number of significant digits. + +## Load + +The library is the single JavaScript file *bignumber.js* (or minified, *bignumber.min.js*). + +Browser: + +```html + +``` + +[Node.js](http://nodejs.org): + +```bash +$ npm install bignumber.js +``` + +```javascript +const BigNumber = require('bignumber.js'); +``` + +ES6 module: + +```javascript +import BigNumber from "./bignumber.mjs" +``` + +AMD loader libraries such as [requireJS](http://requirejs.org/): + +```javascript +require(['bignumber'], function(BigNumber) { + // Use BigNumber here in local scope. No global BigNumber. +}); +``` + +## Use + +The library exports a single constructor function, [`BigNumber`](http://mikemcl.github.io/bignumber.js/#bignumber), which accepts a value of type Number, String or BigNumber, + +```javascript +let x = new BigNumber(123.4567); +let y = BigNumber('123456.7e-3'); +let z = new BigNumber(x); +x.isEqualTo(y) && y.isEqualTo(z) && x.isEqualTo(z); // true +``` + +To get the string value of a BigNumber use [`toString()`](http://mikemcl.github.io/bignumber.js/#toS) or [`toFixed()`](http://mikemcl.github.io/bignumber.js/#toFix). Using `toFixed()` prevents exponential notation being returned, no matter how large or small the value. + +```javascript +let x = new BigNumber('1111222233334444555566'); +x.toString(); // "1.111222233334444555566e+21" +x.toFixed(); // "1111222233334444555566" +``` + +If the limited precision of Number values is not well understood, it is recommended to create BigNumbers from String values rather than Number values to avoid a potential loss of precision. + +*In all further examples below, `let`, semicolons and `toString` calls are not shown. If a commented-out value is in quotes it means `toString` has been called on the preceding expression.* + +```javascript +// Precision loss from using numeric literals with more than 15 significant digits. +new BigNumber(1.0000000000000001) // '1' +new BigNumber(88259496234518.57) // '88259496234518.56' +new BigNumber(99999999999999999999) // '100000000000000000000' + +// Precision loss from using numeric literals outside the range of Number values. +new BigNumber(2e+308) // 'Infinity' +new BigNumber(1e-324) // '0' + +// Precision loss from the unexpected result of arithmetic with Number values. +new BigNumber(0.7 + 0.1) // '0.7999999999999999' +``` + +When creating a BigNumber from a Number, note that a BigNumber is created from a Number's decimal `toString()` value not from its underlying binary value. If the latter is required, then pass the Number's `toString(2)` value and specify base 2. + +```javascript +new BigNumber(Number.MAX_VALUE.toString(2), 2) +``` + +BigNumbers can be created from values in bases from 2 to 36. See [`ALPHABET`](http://mikemcl.github.io/bignumber.js/#alphabet) to extend this range. + +```javascript +a = new BigNumber(1011, 2) // "11" +b = new BigNumber('zz.9', 36) // "1295.25" +c = a.plus(b) // "1306.25" +``` + +Performance is better if base 10 is NOT specified for decimal values. Only specify base 10 when it is desired that the number of decimal places of the input value be limited to the current [`DECIMAL_PLACES`](http://mikemcl.github.io/bignumber.js/#decimal-places) setting. + +A BigNumber is immutable in the sense that it is not changed by its methods. + +```javascript +0.3 - 0.1 // 0.19999999999999998 +x = new BigNumber(0.3) +x.minus(0.1) // "0.2" +x // "0.3" +``` + +The methods that return a BigNumber can be chained. + +```javascript +x.dividedBy(y).plus(z).times(9) +x.times('1.23456780123456789e+9').plus(9876.5432321).dividedBy('4444562598.111772').integerValue() +``` + +Some of the longer method names have a shorter alias. + +```javascript +x.squareRoot().dividedBy(y).exponentiatedBy(3).isEqualTo(x.sqrt().div(y).pow(3)) // true +x.modulo(y).multipliedBy(z).eq(x.mod(y).times(z)) // true +``` + +As with JavaScript's Number type, there are [`toExponential`](http://mikemcl.github.io/bignumber.js/#toE), [`toFixed`](http://mikemcl.github.io/bignumber.js/#toFix) and [`toPrecision`](http://mikemcl.github.io/bignumber.js/#toP) methods. + +```javascript +x = new BigNumber(255.5) +x.toExponential(5) // "2.55500e+2" +x.toFixed(5) // "255.50000" +x.toPrecision(5) // "255.50" +x.toNumber() // 255.5 +``` + + A base can be specified for [`toString`](http://mikemcl.github.io/bignumber.js/#toS). Performance is better if base 10 is NOT specified, i.e. use `toString()` not `toString(10)`. Only specify base 10 when it is desired that the number of decimal places be limited to the current [`DECIMAL_PLACES`](http://mikemcl.github.io/bignumber.js/#decimal-places) setting. + + ```javascript + x.toString(16) // "ff.8" + ``` + +There is a [`toFormat`](http://mikemcl.github.io/bignumber.js/#toFor) method which may be useful for internationalisation. + +```javascript +y = new BigNumber('1234567.898765') +y.toFormat(2) // "1,234,567.90" +``` + +The maximum number of decimal places of the result of an operation involving division (i.e. a division, square root, base conversion or negative power operation) is set using the `set` or `config` method of the `BigNumber` constructor. + +The other arithmetic operations always give the exact result. + +```javascript +BigNumber.set({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 10, ROUNDING_MODE: 4 }) + +x = new BigNumber(2) +y = new BigNumber(3) +z = x.dividedBy(y) // "0.6666666667" +z.squareRoot() // "0.8164965809" +z.exponentiatedBy(-3) // "3.3749999995" +z.toString(2) // "0.1010101011" +z.multipliedBy(z) // "0.44444444448888888889" +z.multipliedBy(z).decimalPlaces(10) // "0.4444444445" +``` + +There is a [`toFraction`](http://mikemcl.github.io/bignumber.js/#toFr) method with an optional *maximum denominator* argument + +```javascript +y = new BigNumber(355) +pi = y.dividedBy(113) // "3.1415929204" +pi.toFraction() // [ "7853982301", "2500000000" ] +pi.toFraction(1000) // [ "355", "113" ] +``` + +and [`isNaN`](http://mikemcl.github.io/bignumber.js/#isNaN) and [`isFinite`](http://mikemcl.github.io/bignumber.js/#isF) methods, as `NaN` and `Infinity` are valid `BigNumber` values. + +```javascript +x = new BigNumber(NaN) // "NaN" +y = new BigNumber(Infinity) // "Infinity" +x.isNaN() && !y.isNaN() && !x.isFinite() && !y.isFinite() // true +``` + +The value of a BigNumber is stored in a decimal floating point format in terms of a coefficient, exponent and sign. + +```javascript +x = new BigNumber(-123.456); +x.c // [ 123, 45600000000000 ] coefficient (i.e. significand) +x.e // 2 exponent +x.s // -1 sign +``` + +For advanced usage, multiple BigNumber constructors can be created, each with their own independent configuration. + +```javascript +// Set DECIMAL_PLACES for the original BigNumber constructor +BigNumber.set({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 10 }) + +// Create another BigNumber constructor, optionally passing in a configuration object +BN = BigNumber.clone({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 5 }) + +x = new BigNumber(1) +y = new BN(1) + +x.div(3) // '0.3333333333' +y.div(3) // '0.33333' +``` + +For further information see the [API](http://mikemcl.github.io/bignumber.js/) reference in the *doc* directory. + +## Test + +The *test/modules* directory contains the test scripts for each method. + +The tests can be run with Node.js or a browser. For Node.js use + + $ npm test + +or + + $ node test/test + +To test a single method, use, for example + + $ node test/methods/toFraction + +For the browser, open *test/test.html*. + +## Build + +For Node, if [uglify-js](https://github.com/mishoo/UglifyJS2) is installed + + npm install uglify-js -g + +then + + npm run build + +will create *bignumber.min.js*. + +A source map will also be created in the root directory. + +## Feedback + +Open an issue, or email + +Michael + +M8ch88l@gmail.com + +## Licence + +The MIT Licence. + +See [LICENCE](https://github.com/MikeMcl/bignumber.js/blob/master/LICENCE). diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.d.ts" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.d.ts" new file mode 100644 index 0000000..dc9b0b1 --- /dev/null +++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/bignumber.js/bignumber.d.ts" @@ -0,0 +1,1829 @@ +// Type definitions for bignumber.js >=8.1.0 +// Project: https://github.com/MikeMcl/bignumber.js +// Definitions by: Michael Mclaughlin
bignumber.js
+ +A JavaScript library for arbitrary-precision arithmetic.
+ + +API
+ ++ See the README on GitHub for a + quick-start introduction. +
+
+ In all examples below, var and semicolons are not shown, and if a commented-out
+ value is in quotes it means toString has been called on the preceding expression.
+
CONSTRUCTOR
+ + +
+ BigNumberBigNumber(n [, base]) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number: integer, 2 to 36 inclusive. (See
+ ALPHABET to extend this range).
+
+ Returns a new instance of a BigNumber object with value n, where n
+ is a numeric value in the specified base, or base 10 if
+ base is omitted or is null or undefined.
+
+x = new BigNumber(123.4567) // '123.4567' +// 'new' is optional +y = BigNumber(x) // '123.4567'+
+ If n is a base 10 value it can be in normal (fixed-point) or
+ exponential notation. Values in other bases must be in normal notation. Values in any base can
+ have fraction digits, i.e. digits after the decimal point.
+
+new BigNumber(43210) // '43210'
+new BigNumber('4.321e+4') // '43210'
+new BigNumber('-735.0918e-430') // '-7.350918e-428'
+new BigNumber('123412421.234324', 5) // '607236.557696'
+
+ Signed 0, signed Infinity and NaN are supported.
+
+new BigNumber('-Infinity') // '-Infinity'
+new BigNumber(NaN) // 'NaN'
+new BigNumber(-0) // '0'
+new BigNumber('.5') // '0.5'
+new BigNumber('+2') // '2'
+
+ String values in hexadecimal literal form, e.g. '0xff', are valid, as are
+ string values with the octal and binary prefixs '0o' and '0b'.
+ String values in octal literal form without the prefix will be interpreted as
+ decimals, e.g. '011' is interpreted as 11, not 9.
+
+new BigNumber(-10110100.1, 2) // '-180.5'
+new BigNumber('-0b10110100.1') // '-180.5'
+new BigNumber('ff.8', 16) // '255.5'
+new BigNumber('0xff.8') // '255.5'
+
+ If a base is specified, n is rounded according to the current
+ DECIMAL_PLACES and
+ ROUNDING_MODE settings. This includes base
+ 10 so don't include a base parameter for decimal values unless
+ this behaviour is wanted.
+
BigNumber.config({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 5 })
+new BigNumber(1.23456789) // '1.23456789'
+new BigNumber(1.23456789, 10) // '1.23457'
+ An error is thrown if base is invalid. See Errors.
+ There is no limit to the number of digits of a value of type string (other than
+ that of JavaScript's maximum array size). See RANGE to set
+ the maximum and minimum possible exponent value of a BigNumber.
+
+new BigNumber('5032485723458348569331745.33434346346912144534543')
+new BigNumber('4.321e10000000')
+ BigNumber NaN is returned if n is invalid
+ (unless BigNumber.DEBUG is true, see below).
+new BigNumber('.1*') // 'NaN'
+new BigNumber('blurgh') // 'NaN'
+new BigNumber(9, 2) // 'NaN'
+
+ To aid in debugging, if BigNumber.DEBUG is true then an error will
+ be thrown on an invalid n. An error will also be thrown if n is of
+ type number with more than 15 significant digits, as calling
+ toString or valueOf on
+ these numbers may not result in the intended value.
+
+console.log(823456789123456.3) // 823456789123456.2 +new BigNumber(823456789123456.3) // '823456789123456.2' +BigNumber.DEBUG = true +// '[BigNumber Error] Number primitive has more than 15 significant digits' +new BigNumber(823456789123456.3) +// '[BigNumber Error] Not a base 2 number' +new BigNumber(9, 2)+
+ A BigNumber can also be created from an object literal.
+ Use isBigNumber to check that it is well-formed.
+
new BigNumber({ s: 1, e: 2, c: [ 777, 12300000000000 ], _isBigNumber: true }) // '777.123'
+
+
+
+
+ Methods
+The static methods of a BigNumber constructor.
+ + + + +clone
+ .clone([object]) ⇒ BigNumber constructor
+
+ object: object
+ Returns a new independent BigNumber constructor with configuration as described by
+ object (see config), or with the default
+ configuration if object is null or undefined.
+
+ Throws if object is not an object. See Errors.
+
BigNumber.config({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 5 })
+BN = BigNumber.clone({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 9 })
+
+x = new BigNumber(1)
+y = new BN(1)
+
+x.div(3) // 0.33333
+y.div(3) // 0.333333333
+
+// BN = BigNumber.clone({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 9 }) is equivalent to:
+BN = BigNumber.clone()
+BN.config({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 9 })
+
+
+
+ configset([object]) ⇒ object
+
+ object: object: an object that contains some or all of the following
+ properties.
+
Configures the settings for this particular BigNumber constructor.
+ +-
+
DECIMAL_PLACES
+ -
+ number: integer,
0to1e+9inclusive
+ Default value:20+
+ -
+ The maximum number of decimal places of the results of operations involving
+ division, i.e. division, square root and base conversion operations, and power
+ operations with negative exponents.
+
+ -
+
BigNumber.config({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 5 }) +BigNumber.set({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 5 }) // equivalent+
+
+
+
+ ROUNDING_MODE
+ -
+ number: integer,
0to8inclusive
+ Default value:4(ROUND_HALF_UP) +
+ -
+ The rounding mode used in the above operations and the default rounding mode of
+
decimalPlaces, +precision, +toExponential, +toFixed, +toFormatand +toPrecision. +
+ - The modes are available as enumerated properties of the BigNumber constructor. +
-
+
BigNumber.config({ ROUNDING_MODE: 0 }) +BigNumber.set({ ROUNDING_MODE: BigNumber.ROUND_UP }) // equivalent+
+
+
+
+ EXPONENTIAL_AT
+ -
+ number: integer, magnitude
0to1e+9inclusive, or +
+ number[]: [ integer-1e+9to0inclusive, integer +0to1e+9inclusive ]
+ Default value:[-7, 20]+
+ -
+ The exponent value(s) at which
toStringreturns exponential notation. +
+ -
+ If a single number is assigned, the value is the exponent magnitude.
+ If an array of two numbers is assigned then the first number is the negative exponent + value at and beneath which exponential notation is used, and the second number is the + positive exponent value at and above which the same. +
+ -
+ For example, to emulate JavaScript numbers in terms of the exponent values at which they
+ begin to use exponential notation, use
[-7, 20]. +
+ -
+
BigNumber.config({ EXPONENTIAL_AT: 2 }) +new BigNumber(12.3) // '12.3' e is only 1 +new BigNumber(123) // '1.23e+2' +new BigNumber(0.123) // '0.123' e is only -1 +new BigNumber(0.0123) // '1.23e-2' + +BigNumber.config({ EXPONENTIAL_AT: [-7, 20] }) +new BigNumber(123456789) // '123456789' e is only 8 +new BigNumber(0.000000123) // '1.23e-7' + +// Almost never return exponential notation: +BigNumber.config({ EXPONENTIAL_AT: 1e+9 }) + +// Always return exponential notation: +BigNumber.config({ EXPONENTIAL_AT: 0 })+
+ -
+ Regardless of the value of
EXPONENTIAL_AT, thetoFixedmethod + will always return a value in normal notation and thetoExponentialmethod + will always return a value in exponential form. +
+ -
+ Calling
toStringwith a base argument, e.g.toString(10), will + also always return normal notation. +
+
+
+
+ RANGE
+ -
+ number: integer, magnitude
1to1e+9inclusive, or +
+ number[]: [ integer-1e+9to-1inclusive, integer +1to1e+9inclusive ]
+ Default value:[-1e+9, 1e+9]+
+ -
+ The exponent value(s) beyond which overflow to
Infinityand underflow to + zero occurs. +
+ -
+ If a single number is assigned, it is the maximum exponent magnitude: values wth a
+ positive exponent of greater magnitude become
Infinityand those with a + negative exponent of greater magnitude become zero. +- + If an array of two numbers is assigned then the first number is the negative exponent + limit and the second number is the positive exponent limit. +
+- + For example, to emulate JavaScript numbers in terms of the exponent values at which they + become zero and
+Infinity, use[-324, 308]. +- +
+BigNumber.config({ RANGE: 500 }) +BigNumber.config().RANGE // [ -500, 500 ] +new BigNumber('9.999e499') // '9.999e+499' +new BigNumber('1e500') // 'Infinity' +new BigNumber('1e-499') // '1e-499' +new BigNumber('1e-500') // '0' + +BigNumber.config({ RANGE: [-3, 4] }) +new BigNumber(99999) // '99999' e is only 4 +new BigNumber(100000) // 'Infinity' e is 5 +new BigNumber(0.001) // '0.01' e is only -3 +new BigNumber(0.0001) // '0' e is -4+- + The largest possible magnitude of a finite BigNumber is +
+ + + +9.999...e+1000000000.
+ The smallest possible magnitude of a non-zero BigNumber is1e-1000000000. + CRYPTO
+ -
+ boolean:
trueorfalse.
+ Default value:false+
+ - + The value that determines whether cryptographically-secure pseudo-random number + generation is used. + +
-
+ If
CRYPTOis set totruethen the +randommethod will generate random digits using +crypto.getRandomValuesin browsers that support it, or +crypto.randomBytesif using Node.js. +
+ -
+ If neither function is supported by the host environment then attempting to set
+
CRYPTOtotruewill fail and an exception will be thrown. +
+ -
+ If
CRYPTOisfalsethen the source of randomness used will be +Math.random(which is assumed to generate at least30bits of + randomness). +
+ - See
random.
+ -
+
+// Node.js +global.crypto = require('crypto') + +BigNumber.config({ CRYPTO: true }) +BigNumber.config().CRYPTO // true +BigNumber.random() // 0.54340758610486147524+
+
+
+
+ MODULO_MODE
+ -
+ number: integer,
0to9inclusive
+ Default value:1(ROUND_DOWN) +
+ - The modulo mode used when calculating the modulus:
a mod n.
+ -
+ The quotient,
q = a / n, is calculated according to the +ROUNDING_MODEthat corresponds to the chosen +MODULO_MODE. +
+ - The remainder,
r, is calculated as:r = a - n * q.
+ - + The modes that are most commonly used for the modulus/remainder operation are shown in + the following table. Although the other rounding modes can be used, they may not give + useful results. + +
-
+
+
+Property Value Description + +ROUND_UP 0 ++ The remainder is positive if the dividend is negative, otherwise it is negative. + ++ +ROUND_DOWN 1 ++ The remainder has the same sign as the dividend. +
+ This uses 'truncating division' and matches the behaviour of JavaScript's + remainder operator%. ++ +ROUND_FLOOR 3 ++ The remainder has the same sign as the divisor. +
+ This matches Python's%operator. ++ +ROUND_HALF_EVEN 6 +The IEEE 754 remainder function. ++ +EUCLID 9 ++ The remainder is always positive. Euclidian division: +
+q = sign(n) * floor(a / abs(n))+
+ - + The rounding/modulo modes are available as enumerated properties of the BigNumber + constructor. + +
- See
modulo.
+ -
+
BigNumber.config({ MODULO_MODE: BigNumber.EUCLID }) +BigNumber.config({ MODULO_MODE: 9 }) // equivalent+
+
+
+
+ POW_PRECISION
+ -
+ number: integer,
0to1e+9inclusive.
+ Default value:0+
+ - + The maximum precision, i.e. number of significant digits, of the result of the power + operation (unless a modulus is specified). + +
- If set to
0, the number of significant digits will not be limited.
+ - See
exponentiatedBy.
+ BigNumber.config({ POW_PRECISION: 100 })
+
+
+
+ FORMAT
+ - object +
-
+ The
FORMATobject configures the format of the string returned by the +toFormatmethod. +
+ -
+ The example below shows the properties of the
FORMATobject that are + recognised, and their default values. +
+ -
+ Unlike the other configuration properties, the values of the properties of the
+
FORMATobject will not be checked for validity. The existing +FORMATobject will simply be replaced by the object that is passed in. + The object can include any number of the properties shown below. +
+ - See
toFormatfor examples of usage.
+ -
+
+BigNumber.config({ + FORMAT: { + // string to prepend + prefix: '', + // decimal separator + decimalSeparator: '.', + // grouping separator of the integer part + groupSeparator: ',', + // primary grouping size of the integer part + groupSize: 3, + // secondary grouping size of the integer part + secondaryGroupSize: 0, + // grouping separator of the fraction part + fractionGroupSeparator: ' ', + // grouping size of the fraction part + fractionGroupSize: 0, + // string to append + suffix: '' + } +});+
+
+
+
+ ALPHABET
+ -
+ string
+ Default value:'0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'+
+ -
+ The alphabet used for base conversion. The length of the alphabet corresponds to the
+ maximum value of the base argument that can be passed to the
+
BigNumberconstructor or +toString. +
+ -
+ There is no maximum length for the alphabet, but it must be at least 2 characters long, and
+ it must not contain whitespace or a repeated character, or the sign indicators
+
'+'and'-', or the decimal separator'.'. +
+ -
+
// duodecimal (base 12) +BigNumber.config({ ALPHABET: '0123456789TE' }) +x = new BigNumber('T', 12) +x.toString() // '10' +x.toString(12) // 'T'+
+
+
+
+
+
Returns an object with the above properties and their current values.
+
+ Throws if object is not an object, or if an invalid value is assigned to
+ one or more of the above properties. See Errors.
+
+BigNumber.config({
+ DECIMAL_PLACES: 40,
+ ROUNDING_MODE: BigNumber.ROUND_HALF_CEIL,
+ EXPONENTIAL_AT: [-10, 20],
+ RANGE: [-500, 500],
+ CRYPTO: true,
+ MODULO_MODE: BigNumber.ROUND_FLOOR,
+ POW_PRECISION: 80,
+ FORMAT: {
+ groupSize: 3,
+ groupSeparator: ' ',
+ decimalSeparator: ','
+ },
+ ALPHABET: '0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ$_'
+});
+
+obj = BigNumber.config();
+obj.DECIMAL_PLACES // 40
+obj.RANGE // [-500, 500]
+
+
+
+
+ isBigNumber.isBigNumber(value) ⇒ boolean
+
+ value: any
+ Returns true if value is a BigNumber instance, otherwise returns
+ false.
+
x = 42 +y = new BigNumber(x) + +BigNumber.isBigNumber(x) // false +y instanceof BigNumber // true +BigNumber.isBigNumber(y) // true + +BN = BigNumber.clone(); +z = new BN(x) +z instanceof BigNumber // false +BigNumber.isBigNumber(z) // true+
+ If value is a BigNumber instance and BigNumber.DEBUG is true,
+ then this method will also check if value is well-formed, and throw if it is not.
+ See Errors.
+
+ The check can be useful if creating a BigNumber from an object literal. + See BigNumber. +
++x = new BigNumber(10) + +// Change x.c to an illegitimate value. +x.c = NaN + +BigNumber.DEBUG = false + +// No error. +BigNumber.isBigNumber(x) // true + +BigNumber.DEBUG = true + +// Error. +BigNumber.isBigNumber(x) // '[BigNumber Error] Invalid BigNumber'+ + + +
maximum.max(n...) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the maximum of the arguments. +
+The return value is always exact and unrounded.
+x = new BigNumber('3257869345.0378653')
+BigNumber.maximum(4e9, x, '123456789.9') // '4000000000'
+
+arr = [12, '13', new BigNumber(14)]
+BigNumber.max.apply(null, arr) // '14'
+
+
+
+ minimum.min(n...) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the minimum of the arguments. +
+The return value is always exact and unrounded.
+x = new BigNumber('3257869345.0378653')
+BigNumber.minimum(4e9, x, '123456789.9') // '123456789.9'
+
+arr = [2, new BigNumber(-14), '-15.9999', -12]
+BigNumber.min.apply(null, arr) // '-15.9999'
+
+
+
+
+ random.random([dp]) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+ dp: number: integer, 0 to 1e+9 inclusive
+ Returns a new BigNumber with a pseudo-random value equal to or greater than 0 and
+ less than 1.
+
+ The return value will have dp decimal places (or less if trailing zeros are
+ produced).
+ If dp is omitted then the number of decimal places will default to the current
+ DECIMAL_PLACES setting.
+
+ Depending on the value of this BigNumber constructor's
+ CRYPTO setting and the support for the
+ crypto object in the host environment, the random digits of the return value are
+ generated by either Math.random (fastest), crypto.getRandomValues
+ (Web Cryptography API in recent browsers) or crypto.randomBytes (Node.js).
+
+ To be able to set CRYPTO to true when using
+ Node.js, the crypto object must be available globally:
+
global.crypto = require('crypto')
+
+ If CRYPTO is true, i.e. one of the
+ crypto methods is to be used, the value of a returned BigNumber should be
+ cryptographically-secure and statistically indistinguishable from a random value.
+
+ Throws if dp is invalid. See Errors.
+
BigNumber.config({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 10 })
+BigNumber.random() // '0.4117936847'
+BigNumber.random(20) // '0.78193327636914089009'
+
+
+
+ sum.sum(n...) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
Returns a BigNumber whose value is the sum of the arguments.
+The return value is always exact and unrounded.
+x = new BigNumber('3257869345.0378653')
+BigNumber.sum(4e9, x, '123456789.9') // '7381326134.9378653'
+
+arr = [2, new BigNumber(14), '15.9999', 12]
+BigNumber.sum.apply(null, arr) // '43.9999'
+
+
+
+ Properties
+
+ The library's enumerated rounding modes are stored as properties of the constructor.
+ (They are not referenced internally by the library itself.)
+
+ Rounding modes 0 to 6 (inclusive) are the same as those of Java's
+ BigDecimal class.
+
| Property | +Value | +Description | +
|---|---|---|
| ROUND_UP | +0 | +Rounds away from zero | +
| ROUND_DOWN | +1 | +Rounds towards zero | +
| ROUND_CEIL | +2 | +Rounds towards Infinity |
+
| ROUND_FLOOR | +3 | +Rounds towards -Infinity |
+
| ROUND_HALF_UP | +4 | +
+ Rounds towards nearest neighbour. + If equidistant, rounds away from zero + |
+
| ROUND_HALF_DOWN | +5 | +
+ Rounds towards nearest neighbour. + If equidistant, rounds towards zero + |
+
| ROUND_HALF_EVEN | +6 | +
+ Rounds towards nearest neighbour. + If equidistant, rounds towards even neighbour + |
+
| ROUND_HALF_CEIL | +7 | +
+ Rounds towards nearest neighbour. + If equidistant, rounds towards Infinity
+ |
+
| ROUND_HALF_FLOOR | +8 | +
+ Rounds towards nearest neighbour. + If equidistant, rounds towards -Infinity
+ |
+
+BigNumber.config({ ROUNDING_MODE: BigNumber.ROUND_CEIL })
+BigNumber.config({ ROUNDING_MODE: 2 }) // equivalent
+
+ DEBUG
+undefined|false|true
+
+ If BigNumber.DEBUG is set true then an error will be thrown
+ if this BigNumber constructor receives an invalid value, such as
+ a value of type number with more than 15 significant digits.
+ See BigNumber.
+
+ An error will also be thrown if the isBigNumber
+ method receives a BigNumber that is not well-formed.
+ See isBigNumber.
+
BigNumber.DEBUG = true+ + +
INSTANCE
+ + +Methods
+The methods inherited by a BigNumber instance from its constructor's prototype object.
+A BigNumber is immutable in the sense that it is not changed by its methods.
+
+ The treatment of ±0, ±Infinity and NaN is
+ consistent with how JavaScript treats these values.
+
Many method names have a shorter alias.
+ + + +absoluteValue.abs() ⇒ BigNumber
+ + Returns a BigNumber whose value is the absolute value, i.e. the magnitude, of the value of + this BigNumber. +
+The return value is always exact and unrounded.
++x = new BigNumber(-0.8) +y = x.absoluteValue() // '0.8' +z = y.abs() // '0.8'+ + + +
+ comparedTo.comparedTo(n [, base]) ⇒ number
+
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
| Returns | |
|---|---|
1 |
+ If the value of this BigNumber is greater than the value of n |
+
-1 |
+ If the value of this BigNumber is less than the value of n |
+
0 |
+ If this BigNumber and n have the same value |
+
null |
+ If the value of either this BigNumber or n is NaN |
+
+x = new BigNumber(Infinity)
+y = new BigNumber(5)
+x.comparedTo(y) // 1
+x.comparedTo(x.minus(1)) // 0
+y.comparedTo(NaN) // null
+y.comparedTo('110', 2) // -1
+
+
+
+
+ decimalPlaces.dp([dp [, rm]]) ⇒ BigNumber|number
+
+
+ dp: number: integer, 0 to 1e+9 inclusive
+ rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive
+
+ If dp is a number, returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber
+ rounded by rounding mode rm to a maximum of dp decimal places.
+
+ If dp is omitted, or is null or undefined, the return
+ value is the number of decimal places of the value of this BigNumber, or null if
+ the value of this BigNumber is ±Infinity or NaN.
+
+ If rm is omitted, or is null or undefined,
+ ROUNDING_MODE is used.
+
+ Throws if dp or rm is invalid. See Errors.
+
+x = new BigNumber(1234.56)
+x.decimalPlaces(1) // '1234.6'
+x.dp() // 2
+x.decimalPlaces(2) // '1234.56'
+x.dp(10) // '1234.56'
+x.decimalPlaces(0, 1) // '1234'
+x.dp(0, 6) // '1235'
+x.decimalPlaces(1, 1) // '1234.5'
+x.dp(1, BigNumber.ROUND_HALF_EVEN) // '1234.6'
+x // '1234.56'
+y = new BigNumber('9.9e-101')
+y.dp() // 102
+
+
+
+ dividedBy.div(n [, base]) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber divided by
+ n, rounded according to the current
+ DECIMAL_PLACES and
+ ROUNDING_MODE settings.
+
+x = new BigNumber(355) +y = new BigNumber(113) +x.dividedBy(y) // '3.14159292035398230088' +x.div(5) // '71' +x.div(47, 16) // '5'+ + + +
+ dividedToIntegerBy.idiv(n [, base]) ⇒
+ BigNumber
+
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the integer part of dividing the value of this BigNumber by
+ n.
+
+x = new BigNumber(5)
+y = new BigNumber(3)
+x.dividedToIntegerBy(y) // '1'
+x.idiv(0.7) // '7'
+x.idiv('0.f', 16) // '5'
+
+
+
+
+ exponentiatedBy.pow(n [, m]) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber: integer
+ m: number|string|BigNumber
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber exponentiated by
+ n, i.e. raised to the power n, and optionally modulo a modulus
+ m.
+
+ Throws if n is not an integer. See Errors.
+
+ If n is negative the result is rounded according to the current
+ DECIMAL_PLACES and
+ ROUNDING_MODE settings.
+
+ As the number of digits of the result of the power operation can grow so large so quickly,
+ e.g. 123.45610000 has over 50000 digits, the number of significant
+ digits calculated is limited to the value of the
+ POW_PRECISION setting (unless a modulus
+ m is specified).
+
+ By default POW_PRECISION is set to 0.
+ This means that an unlimited number of significant digits will be calculated, and that the
+ method's performance will decrease dramatically for larger exponents.
+
+ If m is specified and the value of m, n and this
+ BigNumber are integers, and n is positive, then a fast modular exponentiation
+ algorithm is used, otherwise the operation will be performed as
+ x.exponentiatedBy(n).modulo(m) with a
+ POW_PRECISION of 0.
+
+Math.pow(0.7, 2) // 0.48999999999999994 +x = new BigNumber(0.7) +x.exponentiatedBy(2) // '0.49' +BigNumber(3).pow(-2) // '0.11111111111111111111'+ + + +
+ integerValue.integerValue([rm]) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+
+ rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber rounded to an integer using
+ rounding mode rm.
+
+ If rm is omitted, or is null or undefined,
+ ROUNDING_MODE is used.
+
+ Throws if rm is invalid. See Errors.
+
+x = new BigNumber(123.456) +x.integerValue() // '123' +x.integerValue(BigNumber.ROUND_CEIL) // '124' +y = new BigNumber(-12.7) +y.integerValue() // '-13' +y.integerValue(BigNumber.ROUND_DOWN) // '-12'+
+ The following is an example of how to add a prototype method that emulates JavaScript's
+ Math.round function. Math.ceil, Math.floor and
+ Math.trunc can be emulated in the same way with
+ BigNumber.ROUND_CEIL, BigNumber.ROUND_FLOOR and
+ BigNumber.ROUND_DOWN respectively.
+
+BigNumber.prototype.round = function (n) {
+ return n.integerValue(BigNumber.ROUND_HALF_CEIL);
+};
+x.round() // '123'
+
+
+
+ isEqualTo.eq(n [, base]) ⇒ boolean
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is equal to the value of
+ n, otherwise returns false.
+ As with JavaScript, NaN does not equal NaN.
+
Note: This method uses the comparedTo method internally.
+0 === 1e-324 // true
+x = new BigNumber(0)
+x.isEqualTo('1e-324') // false
+BigNumber(-0).eq(x) // true ( -0 === 0 )
+BigNumber(255).eq('ff', 16) // true
+
+y = new BigNumber(NaN)
+y.isEqualTo(NaN) // false
+
+
+
+ isFinite.isFinite() ⇒ boolean
+
+ Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is a finite number, otherwise
+ returns false.
+
+ The only possible non-finite values of a BigNumber are NaN, Infinity
+ and -Infinity.
+
+x = new BigNumber(1) +x.isFinite() // true +y = new BigNumber(Infinity) +y.isFinite() // false+
+ Note: The native method isFinite() can be used if
+ n <= Number.MAX_VALUE.
+
isGreaterThan.gt(n [, base]) ⇒ boolean
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is greater than the value of
+ n, otherwise returns false.
+
Note: This method uses the comparedTo method internally.
+0.1 > (0.3 - 0.2) // true +x = new BigNumber(0.1) +x.isGreaterThan(BigNumber(0.3).minus(0.2)) // false +BigNumber(0).gt(x) // false +BigNumber(11, 3).gt(11.1, 2) // true+ + + +
+ isGreaterThanOrEqualTo.gte(n [, base]) ⇒ boolean
+
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is greater than or equal to the value
+ of n, otherwise returns false.
+
Note: This method uses the comparedTo method internally.
+(0.3 - 0.2) >= 0.1 // false
+x = new BigNumber(0.3).minus(0.2)
+x.isGreaterThanOrEqualTo(0.1) // true
+BigNumber(1).gte(x) // true
+BigNumber(10, 18).gte('i', 36) // true
+
+
+
+ isInteger.isInteger() ⇒ boolean
+
+ Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is an integer, otherwise returns
+ false.
+
+x = new BigNumber(1) +x.isInteger() // true +y = new BigNumber(123.456) +y.isInteger() // false+ + + +
isLessThan.lt(n [, base]) ⇒ boolean
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is less than the value of
+ n, otherwise returns false.
+
Note: This method uses the comparedTo method internally.
+(0.3 - 0.2) < 0.1 // true +x = new BigNumber(0.3).minus(0.2) +x.isLessThan(0.1) // false +BigNumber(0).lt(x) // true +BigNumber(11.1, 2).lt(11, 3) // true+ + + +
+ isLessThanOrEqualTo.lte(n [, base]) ⇒ boolean
+
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is less than or equal to the value of
+ n, otherwise returns false.
+
Note: This method uses the comparedTo method internally.
+0.1 <= (0.3 - 0.2) // false
+x = new BigNumber(0.1)
+x.isLessThanOrEqualTo(BigNumber(0.3).minus(0.2)) // true
+BigNumber(-1).lte(x) // true
+BigNumber(10, 18).lte('i', 36) // true
+
+
+
+ isNaN.isNaN() ⇒ boolean
+
+ Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is NaN, otherwise
+ returns false.
+
+x = new BigNumber(NaN)
+x.isNaN() // true
+y = new BigNumber('Infinity')
+y.isNaN() // false
+ Note: The native method isNaN() can also be used.
isNegative.isNegative() ⇒ boolean
+
+ Returns true if the sign of this BigNumber is negative, otherwise returns
+ false.
+
+x = new BigNumber(-0) +x.isNegative() // true +y = new BigNumber(2) +y.isNegative() // false+
Note: n < 0 can be used if n <= -Number.MIN_VALUE.
isPositive.isPositive() ⇒ boolean
+
+ Returns true if the sign of this BigNumber is positive, otherwise returns
+ false.
+
+x = new BigNumber(-0) +x.isPositive() // false +y = new BigNumber(2) +y.isPositive() // true+ + + +
isZero.isZero() ⇒ boolean
+
+ Returns true if the value of this BigNumber is zero or minus zero, otherwise
+ returns false.
+
+x = new BigNumber(-0) +x.isZero() && x.isNegative() // true +y = new BigNumber(Infinity) +y.isZero() // false+
Note: n == 0 can be used if n >= Number.MIN_VALUE.
+ minus.minus(n [, base]) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber minus n.
The return value is always exact and unrounded.
++0.3 - 0.1 // 0.19999999999999998 +x = new BigNumber(0.3) +x.minus(0.1) // '0.2' +x.minus(0.6, 20) // '0'+ + + +
modulo.mod(n [, base]) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber modulo n, i.e.
+ the integer remainder of dividing this BigNumber by n.
+
+ The value returned, and in particular its sign, is dependent on the value of the
+ MODULO_MODE setting of this BigNumber constructor.
+ If it is 1 (default value), the result will have the same sign as this BigNumber,
+ and it will match that of Javascript's % operator (within the limits of double
+ precision) and BigDecimal's remainder method.
+
The return value is always exact and unrounded.
+
+ See MODULO_MODE for a description of the other
+ modulo modes.
+
+1 % 0.9 // 0.09999999999999998
+x = new BigNumber(1)
+x.modulo(0.9) // '0.1'
+y = new BigNumber(33)
+y.mod('a', 33) // '3'
+
+
+
+
+ multipliedBy.times(n [, base]) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber multiplied by n.
+
The return value is always exact and unrounded.
+
+0.6 * 3 // 1.7999999999999998
+x = new BigNumber(0.6)
+y = x.multipliedBy(3) // '1.8'
+BigNumber('7e+500').times(y) // '1.26e+501'
+x.multipliedBy('-a', 16) // '-6'
+
+
+
+ negated.negated() ⇒ BigNumber
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber negated, i.e. multiplied by
+ -1.
+
+x = new BigNumber(1.8) +x.negated() // '-1.8' +y = new BigNumber(-1.3) +y.negated() // '1.3'+ + + +
plus.plus(n [, base]) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+ n: number|string|BigNumber
+ base: number
+ See BigNumber for further parameter details.
+
Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber plus n.
The return value is always exact and unrounded.
+
+0.1 + 0.2 // 0.30000000000000004
+x = new BigNumber(0.1)
+y = x.plus(0.2) // '0.3'
+BigNumber(0.7).plus(x).plus(y) // '1'
+x.plus('0.1', 8) // '0.225'
+
+
+
+
+ precision.sd([d [, rm]]) ⇒ BigNumber|number
+
+
+ d: number|boolean: integer, 1 to 1e+9
+ inclusive, or true or false
+ rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive.
+
+ If d is a number, returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber
+ rounded to a precision of d significant digits using rounding mode
+ rm.
+
+ If d is omitted or is null or undefined, the return
+ value is the number of significant digits of the value of this BigNumber, or null
+ if the value of this BigNumber is ±Infinity or NaN.
+ If d is true then any trailing zeros of the integer
+ part of a number are counted as significant digits, otherwise they are not.
+
+ If rm is omitted or is null or undefined,
+ ROUNDING_MODE will be used.
+
+ Throws if d or rm is invalid. See Errors.
+
+x = new BigNumber(9876.54321) +x.precision(6) // '9876.54' +x.sd() // 9 +x.precision(6, BigNumber.ROUND_UP) // '9876.55' +x.sd(2) // '9900' +x.precision(2, 1) // '9800' +x // '9876.54321' +y = new BigNumber(987000) +y.precision() // 3 +y.sd(true) // 6+ + + +
shiftedBy.shiftedBy(n) ⇒ BigNumber
+
+ n: number: integer,
+ -9007199254740991 to 9007199254740991 inclusive
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the value of this BigNumber shifted by n
+ places.
+
+ The shift is of the decimal point, i.e. of powers of ten, and is to the left if n
+ is negative or to the right if n is positive.
+
The return value is always exact and unrounded.
+
+ Throws if n is invalid. See Errors.
+
+x = new BigNumber(1.23) +x.shiftedBy(3) // '1230' +x.shiftedBy(-3) // '0.00123'+ + + +
squareRoot.sqrt() ⇒ BigNumber
+
+ Returns a BigNumber whose value is the square root of the value of this BigNumber,
+ rounded according to the current
+ DECIMAL_PLACES and
+ ROUNDING_MODE settings.
+
+ The return value will be correctly rounded, i.e. rounded as if the result was first calculated + to an infinite number of correct digits before rounding. +
++x = new BigNumber(16) +x.squareRoot() // '4' +y = new BigNumber(3) +y.sqrt() // '1.73205080756887729353'+ + + +
+ toExponential.toExponential([dp [, rm]]) ⇒ string
+
+
+ dp: number: integer, 0 to 1e+9 inclusive
+ rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive
+
+ Returns a string representing the value of this BigNumber in exponential notation rounded
+ using rounding mode rm to dp decimal places, i.e with one digit
+ before the decimal point and dp digits after it.
+
+ If the value of this BigNumber in exponential notation has fewer than dp fraction
+ digits, the return value will be appended with zeros accordingly.
+
+ If dp is omitted, or is null or undefined, the number
+ of digits after the decimal point defaults to the minimum number of digits necessary to
+ represent the value exactly.
+ If rm is omitted or is null or undefined,
+ ROUNDING_MODE is used.
+
+ Throws if dp or rm is invalid. See Errors.
+
+x = 45.6 +y = new BigNumber(x) +x.toExponential() // '4.56e+1' +y.toExponential() // '4.56e+1' +x.toExponential(0) // '5e+1' +y.toExponential(0) // '5e+1' +x.toExponential(1) // '4.6e+1' +y.toExponential(1) // '4.6e+1' +y.toExponential(1, 1) // '4.5e+1' (ROUND_DOWN) +x.toExponential(3) // '4.560e+1' +y.toExponential(3) // '4.560e+1'+ + + +
+ toFixed.toFixed([dp [, rm]]) ⇒ string
+
+
+ dp: number: integer, 0 to 1e+9 inclusive
+ rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive
+
+ Returns a string representing the value of this BigNumber in normal (fixed-point) notation
+ rounded to dp decimal places using rounding mode rm.
+
+ If the value of this BigNumber in normal notation has fewer than dp fraction
+ digits, the return value will be appended with zeros accordingly.
+
+ Unlike Number.prototype.toFixed, which returns exponential notation if a number
+ is greater or equal to 1021, this method will always return normal
+ notation.
+
+ If dp is omitted or is null or undefined, the return
+ value will be unrounded and in normal notation. This is also unlike
+ Number.prototype.toFixed, which returns the value to zero decimal places.
+ It is useful when fixed-point notation is required and the current
+ EXPONENTIAL_AT setting causes
+ toString to return exponential notation.
+ If rm is omitted or is null or undefined,
+ ROUNDING_MODE is used.
+
+ Throws if dp or rm is invalid. See Errors.
+
+x = 3.456 +y = new BigNumber(x) +x.toFixed() // '3' +y.toFixed() // '3.456' +y.toFixed(0) // '3' +x.toFixed(2) // '3.46' +y.toFixed(2) // '3.46' +y.toFixed(2, 1) // '3.45' (ROUND_DOWN) +x.toFixed(5) // '3.45600' +y.toFixed(5) // '3.45600'+ + + +
+ toFormat.toFormat([dp [, rm[, format]]]) ⇒ string
+
+
+ dp: number: integer, 0 to 1e+9 inclusive
+ rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive
+ format: object: see FORMAT
+
+
+ Returns a string representing the value of this BigNumber in normal (fixed-point) notation
+ rounded to dp decimal places using rounding mode rm, and formatted
+ according to the properties of the format object.
+
+ See FORMAT and the examples below for the properties of the
+ format object, their types, and their usage. A formatting object may contain
+ some or all of the recognised properties.
+
+ If dp is omitted or is null or undefined, then the
+ return value is not rounded to a fixed number of decimal places.
+ If rm is omitted or is null or undefined,
+ ROUNDING_MODE is used.
+ If format is omitted or is null or undefined, the
+ FORMAT object is used.
+
+ Throws if dp, rm or format is invalid. See
+ Errors.
+
+fmt = {
+ prefix = '',
+ decimalSeparator: '.',
+ groupSeparator: ',',
+ groupSize: 3,
+ secondaryGroupSize: 0,
+ fractionGroupSeparator: ' ',
+ fractionGroupSize: 0,
+ suffix = ''
+}
+
+x = new BigNumber('123456789.123456789')
+
+// Set the global formatting options
+BigNumber.config({ FORMAT: fmt })
+
+x.toFormat() // '123,456,789.123456789'
+x.toFormat(3) // '123,456,789.123'
+
+// If a reference to the object assigned to FORMAT has been retained,
+// the format properties can be changed directly
+fmt.groupSeparator = ' '
+fmt.fractionGroupSize = 5
+x.toFormat() // '123 456 789.12345 6789'
+
+// Alternatively, pass the formatting options as an argument
+fmt = {
+ prefix: '=> ',
+ decimalSeparator: ',',
+ groupSeparator: '.',
+ groupSize: 3,
+ secondaryGroupSize: 2
+}
+
+x.toFormat() // '123 456 789.12345 6789'
+x.toFormat(fmt) // '=> 12.34.56.789,123456789'
+x.toFormat(2, fmt) // '=> 12.34.56.789,12'
+x.toFormat(3, BigNumber.ROUND_UP, fmt) // '=> 12.34.56.789,124'
+
+
+
+
+ toFraction.toFraction([maximum_denominator])
+ ⇒ [BigNumber, BigNumber]
+
+
+ maximum_denominator:
+ number|string|BigNumber: integer >= 1 and <=
+ Infinity
+
+ Returns an array of two BigNumbers representing the value of this BigNumber as a simple
+ fraction with an integer numerator and an integer denominator. The denominator will be a
+ positive non-zero value less than or equal to maximum_denominator.
+
+ If a maximum_denominator is not specified, or is null or
+ undefined, the denominator will be the lowest value necessary to represent the
+ number exactly.
+
+ Throws if maximum_denominator is invalid. See Errors.
+
+x = new BigNumber(1.75)
+x.toFraction() // '7, 4'
+
+pi = new BigNumber('3.14159265358')
+pi.toFraction() // '157079632679,50000000000'
+pi.toFraction(100000) // '312689, 99532'
+pi.toFraction(10000) // '355, 113'
+pi.toFraction(100) // '311, 99'
+pi.toFraction(10) // '22, 7'
+pi.toFraction(1) // '3, 1'
+
+
+
+ toJSON.toJSON() ⇒ string
+ As valueOf.
+x = new BigNumber('177.7e+457')
+y = new BigNumber(235.4325)
+z = new BigNumber('0.0098074')
+
+// Serialize an array of three BigNumbers
+str = JSON.stringify( [x, y, z] )
+// "["1.777e+459","235.4325","0.0098074"]"
+
+// Return an array of three BigNumbers
+JSON.parse(str, function (key, val) {
+ return key === '' ? val : new BigNumber(val)
+})
+
+
+
+ toNumber.toNumber() ⇒ number
+ Returns the value of this BigNumber as a JavaScript number primitive.
++ This method is identical to using type coercion with the unary plus operator. +
+
+x = new BigNumber(456.789)
+x.toNumber() // 456.789
++x // 456.789
+
+y = new BigNumber('45987349857634085409857349856430985')
+y.toNumber() // 4.598734985763409e+34
+
+z = new BigNumber(-0)
+1 / z.toNumber() // -Infinity
+1 / +z // -Infinity
+
+
+
+
+ toPrecision.toPrecision([sd [, rm]]) ⇒ string
+
+
+ sd: number: integer, 1 to 1e+9 inclusive
+ rm: number: integer, 0 to 8 inclusive
+
+ Returns a string representing the value of this BigNumber rounded to sd
+ significant digits using rounding mode rm.
+
+ If sd is less than the number of digits necessary to represent the integer part
+ of the value in normal (fixed-point) notation, then exponential notation is used.
+
+ If sd is omitted, or is null or undefined, then the
+ return value is the same as n.toString().
+ If rm is omitted or is null or undefined,
+ ROUNDING_MODE is used.
+
+ Throws if sd or rm is invalid. See Errors.
+
+x = 45.6 +y = new BigNumber(x) +x.toPrecision() // '45.6' +y.toPrecision() // '45.6' +x.toPrecision(1) // '5e+1' +y.toPrecision(1) // '5e+1' +y.toPrecision(2, 0) // '4.6e+1' (ROUND_UP) +y.toPrecision(2, 1) // '4.5e+1' (ROUND_DOWN) +x.toPrecision(5) // '45.600' +y.toPrecision(5) // '45.600'+ + + +
toString.toString([base]) ⇒ string
+
+ base: number: integer, 2 to ALPHABET.length
+ inclusive (see ALPHABET).
+
+ Returns a string representing the value of this BigNumber in the specified base, or base
+ 10 if base is omitted or is null or
+ undefined.
+
+ For bases above 10, and using the default base conversion alphabet
+ (see ALPHABET), values from 10 to
+ 35 are represented by a-z
+ (as with Number.prototype.toString).
+
+ If a base is specified the value is rounded according to the current
+ DECIMAL_PLACES
+ and ROUNDING_MODE settings.
+
+ If a base is not specified, and this BigNumber has a positive
+ exponent that is equal to or greater than the positive component of the
+ current EXPONENTIAL_AT setting,
+ or a negative exponent equal to or less than the negative component of the
+ setting, then exponential notation is returned.
+
If base is null or undefined it is ignored.
+ Throws if base is invalid. See Errors.
+
+x = new BigNumber(750000)
+x.toString() // '750000'
+BigNumber.config({ EXPONENTIAL_AT: 5 })
+x.toString() // '7.5e+5'
+
+y = new BigNumber(362.875)
+y.toString(2) // '101101010.111'
+y.toString(9) // '442.77777777777777777778'
+y.toString(32) // 'ba.s'
+
+BigNumber.config({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 4 });
+z = new BigNumber('1.23456789')
+z.toString() // '1.23456789'
+z.toString(10) // '1.2346'
+
+
+
+ valueOf.valueOf() ⇒ string
+
+ As toString, but does not accept a base argument and includes
+ the minus sign for negative zero.
+
+x = new BigNumber('-0')
+x.toString() // '0'
+x.valueOf() // '-0'
+y = new BigNumber('1.777e+457')
+y.valueOf() // '1.777e+457'
+
+
+
+ Properties
+The properties of a BigNumber instance:
+| Property | +Description | +Type | +Value | +
|---|---|---|---|
| c | +coefficient* | +number[] |
+ Array of base 1e14 numbers |
+
| e | +exponent | +number | +Integer, -1000000000 to 1000000000 inclusive |
+
| s | +sign | +number | +-1 or 1 |
+
*significand
+
+ The value of any of the c, e and s properties may also
+ be null.
+
+ The above properties are best considered to be read-only. In early versions of this library it + was okay to change the exponent of a BigNumber by writing to its exponent property directly, + but this is no longer reliable as the value of the first element of the coefficient array is + now dependent on the exponent. +
++ Note that, as with JavaScript numbers, the original exponent and fractional trailing zeros are + not necessarily preserved. +
+x = new BigNumber(0.123) // '0.123'
+x.toExponential() // '1.23e-1'
+x.c // '1,2,3'
+x.e // -1
+x.s // 1
+
+y = new Number(-123.4567000e+2) // '-12345.67'
+y.toExponential() // '-1.234567e+4'
+z = new BigNumber('-123.4567000e+2') // '-12345.67'
+z.toExponential() // '-1.234567e+4'
+z.c // '1,2,3,4,5,6,7'
+z.e // 4
+z.s // -1
+
+
+
+ Zero, NaN and Infinity
+
+ The table below shows how ±0, NaN and
+ ±Infinity are stored.
+
| + | c | +e | +s | +
|---|---|---|---|
| ±0 | +[0] |
+ 0 |
+ ±1 |
+
| NaN | +null |
+ null |
+ null |
+
| ±Infinity | +null |
+ null |
+ ±1 |
+
+x = new Number(-0) // 0 +1 / x == -Infinity // true + +y = new BigNumber(-0) // '0' +y.c // '0' ( [0].toString() ) +y.e // 0 +y.s // -1+ + + +
Errors
+The table below shows the errors that are thrown.
+
+ The errors are generic Error objects whose message begins
+ '[BigNumber Error]'.
+
| Method | +Throws | +
|---|---|
+ BigNumber+ comparedTo+ dividedBy+ dividedToIntegerBy+ isEqualTo+ isGreaterThan+ isGreaterThanOrEqualTo+ isLessThan+ isLessThanOrEqualTo+ minus+ modulo+ plus+ multipliedBy
+ |
+ Base not a primitive number | +
| Base not an integer | +|
| Base out of range | +|
| Number primitive has more than 15 significant digits* | +|
| Not a base... number* | +|
| Not a number* | +|
clone |
+ Object expected | +
config |
+ Object expected | +
DECIMAL_PLACES not a primitive number |
+ |
DECIMAL_PLACES not an integer |
+ |
DECIMAL_PLACES out of range |
+ |
ROUNDING_MODE not a primitive number |
+ |
ROUNDING_MODE not an integer |
+ |
ROUNDING_MODE out of range |
+ |
EXPONENTIAL_AT not a primitive number |
+ |
EXPONENTIAL_AT not an integer |
+ |
EXPONENTIAL_AT out of range |
+ |
RANGE not a primitive number |
+ |
RANGE not an integer |
+ |
RANGE cannot be zero |
+ |
RANGE cannot be zero |
+ |
CRYPTO not true or false |
+ |
crypto unavailable |
+ |
MODULO_MODE not a primitive number |
+ |
MODULO_MODE not an integer |
+ |
MODULO_MODE out of range |
+ |
POW_PRECISION not a primitive number |
+ |
POW_PRECISION not an integer |
+ |
POW_PRECISION out of range |
+ |
FORMAT not an object |
+ |
ALPHABET invalid |
+ |
+ decimalPlaces+ precision+ random+ shiftedBy+ toExponential+ toFixed+ toFormat+ toPrecision
+ |
+ Argument not a primitive number | +
| Argument not an integer | +|
| Argument out of range | +|
+ decimalPlaces+ precision
+ |
+ Argument not true or false | +
exponentiatedBy |
+ Argument not an integer | +
isBigNumber |
+ Invalid BigNumber* | +
+ minimum+ maximum
+ |
+ Not a number* | +
+ random
+ |
+ crypto unavailable | +
+ toFormat
+ |
+ Argument not an object | +
toFraction |
+ Argument not an integer | +
| Argument out of range | +|
toString |
+ Base not a primitive number | +
| Base not an integer | +|
| Base out of range | +
*Only thrown if BigNumber.DEBUG is true.
To determine if an exception is a BigNumber Error:
+
+try {
+ // ...
+} catch (e) {
+ if (e instanceof Error && e.message.indexOf('[BigNumber Error]') === 0) {
+ // ...
+ }
+}
+
+
+
+ Type coercion
+
+ To prevent the accidental use of a BigNumber in primitive number operations, or the
+ accidental addition of a BigNumber to a string, the valueOf method can be safely
+ overwritten as shown below.
+
+ The valueOf method is the same as the
+ toJSON method, and both are the same as the
+ toString method except they do not take a base
+ argument and they include the minus sign for negative zero.
+
+BigNumber.prototype.valueOf = function () {
+ throw Error('valueOf called!')
+}
+
+x = new BigNumber(1)
+x / 2 // '[BigNumber Error] valueOf called!'
+x + 'abc' // '[BigNumber Error] valueOf called!'
+
+
+
+
+ FAQ
+ +Why are trailing fractional zeros removed from BigNumbers?
++ Some arbitrary-precision libraries retain trailing fractional zeros as they can indicate the + precision of a value. This can be useful but the results of arithmetic operations can be + misleading. +
+
+x = new BigDecimal("1.0")
+y = new BigDecimal("1.1000")
+z = x.add(y) // 2.1000
+
+x = new BigDecimal("1.20")
+y = new BigDecimal("3.45000")
+z = x.multiply(y) // 4.1400000
+ + To specify the precision of a value is to specify that the value lies + within a certain range. +
+
+ In the first example, x has a value of 1.0. The trailing zero shows
+ the precision of the value, implying that it is in the range 0.95 to
+ 1.05. Similarly, the precision indicated by the trailing zeros of y
+ indicates that the value is in the range 1.09995 to 1.10005.
+
+ If we add the two lowest values in the ranges we have, 0.95 + 1.09995 = 2.04995,
+ and if we add the two highest values we have, 1.05 + 1.10005 = 2.15005, so the
+ range of the result of the addition implied by the precision of its operands is
+ 2.04995 to 2.15005.
+
+ The result given by BigDecimal of 2.1000 however, indicates that the value is in
+ the range 2.09995 to 2.10005 and therefore the precision implied by
+ its trailing zeros may be misleading.
+
+ In the second example, the true range is 4.122744 to 4.157256 yet
+ the BigDecimal answer of 4.1400000 indicates a range of 4.13999995
+ to 4.14000005. Again, the precision implied by the trailing zeros may be
+ misleading.
+
+ This library, like binary floating point and most calculators, does not retain trailing
+ fractional zeros. Instead, the toExponential, toFixed and
+ toPrecision methods enable trailing zeros to be added if and when required.
+
Welcome back, ' + escapeHtml(name) + '!
'); + } else { + res.write('Hello, new visitor!
'); + } + + res.write(''); +} + +http.createServer(onRequest).listen(3000); +``` + +## Testing + +```sh +$ npm test +``` + +## Benchmark + +``` +$ npm run bench + +> cookie@0.4.2 bench +> node benchmark/index.js + + node@16.14.0 + v8@9.4.146.24-node.20 + uv@1.43.0 + zlib@1.2.11 + brotli@1.0.9 + ares@1.18.1 + modules@93 + nghttp2@1.45.1 + napi@8 + llhttp@6.0.4 + openssl@1.1.1m+quic + cldr@40.0 + icu@70.1 + tz@2021a3 + unicode@14.0 + ngtcp2@0.1.0-DEV + nghttp3@0.1.0-DEV + +> node benchmark/parse-top.js + + cookie.parse - top sites + + 15 tests completed. + + parse accounts.google.com x 2,421,245 ops/sec ±0.80% (188 runs sampled) + parse apple.com x 2,684,710 ops/sec ±0.59% (189 runs sampled) + parse cloudflare.com x 2,231,418 ops/sec ±0.76% (186 runs sampled) + parse docs.google.com x 2,316,357 ops/sec ±1.28% (187 runs sampled) + parse drive.google.com x 2,363,543 ops/sec ±0.49% (189 runs sampled) + parse en.wikipedia.org x 839,414 ops/sec ±0.53% (189 runs sampled) + parse linkedin.com x 553,797 ops/sec ±0.63% (190 runs sampled) + parse maps.google.com x 1,314,779 ops/sec ±0.72% (189 runs sampled) + parse microsoft.com x 153,783 ops/sec ±0.53% (190 runs sampled) + parse play.google.com x 2,249,574 ops/sec ±0.59% (187 runs sampled) + parse plus.google.com x 2,258,682 ops/sec ±0.60% (188 runs sampled) + parse sites.google.com x 2,247,069 ops/sec ±0.68% (189 runs sampled) + parse support.google.com x 1,456,840 ops/sec ±0.70% (187 runs sampled) + parse www.google.com x 1,046,028 ops/sec ±0.58% (188 runs sampled) + parse youtu.be x 937,428 ops/sec ±1.47% (190 runs sampled) + parse youtube.com x 963,878 ops/sec ±0.59% (190 runs sampled) + +> node benchmark/parse.js + + cookie.parse - generic + + 6 tests completed. + + simple x 2,745,604 ops/sec ±0.77% (185 runs sampled) + decode x 557,287 ops/sec ±0.60% (188 runs sampled) + unquote x 2,498,475 ops/sec ±0.55% (189 runs sampled) + duplicates x 868,591 ops/sec ±0.89% (187 runs sampled) + 10 cookies x 306,745 ops/sec ±0.49% (190 runs sampled) + 100 cookies x 22,414 ops/sec ±2.38% (182 runs sampled) +``` + +## References + +- [RFC 6265: HTTP State Management Mechanism][rfc-6265] +- [Same-site Cookies][rfc-6265bis-09-5.4.7] + +[rfc-west-cookie-priority-00-4.1]: https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-west-cookie-priority-00#section-4.1 +[rfc-6265bis-09-5.4.7]: https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-httpbis-rfc6265bis-09#section-5.4.7 +[rfc-6265]: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6265 +[rfc-6265-5.1.4]: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6265#section-5.1.4 +[rfc-6265-5.2.1]: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6265#section-5.2.1 +[rfc-6265-5.2.2]: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6265#section-5.2.2 +[rfc-6265-5.2.3]: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6265#section-5.2.3 +[rfc-6265-5.2.4]: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6265#section-5.2.4 +[rfc-6265-5.2.5]: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6265#section-5.2.5 +[rfc-6265-5.2.6]: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6265#section-5.2.6 +[rfc-6265-5.3]: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6265#section-5.3 + +## License + +[MIT](LICENSE) + +[coveralls-image]: https://badgen.net/coveralls/c/github/jshttp/cookie/master +[coveralls-url]: https://coveralls.io/r/jshttp/cookie?branch=master +[github-actions-ci-image]: https://img.shields.io/github/workflow/status/jshttp/cookie/ci/master?label=ci +[github-actions-ci-url]: https://github.com/jshttp/cookie/actions/workflows/ci.yml +[node-version-image]: https://badgen.net/npm/node/cookie +[node-version-url]: https://nodejs.org/en/download +[npm-downloads-image]: https://badgen.net/npm/dm/cookie +[npm-url]: https://npmjs.org/package/cookie +[npm-version-image]: https://badgen.net/npm/v/cookie diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/SECURITY.md" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/SECURITY.md" new file mode 100644 index 0000000..fd4a6c5 --- /dev/null +++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/SECURITY.md" @@ -0,0 +1,25 @@ +# Security Policies and Procedures + +## Reporting a Bug + +The `cookie` team and community take all security bugs seriously. Thank +you for improving the security of the project. We appreciate your efforts and +responsible disclosure and will make every effort to acknowledge your +contributions. + +Report security bugs by emailing the current owner(s) of `cookie`. This +information can be found in the npm registry using the command +`npm owner ls cookie`. +If unsure or unable to get the information from the above, open an issue +in the [project issue tracker](https://github.com/jshttp/cookie/issues) +asking for the current contact information. + +To ensure the timely response to your report, please ensure that the entirety +of the report is contained within the email body and not solely behind a web +link or an attachment. + +At least one owner will acknowledge your email within 48 hours, and will send a +more detailed response within 48 hours indicating the next steps in handling +your report. After the initial reply to your report, the owners will +endeavor to keep you informed of the progress towards a fix and full +announcement, and may ask for additional information or guidance. diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/index.js" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/index.js" new file mode 100644 index 0000000..9c3d07d --- /dev/null +++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/index.js" @@ -0,0 +1,270 @@ +/*! + * cookie + * Copyright(c) 2012-2014 Roman Shtylman + * Copyright(c) 2015 Douglas Christopher Wilson + * MIT Licensed + */ + +'use strict'; + +/** + * Module exports. + * @public + */ + +exports.parse = parse; +exports.serialize = serialize; + +/** + * Module variables. + * @private + */ + +var __toString = Object.prototype.toString + +/** + * RegExp to match field-content in RFC 7230 sec 3.2 + * + * field-content = field-vchar [ 1*( SP / HTAB ) field-vchar ] + * field-vchar = VCHAR / obs-text + * obs-text = %x80-FF + */ + +var fieldContentRegExp = /^[\u0009\u0020-\u007e\u0080-\u00ff]+$/; + +/** + * Parse a cookie header. + * + * Parse the given cookie header string into an object + * The object has the various cookies as keys(names) => values + * + * @param {string} str + * @param {object} [options] + * @return {object} + * @public + */ + +function parse(str, options) { + if (typeof str !== 'string') { + throw new TypeError('argument str must be a string'); + } + + var obj = {} + var opt = options || {}; + var dec = opt.decode || decode; + + var index = 0 + while (index < str.length) { + var eqIdx = str.indexOf('=', index) + + // no more cookie pairs + if (eqIdx === -1) { + break + } + + var endIdx = str.indexOf(';', index) + + if (endIdx === -1) { + endIdx = str.length + } else if (endIdx < eqIdx) { + // backtrack on prior semicolon + index = str.lastIndexOf(';', eqIdx - 1) + 1 + continue + } + + var key = str.slice(index, eqIdx).trim() + + // only assign once + if (undefined === obj[key]) { + var val = str.slice(eqIdx + 1, endIdx).trim() + + // quoted values + if (val.charCodeAt(0) === 0x22) { + val = val.slice(1, -1) + } + + obj[key] = tryDecode(val, dec); + } + + index = endIdx + 1 + } + + return obj; +} + +/** + * Serialize data into a cookie header. + * + * Serialize the a name value pair into a cookie string suitable for + * http headers. An optional options object specified cookie parameters. + * + * serialize('foo', 'bar', { httpOnly: true }) + * => "foo=bar; httpOnly" + * + * @param {string} name + * @param {string} val + * @param {object} [options] + * @return {string} + * @public + */ + +function serialize(name, val, options) { + var opt = options || {}; + var enc = opt.encode || encode; + + if (typeof enc !== 'function') { + throw new TypeError('option encode is invalid'); + } + + if (!fieldContentRegExp.test(name)) { + throw new TypeError('argument name is invalid'); + } + + var value = enc(val); + + if (value && !fieldContentRegExp.test(value)) { + throw new TypeError('argument val is invalid'); + } + + var str = name + '=' + value; + + if (null != opt.maxAge) { + var maxAge = opt.maxAge - 0; + + if (isNaN(maxAge) || !isFinite(maxAge)) { + throw new TypeError('option maxAge is invalid') + } + + str += '; Max-Age=' + Math.floor(maxAge); + } + + if (opt.domain) { + if (!fieldContentRegExp.test(opt.domain)) { + throw new TypeError('option domain is invalid'); + } + + str += '; Domain=' + opt.domain; + } + + if (opt.path) { + if (!fieldContentRegExp.test(opt.path)) { + throw new TypeError('option path is invalid'); + } + + str += '; Path=' + opt.path; + } + + if (opt.expires) { + var expires = opt.expires + + if (!isDate(expires) || isNaN(expires.valueOf())) { + throw new TypeError('option expires is invalid'); + } + + str += '; Expires=' + expires.toUTCString() + } + + if (opt.httpOnly) { + str += '; HttpOnly'; + } + + if (opt.secure) { + str += '; Secure'; + } + + if (opt.priority) { + var priority = typeof opt.priority === 'string' + ? opt.priority.toLowerCase() + : opt.priority + + switch (priority) { + case 'low': + str += '; Priority=Low' + break + case 'medium': + str += '; Priority=Medium' + break + case 'high': + str += '; Priority=High' + break + default: + throw new TypeError('option priority is invalid') + } + } + + if (opt.sameSite) { + var sameSite = typeof opt.sameSite === 'string' + ? opt.sameSite.toLowerCase() : opt.sameSite; + + switch (sameSite) { + case true: + str += '; SameSite=Strict'; + break; + case 'lax': + str += '; SameSite=Lax'; + break; + case 'strict': + str += '; SameSite=Strict'; + break; + case 'none': + str += '; SameSite=None'; + break; + default: + throw new TypeError('option sameSite is invalid'); + } + } + + return str; +} + +/** + * URL-decode string value. Optimized to skip native call when no %. + * + * @param {string} str + * @returns {string} + */ + +function decode (str) { + return str.indexOf('%') !== -1 + ? decodeURIComponent(str) + : str +} + +/** + * URL-encode value. + * + * @param {string} str + * @returns {string} + */ + +function encode (val) { + return encodeURIComponent(val) +} + +/** + * Determine if value is a Date. + * + * @param {*} val + * @private + */ + +function isDate (val) { + return __toString.call(val) === '[object Date]' || + val instanceof Date +} + +/** + * Try decoding a string using a decoding function. + * + * @param {string} str + * @param {function} decode + * @private + */ + +function tryDecode(str, decode) { + try { + return decode(str); + } catch (e) { + return str; + } +} diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/package.json" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/package.json" new file mode 100644 index 0000000..ed5606a --- /dev/null +++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/cookie/package.json" @@ -0,0 +1,44 @@ +{ + "name": "cookie", + "description": "HTTP server cookie parsing and serialization", + "version": "0.5.0", + "author": "Roman ShtylmanLocation ' + escapeHtml(url) + ' not found
' + + // send a 404 + res.statusCode = 404 + res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html; charset=UTF-8') + res.setHeader('Content-Length', String(Buffer.byteLength(body, 'utf-8'))) + res.end(body, 'utf-8') +}) +``` + +### Encode a URL for use in a header field + +```js +var encodeUrl = require('encodeurl') +var escapeHtml = require('escape-html') +var url = require('url') + +http.createServer(function onRequest (req, res) { + // parse inbound url + var href = url.parse(req) + + // set new host for redirect + href.host = 'localhost' + href.protocol = 'https:' + href.slashes = true + + // create location header + var location = encodeUrl(url.format(href)) + + // create html message + var body = 'Redirecting to new site: ' + escapeHtml(location) + '
' + + // send a 301 + res.statusCode = 301 + res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html; charset=UTF-8') + res.setHeader('Content-Length', String(Buffer.byteLength(body, 'utf-8'))) + res.setHeader('Location', location) + res.end(body, 'utf-8') +}) +``` + +## Testing + +```sh +$ npm test +$ npm run lint +``` + +## References + +- [RFC 3986: Uniform Resource Identifier (URI): Generic Syntax][rfc-3986] +- [WHATWG URL Living Standard][whatwg-url] + +[rfc-3986]: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3986 +[whatwg-url]: https://url.spec.whatwg.org/ + +## License + +[MIT](LICENSE) + +[npm-image]: https://img.shields.io/npm/v/encodeurl.svg +[npm-url]: https://npmjs.org/package/encodeurl +[node-version-image]: https://img.shields.io/node/v/encodeurl.svg +[node-version-url]: https://nodejs.org/en/download +[travis-image]: https://img.shields.io/travis/pillarjs/encodeurl.svg +[travis-url]: https://travis-ci.org/pillarjs/encodeurl +[coveralls-image]: https://img.shields.io/coveralls/pillarjs/encodeurl.svg +[coveralls-url]: https://coveralls.io/r/pillarjs/encodeurl?branch=master +[downloads-image]: https://img.shields.io/npm/dm/encodeurl.svg +[downloads-url]: https://npmjs.org/package/encodeurl diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/encodeurl/index.js" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/encodeurl/index.js" new file mode 100644 index 0000000..fc4906c --- /dev/null +++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/encodeurl/index.js" @@ -0,0 +1,60 @@ +/*! + * encodeurl + * Copyright(c) 2016 Douglas Christopher Wilson + * MIT Licensed + */ + +'use strict' + +/** + * Module exports. + * @public + */ + +module.exports = encodeUrl + +/** + * RegExp to match non-URL code points, *after* encoding (i.e. not including "%") + * and including invalid escape sequences. + * @private + */ + +var ENCODE_CHARS_REGEXP = /(?:[^\x21\x25\x26-\x3B\x3D\x3F-\x5B\x5D\x5F\x61-\x7A\x7E]|%(?:[^0-9A-Fa-f]|[0-9A-Fa-f][^0-9A-Fa-f]|$))+/g + +/** + * RegExp to match unmatched surrogate pair. + * @private + */ + +var UNMATCHED_SURROGATE_PAIR_REGEXP = /(^|[^\uD800-\uDBFF])[\uDC00-\uDFFF]|[\uD800-\uDBFF]([^\uDC00-\uDFFF]|$)/g + +/** + * String to replace unmatched surrogate pair with. + * @private + */ + +var UNMATCHED_SURROGATE_PAIR_REPLACE = '$1\uFFFD$2' + +/** + * Encode a URL to a percent-encoded form, excluding already-encoded sequences. + * + * This function will take an already-encoded URL and encode all the non-URL + * code points. This function will not encode the "%" character unless it is + * not part of a valid sequence (`%20` will be left as-is, but `%foo` will + * be encoded as `%25foo`). + * + * This encode is meant to be "safe" and does not throw errors. It will try as + * hard as it can to properly encode the given URL, including replacing any raw, + * unpaired surrogate pairs with the Unicode replacement character prior to + * encoding. + * + * @param {string} url + * @return {string} + * @public + */ + +function encodeUrl (url) { + return String(url) + .replace(UNMATCHED_SURROGATE_PAIR_REGEXP, UNMATCHED_SURROGATE_PAIR_REPLACE) + .replace(ENCODE_CHARS_REGEXP, encodeURI) +} diff --git "a/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/encodeurl/package.json" "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/encodeurl/package.json" new file mode 100644 index 0000000..b9f25ef --- /dev/null +++ "b/\344\275\225\345\273\272\346\201\222/3.01,express \346\241\206\346\236\2661/node_modules/encodeurl/package.json" @@ -0,0 +1,40 @@ +{ + "name": "encodeurl", + "description": "Encode a URL to a percent-encoded form, excluding already-encoded sequences", + "version": "1.0.2", + "contributors": [ + "Douglas Christopher Wilson